Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We note that Standrew S.A. (WSE:STD) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
When Is Debt A Problem?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
See our latest analysis for Standrew
How Much Debt Does Standrew Carry?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Standrew had debt of zł9.51m at the end of September 2022, a reduction from zł10.3m over a year. However, it also had zł481.9k in cash, and so its net debt is zł9.03m.
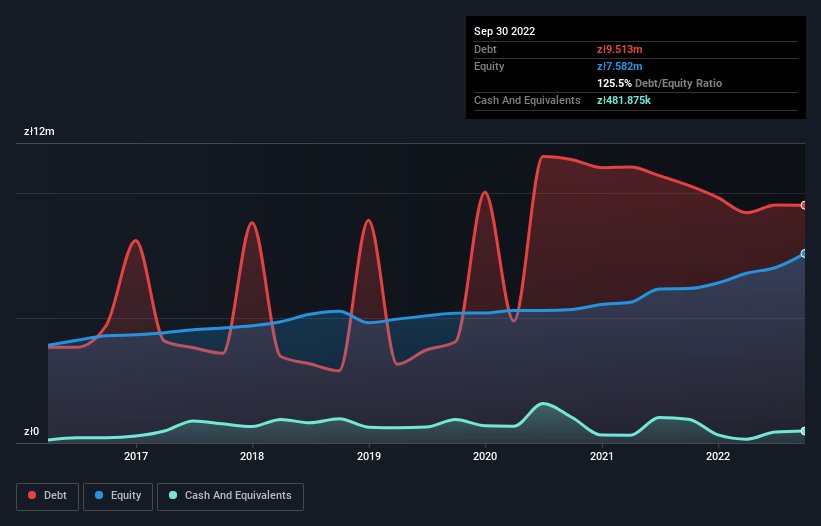
A Look At Standrew's Liabilities
According to the last reported balance sheet, Standrew had liabilities of zł8.81m due within 12 months, and liabilities of zł4.55m due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of zł481.9k as well as receivables valued at zł3.93m due within 12 months. So its liabilities total zł8.95m more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
Given Standrew has a market capitalization of zł45.4m, it's hard to believe these liabilities pose much threat. However, we do think it is worth keeping an eye on its balance sheet strength, as it may change over time.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Standrew has a debt to EBITDA ratio of 3.4 and its EBIT covered its interest expense 2.7 times. This suggests that while the debt levels are significant, we'd stop short of calling them problematic. Looking on the bright side, Standrew boosted its EBIT by a silky 92% in the last year. Like a mother's loving embrace of a newborn that sort of growth builds resilience, putting the company in a stronger position to manage its debt. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But it is Standrew's earnings that will influence how the balance sheet holds up in the future. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Looking at the most recent three years, Standrew recorded free cash flow of 38% of its EBIT, which is weaker than we'd expect. That weak cash conversion makes it more difficult to handle indebtedness.
Our View
On our analysis Standrew's EBIT growth rate should signal that it won't have too much trouble with its debt. But the other factors we noted above weren't so encouraging. To be specific, it seems about as good at covering its interest expense with its EBIT as wet socks are at keeping your feet warm. Considering this range of data points, we think Standrew is in a good position to manage its debt levels. Having said that, the load is sufficiently heavy that we would recommend any shareholders keep a close eye on it. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. To that end, you should learn about the 4 warning signs we've spotted with Standrew (including 2 which are potentially serious) .
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
The New Payments ETF Is Live on NASDAQ:
Money is moving to real-time rails, and a newly listed ETF now gives investors direct exposure. Fast settlement. Institutional custody. Simple access.
Explore how this launch could reshape portfolios
Sponsored ContentNew: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About WSE:STD
Slight risk with imperfect balance sheet.
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

THE KINGDOM OF BROWN GOODS: WHY MGPI IS BEING CRUSHED BY INVENTORY & PRIMED FOR RESURRECTION


Why Vertical Aerospace (NYSE: EVTL) is Worth Possibly Over 13x its Current Price

The Quiet Giant That Became AI’s Power Grid
Recently Updated Narratives


A case for USD $14.81 per share based on book value. Be warned, this is a micro-cap dependent on a single mine.

Occidental Petroleum to Become Fairly Priced at $68.29 According to Future Projections

Agfa-Gevaert is a digital and materials turnaround opportunity, with growth potential in ZIRFON, but carrying legacy risks.
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)





