- United States
- /
- Aerospace & Defense
- /
- NYSE:HXL
These 4 Measures Indicate That Hexcel (NYSE:HXL) Is Using Debt Reasonably Well
Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. As with many other companies Hexcel Corporation (NYSE:HXL) makes use of debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Hexcel
How Much Debt Does Hexcel Carry?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that Hexcel had US$795.6m of debt in September 2022, down from US$874.7m, one year before. However, because it has a cash reserve of US$90.9m, its net debt is less, at about US$704.7m.
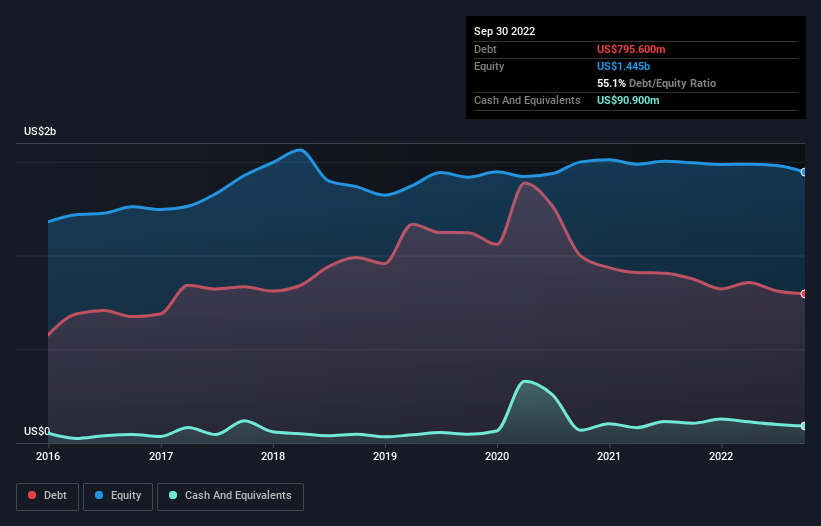
A Look At Hexcel's Liabilities
The latest balance sheet data shows that Hexcel had liabilities of US$283.7m due within a year, and liabilities of US$1.05b falling due after that. On the other hand, it had cash of US$90.9m and US$235.6m worth of receivables due within a year. So it has liabilities totalling US$1.00b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Since publicly traded Hexcel shares are worth a total of US$5.22b, it seems unlikely that this level of liabilities would be a major threat. But there are sufficient liabilities that we would certainly recommend shareholders continue to monitor the balance sheet, going forward.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Hexcel has net debt worth 2.4 times EBITDA, which isn't too much, but its interest cover looks a bit on the low side, with EBIT at only 4.4 times the interest expense. While that doesn't worry us too much, it does suggest the interest payments are somewhat of a burden. Pleasingly, Hexcel is growing its EBIT faster than former Australian PM Bob Hawke downs a yard glass, boasting a 599% gain in the last twelve months. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Hexcel can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. Over the last three years, Hexcel actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT. That sort of strong cash conversion gets us as excited as the crowd when the beat drops at a Daft Punk concert.
Our View
Happily, Hexcel's impressive conversion of EBIT to free cash flow implies it has the upper hand on its debt. But, on a more sombre note, we are a little concerned by its interest cover. Zooming out, Hexcel seems to use debt quite reasonably; and that gets the nod from us. While debt does bring risk, when used wisely it can also bring a higher return on equity. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. Be aware that Hexcel is showing 1 warning sign in our investment analysis , you should know about...
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
Mobile Infrastructure for Defense and Disaster
The next wave in robotics isn't humanoid. Its fully autonomous towers delivering 5G, ISR, and radar in under 30 minutes, anywhere.
Get the investor briefing before the next round of contracts
Sponsored On Behalf of CiTechValuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Hexcel might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NYSE:HXL
Hexcel
Develops, manufactures, and markets carbon fibers, structural reinforcements, honeycomb structures, resins, and composite materials and parts for use in commercial aerospace, space and defense, and industrial applications.
Reasonable growth potential with adequate balance sheet.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

THE KINGDOM OF BROWN GOODS: WHY MGPI IS BEING CRUSHED BY INVENTORY & PRIMED FOR RESURRECTION


Why Vertical Aerospace (NYSE: EVTL) is Worth Possibly Over 13x its Current Price

The Quiet Giant That Became AI’s Power Grid
Recently Updated Narratives


MINISO's fair value is projected at 26.69 with an anticipated PE ratio shift of 20x


Fiverr International will transform the freelance industry with AI-powered growth

Jackson Financial Stock: When Insurance Math Meets a Shifting Claims Landscape
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026
Trending Discussion


