
The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. We note that CCR S.A. (BVMF:CCRO3) does have debt on its balance sheet. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
Check out the opportunities and risks within the BR Infrastructure industry.
What Is CCR's Debt?
As you can see below, at the end of June 2022, CCR had R$28.3b of debt, up from R$21.2b a year ago. Click the image for more detail. On the flip side, it has R$6.38b in cash leading to net debt of about R$21.9b.
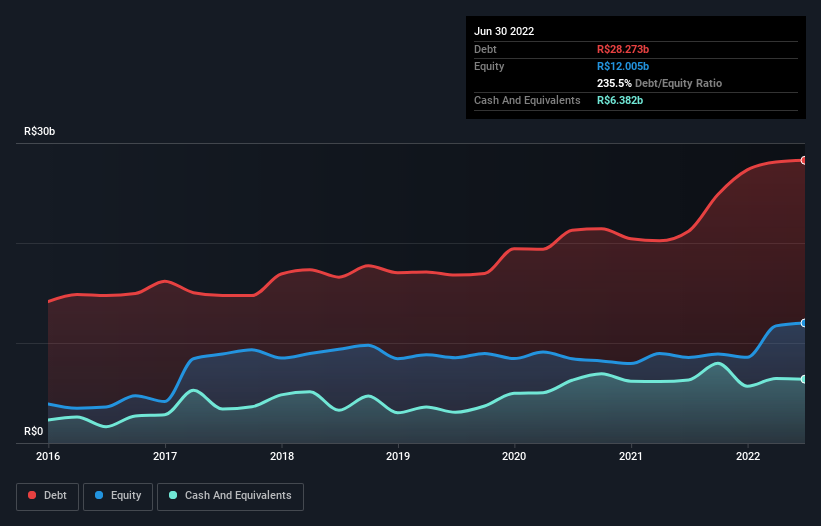
A Look At CCR's Liabilities
According to the last reported balance sheet, CCR had liabilities of R$6.35b due within 12 months, and liabilities of R$29.5b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of R$6.38b as well as receivables valued at R$4.02b due within 12 months. So its liabilities total R$25.5b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
Given this deficit is actually higher than the company's market capitalization of R$24.9b, we think shareholders really should watch CCR's debt levels, like a parent watching their child ride a bike for the first time. Hypothetically, extremely heavy dilution would be required if the company were forced to pay down its liabilities by raising capital at the current share price.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
CCR has net debt worth 1.9 times EBITDA, which isn't too much, but its interest cover looks a bit on the low side, with EBIT at only 5.4 times the interest expense. While that doesn't worry us too much, it does suggest the interest payments are somewhat of a burden. Notably, CCR's EBIT launched higher than Elon Musk, gaining a whopping 160% on last year. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if CCR can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. In the last three years, CCR created free cash flow amounting to 9.6% of its EBIT, an uninspiring performance. That limp level of cash conversion undermines its ability to manage and pay down debt.
Our View
Neither CCR's ability to handle its total liabilities nor its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow gave us confidence in its ability to take on more debt. But its EBIT growth rate tells a very different story, and suggests some resilience. It's also worth noting that CCR is in the Infrastructure industry, which is often considered to be quite defensive. Looking at all the angles mentioned above, it does seem to us that CCR is a somewhat risky investment as a result of its debt. That's not necessarily a bad thing, since leverage can boost returns on equity, but it is something to be aware of. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. Be aware that CCR is showing 3 warning signs in our investment analysis , you should know about...
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
If you're looking to trade CCR, open an account with the lowest-cost platform trusted by professionals, Interactive Brokers.
With clients in over 200 countries and territories, and access to 160 markets, IBKR lets you trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds from a single integrated account.
Enjoy no hidden fees, no account minimums, and FX conversion rates as low as 0.03%, far better than what most brokers offer.
Sponsored ContentNew: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About BOVESPA:CCRO3
CCR
Engages in the provision of infrastructure services for highway concessions, urban mobility, and airports in Brazil.
Mediocre balance sheet with limited growth.
Market Insights
Community Narratives


