Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. We can see that Meridian Energy Limited (NZSE:MEL) does use debt in its business. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Meridian Energy
What Is Meridian Energy's Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of June 2023 Meridian Energy had NZ$1.24b of debt, an increase on NZ$1.16b, over one year. However, it does have NZ$212.0m in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about NZ$1.02b.
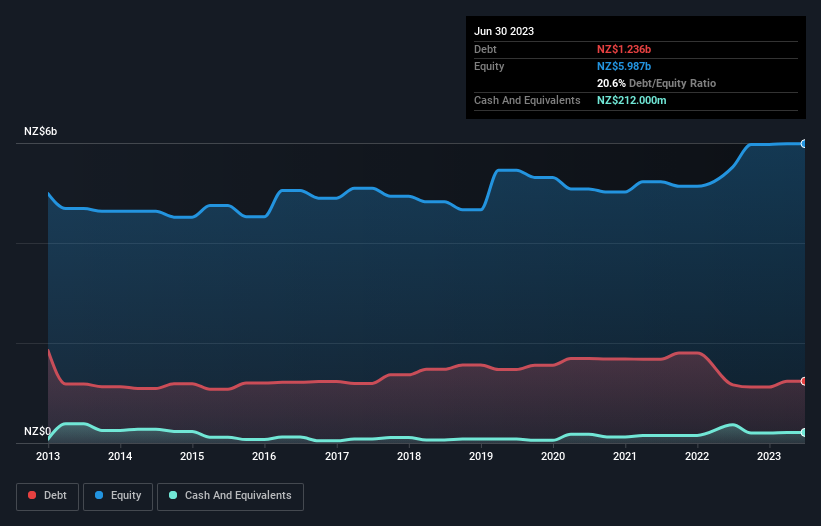
A Look At Meridian Energy's Liabilities
The latest balance sheet data shows that Meridian Energy had liabilities of NZ$720.0m due within a year, and liabilities of NZ$3.32b falling due after that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of NZ$212.0m as well as receivables valued at NZ$347.0m due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling NZ$3.48b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
While this might seem like a lot, it is not so bad since Meridian Energy has a market capitalization of NZ$12.9b, and so it could probably strengthen its balance sheet by raising capital if it needed to. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Meridian Energy's net debt of 2.4 times EBITDA suggests graceful use of debt. And the alluring interest cover (EBIT of 7.7 times interest expense) certainly does not do anything to dispel this impression. Shareholders should be aware that Meridian Energy's EBIT was down 73% last year. If that earnings trend continues then paying off its debt will be about as easy as herding cats on to a roller coaster. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Meridian Energy can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Over the most recent three years, Meridian Energy recorded free cash flow worth 61% of its EBIT, which is around normal, given free cash flow excludes interest and tax. This free cash flow puts the company in a good position to pay down debt, when appropriate.
Our View
Meridian Energy's EBIT growth rate was a real negative on this analysis, although the other factors we considered cast it in a significantly better light. For example, its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow is relatively strong. Looking at all the angles mentioned above, it does seem to us that Meridian Energy is a somewhat risky investment as a result of its debt. That's not necessarily a bad thing, since leverage can boost returns on equity, but it is something to be aware of. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. Case in point: We've spotted 2 warning signs for Meridian Energy you should be aware of, and 1 of them is a bit unpleasant.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NZSE:MEL
Meridian Energy
Engages in the generation and retailing of electricity to residential, business, and industrial customers in New Zealand, Australia, and the United Kingdom.
Moderate growth potential with mediocre balance sheet.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

THE KINGDOM OF BROWN GOODS: WHY MGPI IS BEING CRUSHED BY INVENTORY & PRIMED FOR RESURRECTION


Why Vertical Aerospace (NYSE: EVTL) is Worth Possibly Over 13x its Current Price

The Quiet Giant That Became AI’s Power Grid
Recently Updated Narratives

GE Vernova revenue will grow by 13% with a future PE of 64.7x

A buy recommendation

Growing between 25-50% for the next 3-5 years
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026




