Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We note that Reliance, Inc. (NYSE:RS) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
Check out our latest analysis for Reliance
What Is Reliance's Net Debt?
As you can see below, Reliance had US$1.14b of debt, at June 2024, which is about the same as the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. On the flip side, it has US$350.8m in cash leading to net debt of about US$792.8m.
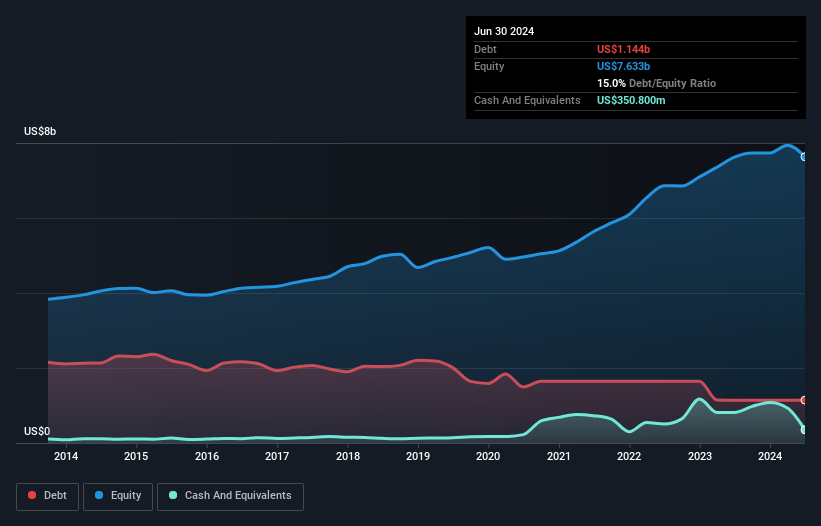
How Healthy Is Reliance's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Reliance had liabilities of US$883.5m due within 12 months, and liabilities of US$1.93b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting this, it had US$350.8m in cash and US$1.66b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling US$803.6m more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Since publicly traded Reliance shares are worth a very impressive total of US$16.9b, it seems unlikely that this level of liabilities would be a major threat. But there are sufficient liabilities that we would certainly recommend shareholders continue to monitor the balance sheet, going forward.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Reliance's net debt is only 0.46 times its EBITDA. And its EBIT easily covers its interest expense, being 37.5 times the size. So we're pretty relaxed about its super-conservative use of debt. The modesty of its debt load may become crucial for Reliance if management cannot prevent a repeat of the 28% cut to EBIT over the last year. When a company sees its earnings tank, it can sometimes find its relationships with its lenders turn sour. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Reliance can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Over the most recent three years, Reliance recorded free cash flow worth 60% of its EBIT, which is around normal, given free cash flow excludes interest and tax. This free cash flow puts the company in a good position to pay down debt, when appropriate.
Our View
Based on what we've seen Reliance is not finding it easy, given its EBIT growth rate, but the other factors we considered give us cause to be optimistic. In particular, we are dazzled with its interest cover. When we consider all the elements mentioned above, it seems to us that Reliance is managing its debt quite well. Having said that, the load is sufficiently heavy that we would recommend any shareholders keep a close eye on it. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. To that end, you should learn about the 2 warning signs we've spotted with Reliance (including 1 which can't be ignored) .
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com
About NYSE:RS
Reliance
Operates as a diversified metal solutions provider and metals service center company primarily in the United States and Canada.
Flawless balance sheet established dividend payer.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)


Fiducian: Compliance Clouds or Value Opportunity?

Willamette Valley Vineyards (WVVI): Not-So-Great Value
Recently Updated Narratives

THE KINGDOM OF BROWN GOODS: WHY MGPI IS BEING CRUSHED BY INVENTORY & PRIMED FOR RESURRECTION


The "Molecular Pencil": Why Beam's Technology is Built to Win


ADNOC Gas future shines with a 21.4% revenue surge
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026





