The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. We can see that Trinity Industries, Inc. (NYSE:TRN) does use debt in its business. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Trinity Industries
How Much Debt Does Trinity Industries Carry?
The chart below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Trinity Industries had US$5.70b in debt in September 2024; about the same as the year before. However, because it has a cash reserve of US$228.9m, its net debt is less, at about US$5.47b.
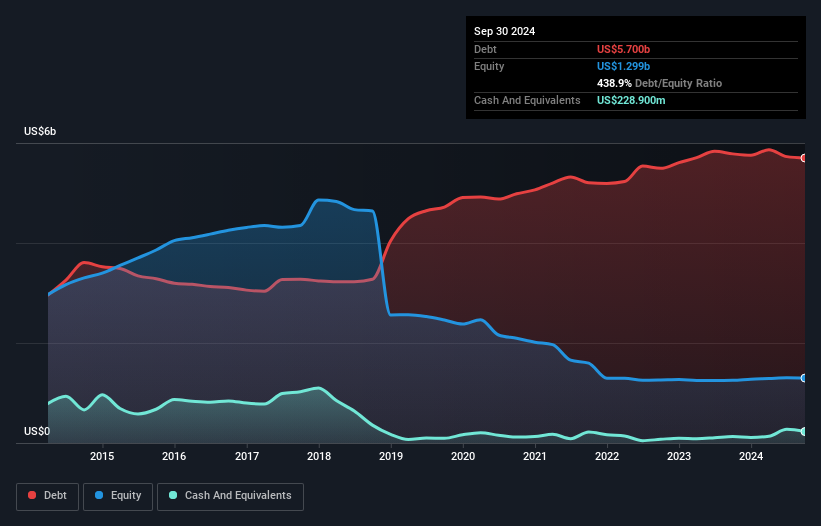
How Strong Is Trinity Industries' Balance Sheet?
The latest balance sheet data shows that Trinity Industries had liabilities of US$601.4m due within a year, and liabilities of US$6.94b falling due after that. Offsetting this, it had US$228.9m in cash and US$418.8m in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by US$6.90b.
The deficiency here weighs heavily on the US$2.95b company itself, as if a child were struggling under the weight of an enormous back-pack full of books, his sports gear, and a trumpet. So we definitely think shareholders need to watch this one closely. After all, Trinity Industries would likely require a major re-capitalisation if it had to pay its creditors today.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Weak interest cover of 1.6 times and a disturbingly high net debt to EBITDA ratio of 7.4 hit our confidence in Trinity Industries like a one-two punch to the gut. This means we'd consider it to have a heavy debt load. Looking on the bright side, Trinity Industries boosted its EBIT by a silky 69% in the last year. Like the milk of human kindness that sort of growth increases resilience, making the company more capable of managing debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Trinity Industries can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Over the last three years, Trinity Industries saw substantial negative free cash flow, in total. While that may be a result of expenditure for growth, it does make the debt far more risky.
Our View
To be frank both Trinity Industries's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow and its track record of staying on top of its total liabilities make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But on the bright side, its EBIT growth rate is a good sign, and makes us more optimistic. Overall, it seems to us that Trinity Industries's balance sheet is really quite a risk to the business. For this reason we're pretty cautious about the stock, and we think shareholders should keep a close eye on its liquidity. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For instance, we've identified 4 warning signs for Trinity Industries (1 makes us a bit uncomfortable) you should be aware of.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
The New Payments ETF Is Live on NASDAQ:
Money is moving to real-time rails, and a newly listed ETF now gives investors direct exposure. Fast settlement. Institutional custody. Simple access.
Explore how this launch could reshape portfolios
Sponsored ContentValuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Trinity Industries might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NYSE:TRN
Trinity Industries
Provides railcar products and services under the TrinityRail trade name in North America.
Average dividend payer with low risk.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

THE KINGDOM OF BROWN GOODS: WHY MGPI IS BEING CRUSHED BY INVENTORY & PRIMED FOR RESURRECTION


Why Vertical Aerospace (NYSE: EVTL) is Worth Possibly Over 13x its Current Price

The Quiet Giant That Became AI’s Power Grid
Recently Updated Narratives


MINISO's fair value is projected at 26.69 with an anticipated PE ratio shift of 20x


Fiverr International will transform the freelance industry with AI-powered growth

Stride Stock: Online Education Finds Its Second Act
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)




