Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. As with many other companies OCI N.V. (AMS:OCI) makes use of debt. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for OCI
What Is OCI's Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at June 2023 OCI had debt of US$3.85b, up from US$2.81b in one year. On the flip side, it has US$1.65b in cash leading to net debt of about US$2.20b.
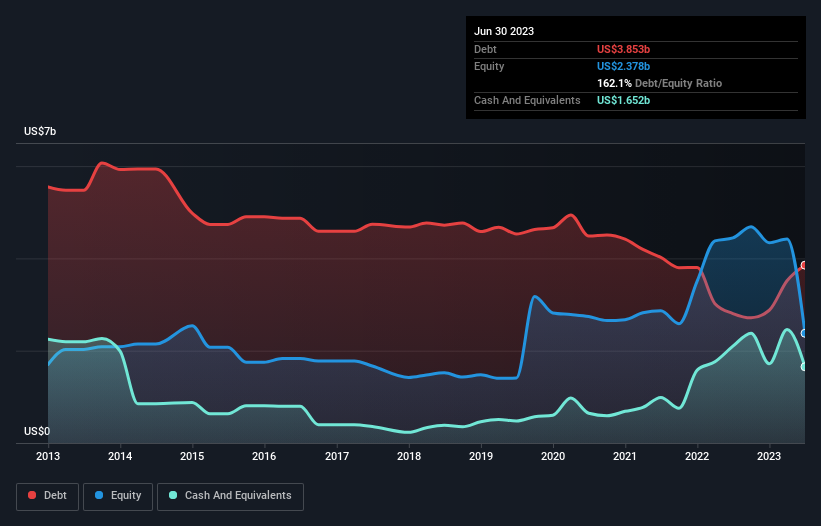
How Strong Is OCI's Balance Sheet?
The latest balance sheet data shows that OCI had liabilities of US$2.44b due within a year, and liabilities of US$4.61b falling due after that. On the other hand, it had cash of US$1.65b and US$626.6m worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by US$4.77b.
This deficit is considerable relative to its market capitalization of US$5.87b, so it does suggest shareholders should keep an eye on OCI's use of debt. This suggests shareholders would be heavily diluted if the company needed to shore up its balance sheet in a hurry.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
With net debt sitting at just 1.2 times EBITDA, OCI is arguably pretty conservatively geared. And this view is supported by the solid interest coverage, with EBIT coming in at 7.5 times the interest expense over the last year. The modesty of its debt load may become crucial for OCI if management cannot prevent a repeat of the 57% cut to EBIT over the last year. Falling earnings (if the trend continues) could eventually make even modest debt quite risky. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine OCI's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, OCI actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last three years. That sort of strong cash generation warms our hearts like a puppy in a bumblebee suit.
Our View
Neither OCI's ability to grow its EBIT nor its level of total liabilities gave us confidence in its ability to take on more debt. But the good news is it seems to be able to convert EBIT to free cash flow with ease. Looking at all the angles mentioned above, it does seem to us that OCI is a somewhat risky investment as a result of its debt. Not all risk is bad, as it can boost share price returns if it pays off, but this debt risk is worth keeping in mind. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For example, we've discovered 3 warning signs for OCI (1 is a bit unpleasant!) that you should be aware of before investing here.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About ENXTAM:OCI
OCI
Produces and distributes hydrogen-based and natural gas-based products to agricultural, transportation, and industrial customers in Europe, the Americas, the Middle East, Africa, Asia, and Oceania.
Flawless balance sheet with moderate growth potential.
Market Insights
Community Narratives



