Quote of the week: "We truly now have the opportunity to reap the full potential of individualized medicine. The road ahead must be focused on expanding our genomic tools and further integrating individualized medicine. We've only just begun to glimpse what is possible."
- Gianrico Farrugia, M.D., president and CEO of Mayo Clinic
Software, AI, and data science are revolutionizing every industry, but healthcare in particular could see profound changes in the coming decades.
Last week, we mentioned robotic surgery and service robots, which have been revolutionising medical procedures and healthcare, respectively.
The field of genomic medicine is still in its infancy, but it holds the potential to become an even bigger game changer.
This field is more obscure than robotaxis or chatbots, so we’re having a look at some of the fundamental concepts and the different types of companies in the space.
What Happened in Markets this Week?
Here’s a quick summary of what’s been going on:
📉 US credit rating downgrade could add to pressure on government debt ( The Guardian )
- Moody’s downgrade of U.S. credit to AA1, the last of the Big Three to do so, highlights growing market unease over rising debt and persistent deficits.
- While some investors brush it off as symbolic, the downgrade could push Treasury yields higher as markets demand more compensation for fiscal risk.
- With $36 trillion in national debt and no credible plan to rein it in, bondholders may start pricing in greater long-term risk. Even if default isn’t a real threat, monetizing the debt (money printing) is. Treasury Secretary Bessent called it a "lagging indicator," but markets are watching closely.
- Rising yields and mounting debt suggest it’s time to reassess duration risk in your portfolio if you have bond exposure. This downgrade is more than just noise.
🇯🇵 Japan’s exports to the U.S. shrink for the first time this year ( CNBC )
- Japan’s exports to the U.S. shrank 1.8% in April, the first drop in 2025, largely due to Trump’s revived tariffs on autos and metals.
- The trade surplus narrowed, and transport equipment exports (Japan’s bread and butter) fell 4.1%, undercutting the recovery narrative.
- With trade talks in limbo and “reciprocal” tariffs only temporarily suspended, uncertainty is throttling exporter confidence and GDP growth. Q1 GDP already contracted 0.7%, and economists expect net exports to remain a drag. A delayed rate hike from the Bank of Japan now looks likely.
- Tariff whiplash is bruising Japan’s economy, and unless trade friction eases, Japan may face a stalled 2025.
⚠️ Cloudflare CEO warns that zero-click searches are killing the web’s business model ( MSN )
- Cloudflare CEO Matthew Prince warns that AI and “zero-click” search is gutting web traffic, and with it, content monetization.
- Search used to send traffic back to websites. Now, AI tools and Google answer boxes keep users on-platform, starving creators of views and revenue.
- AI’s “scrape-to-click” ratio is staggering: OpenAI at 250:1, Anthropic at 6,000:1. Compare that to Google’s 2:1 a decade ago. With fewer users clicking through, ad revenue, subscriptions, and creator incentives are crumbling. Prince argues the entire web business model is at risk unless value flows back to original sources.
- If AI keeps taking without giving back, content creators may stop creating, and that’s bad news for everyone’s feed.
👻 Investors Spooked as US Bond Auction Sees Weak Demand ( Barron's )
- Investors were quick to shrug off the US credit downgrade from Moody’s. At the time, some analysts said bond auctions by the US Treasury were a better indicator of where yields were headed. Just two days later, a Treasury auction of 20-year bonds reflected lackluster demand.
- The auction of $16 billion in new bonds was completed at a yield of 5.05% compared to the 4.61% average over the past six auctions. Basically, investors wanted more compensation (yield) for the risk they perceived they were taking.
- The timing coincided with the GOP’s proposed tax package, which could add $3.3 trillion to the deficit ( tax cuts resulting in less government revenue ).
- Some analysts pointed out that demand for 20-year bonds can be fickle, and that investors typically opt for 10-year treasuries.
- But either way you look at it, a sustained lack of demand for long-dated bonds would indicate that investors really are concerned about the US fiscal path.
📈 Bitcoin Touches Record High on Optimism Around US Regulations ( Bloomberg )
- Bitcoin surged to a record $111k as investors cheered bipartisan momentum behind a U.S. stablecoin bill and a friendlier regulatory tone under Trump.
- It appears investors are betting big, with short-term call options eyeing $110K–$300K, and over $3.6B flowing into U.S. Bitcoin ETFs this month alone. The 12 U.S. listed ETFs currently have $133Bn in AUM.
- With tighter rules for stablecoin issuers and a clear framework emerging, institutions are piling back in, boosted by a weaker dollar and ballooning U.S. deficits. MicroStrategy-style treasury strategies are spreading (Metaplanet, Twenty One Capital, etc), and Bitcoin bills like SB 21 in Texas (following New Hampshire and Arizona) are adding fuel to the fire.
- With regulatory clarity improving and institutional demand rising, investors appear to be reviewing and changing their Bitcoin exposure.
🎨 Jony Ive to lead OpenAI’s design work following $6.5B acquisition of his company ( TechCrunch )
- OpenAI is acquiring Jony Ive’s startup io in a $6.5B all-stock deal, bringing Apple’s legendary designer and a team of ex-Apple engineers in-house.
- Ive’s company, LoveFrom, will lead OpenAI’s design efforts, aiming to launch AI-powered consumer devices by 2026. Altman noted how phones and laptops are too “cumbersome” to interact with ChatGPT, and given the strong sales and adoption of Meta’s smart glasses, the device they create could be screenless.
- This acquisition turbocharges OpenAI’s consumer push and inches it closer to competing with Apple directly.
- Investors took note, and Apple stock slid 2% post-announcement.
- With Altman and Ive focused on redefining human-device interaction, legacy hardware makers could face disruption sooner than expected.
🧬 The Healthcare Disruptors: Genomic Medicine and AI Drug Discovery
Amongst all the disruptive technologies currently being developed, health-tech - and more specifically genomic medicine - is most out of favor amongst investors.
The chart below compares the performance since 2020 of some of the ETFs in this space with the S&P 500 (purple) and the S&P 500 Healthcare index (green).
Most of the genomic medicine ETFs (red) are still well into negative territory, with the more general health-tech funds doing only slightly better.
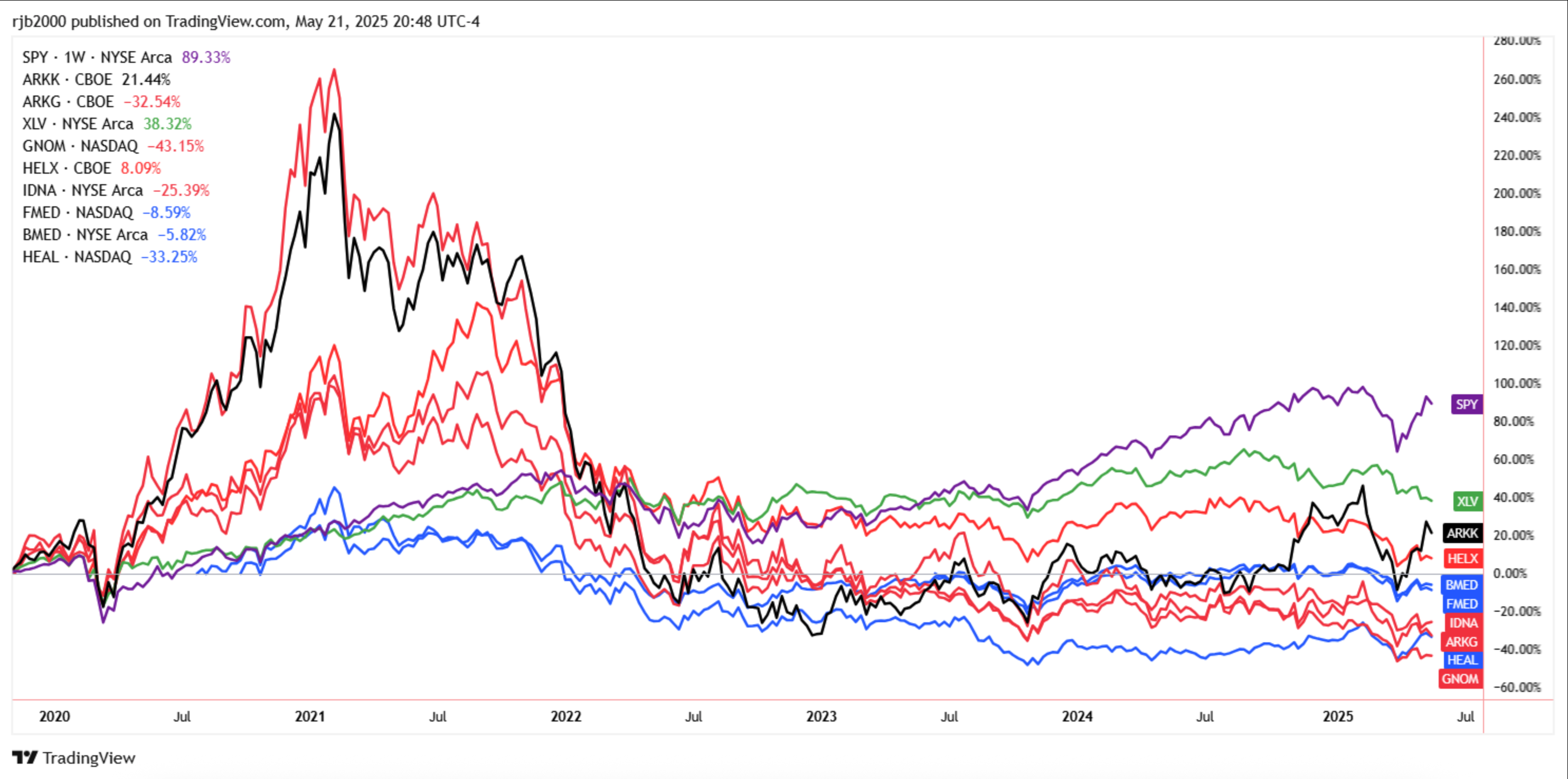
Genomic Medicine ETFs vs the S&P 500 Index - TradingView
There are a couple of reasons for this underperformance:
- 😩 The market is still dealing with the hangover from the bubble that formed in this space in 2020 and 2021.
- 🤖 Growth investors are understandably more interested in AI, automation, and other technologies.
- 💊 Even within healthcare, there have been more exciting options: weight-loss drugs.
Clearly, investors are impatient, but it’s important to remember that bargains are usually found in out-of-favor industries.
🎯 The Opportunity
Genomic research offers the potential to better understand diseases and develop therapies based on an individual's genetic profile.
The implications for healthcare are enormous:
- 🔀 Personalized medicine will begin to replace the ‘one size fits all’ approach.
- 🩻 Diseases can be detected earlier. Genomic screening can be used to identify individuals at risk of hereditary diseases, while diagnostic costs will be feasible at scale.
- 👨⚕️ Diseases can be treated earlier, and ongoing treatment may not be necessary.
- 🤖 Genomic research and AI are being used to accelerate and improve the drug discovery process.
✨ To put it into perspective, global healthcare spending accounts for 10% of GDP, or around $10 trillion, and the genomic medicine market is currently worth just $50 billion, or 0.5%.
While it’s not going to displace all that spending overnight, the value of detecting diseases earlier and avoiding ongoing treatment costs is considerable.
📖 A Primer on the Genomic Lexicon
Genomics isn’t something many people are familiar with, so we’ll start with the basic terminology you’ll come across if you’re taking a closer look at the industry.
Don't worry, we'll keep it as straightforward as we can!
🧱 The Building Blocks
- DNA: The "blueprint of life," DNA is a long molecule that contains the unique genetic code for every living organism. It carries the instructions for building and operating an individual.
- Gene: A specific segment of DNA that holds the instructions for building a particular protein or performing a specific function. Think of it as a single recipe in a massive cookbook (the genome). Humans have about 20,000-25,000 genes.
- Genome: An organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes. This would be the entire cookbook, containing all the recipes needed to build and maintain you.
- Chromosome: These are thread-like structures found in the nucleus of our cells. They are made of DNA tightly coiled around proteins. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes (46 in total), inheriting one set from each parent.
🏭 From DNA to Proteins
- RNA (Ribonucleic Acid): If DNA is the master blueprint, RNA is like a working copy or a messenger. It plays a crucial role in carrying instructions from the DNA to the parts of the cell that make proteins.
- mRNA (Messenger RNA): A specific type of RNA that transcribes the genetic information from DNA and carries it to the ribosomes (the cell's protein-making machinery). This became a household name with mRNA vaccines!
🔬🔭 The '-omics' Revolution
The suffix "-omics" refers to the study of a complete set of biological molecules. There are lots of ‘-omics’ fields, including:
- Genomics: The study of an organism's entire genome – all its genes and their functions. Genomics aims to understand the structure, function, evolution, and mapping of genomes.
- Transcriptomics: The study of the transcriptome – the complete set of RNA transcripts (including mRNA) produced by an organism under specific conditions.
- Proteomics: The study of proteomes – the entire set of proteins produced by an organism. Proteins are the workhorses of the cell, carrying out most of the functions, so proteomics helps us understand cellular activity directly.
The term Multiomics refers to an integrated approach that studies data from all the -omics fields. By combining these layers of information, scientists get a much more complete and holistic picture of what’s happening in a cell or organism, leading to deeper insights into diseases and potential treatments.
✂️🩹 Key Technologies and Therapies
Genomic Sequencing: The process of determining the precise order of nucleotides (the A, T, C, G building blocks) within a DNA molecule. It's like reading the entire genetic instruction manual letter by letter.
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): A revolutionary technology that allows for rapid and relatively inexpensive sequencing of large amounts of DNA or RNA. This has dramatically accelerated genomic research and its applications, making personalized medicine a tangible goal.
The Human Genome Project, completed between 1990 and 2003, sequenced the human genome for the first time at a cost of nearly $3 billion. By the time the project finished, the cost had fallen to only $100 million.
With next-generation sequencing, costs have continued to fall, outpacing Moore’s Law, and are on track to be below $100 in the next few years.
These cost declines are the driving force behind the genomic revolution. Without the cost declines (and faster sequencing), research, diagnosis and treatment wouldn’t be possible.
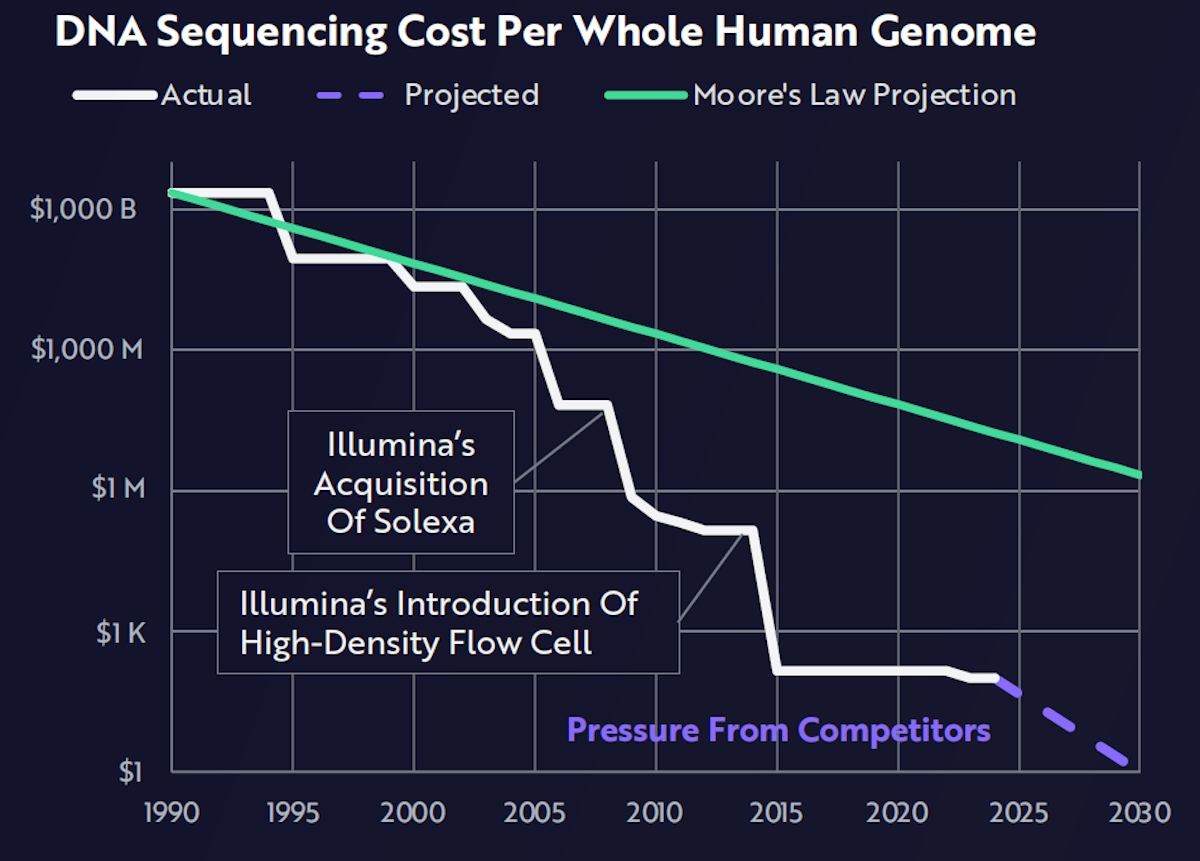
DNA Sequencing Costs - ARK Invest
Gene Editing: A group of technologies that give scientists the ability to change an organism's DNA. Tools like CRISPR-Cas9 act like "molecular scissors" that can cut DNA at specific spots, allowing researchers to add, remove, or alter genetic material. This has enormous potential for treating genetic diseases.
Gene Therapy: A technique that uses genes to treat or prevent disease. This can involve replacing a mutated gene with a healthy copy, inactivating a mutated gene, or introducing a new gene to help fight disease.
Cell Therapy: Involves introducing new, healthy cells into a patient's body to replace diseased or damaged cells. Examples include stem cell therapies or immune cell therapies.
Gene-Modified Cell Therapy: A sophisticated approach that combines cell therapy with gene editing. Cells are taken from a patient (or a donor), genetically modified in a lab to enhance their therapeutic capabilities (e.g., making immune cells better at fighting cancer), and then infused back into the patient.
Liquid Biopsies: A minimally invasive diagnostic test that detects and analyzes biomarkers (like pieces of tumor DNA or tumor cells) in bodily fluids, most commonly blood. This allows for earlier cancer detection, monitoring treatment response, and identifying resistance mechanisms without the need for surgical biopsies.
🤖 The AI Catalyst: Supercharging Drug Discovery and Development
Discovering and developing new drugs is a slow, expensive process, with a high failure rate.
- Typically, getting a new drug to market takes over 10 years, at a cost of over $1 billion !
For the pharmaceutical and life sciences industries AI, data science and raw compute power are a paradigm shift. A few examples of the way technology helps the R&D process include:
- Unlocking Genomic Data: The sheer volume of data generated by NGS is overwhelming. AI is essential for interpreting this data, finding disease-associated genetic variants, and understanding complex gene interactions.
- Smarter Target Identification: AI can sift through genomic, proteomic, and clinical data to identify novel biological targets that are most likely to be effective in treating a disease.
- Accelerated Drug Design: Instead of random screening, AI can predict how well potential drug molecules will bind to a target and their likely efficacy or toxicity.
- Optimized Clinical Trials: AI can help design more efficient clinical trials by:
- Identifying the right patient populations using biomarker analysis.
- Predicting patient responses and potential adverse events.
- Improving trial monitoring and data analysis.
- Reducing Failure Rates: By improving predictions early in the pipeline, AI can help reduce the high attrition rates that plague drug development, saving billions and years of wasted effort.
This means:
- 🏃♀️ Faster early-stage discovery
- 📉 Significantly lower R&D costs
- 💸 Increased probability of success.
Technology is essential for genomic research, but it’s also a game changer for the broader pharmaceutical industry. An important benefit of this is that discovering treatments for complex and rare diseases is more feasible.
💼 The Genomic and AI Health Ecosystem
The convergence of genomics and AI is creating a diverse ecosystem of investment opportunities.
Gene Editing and Therapy Developers
Right at the leading edge are the companies focused on creating treatments using technologies like CRISPR or developing gene therapies for specific diseases.
Examples include:
Companies in this space often have little or no revenue, and big bills. They are typically years away from breakeven, which means securing ongoing funding is crucial.
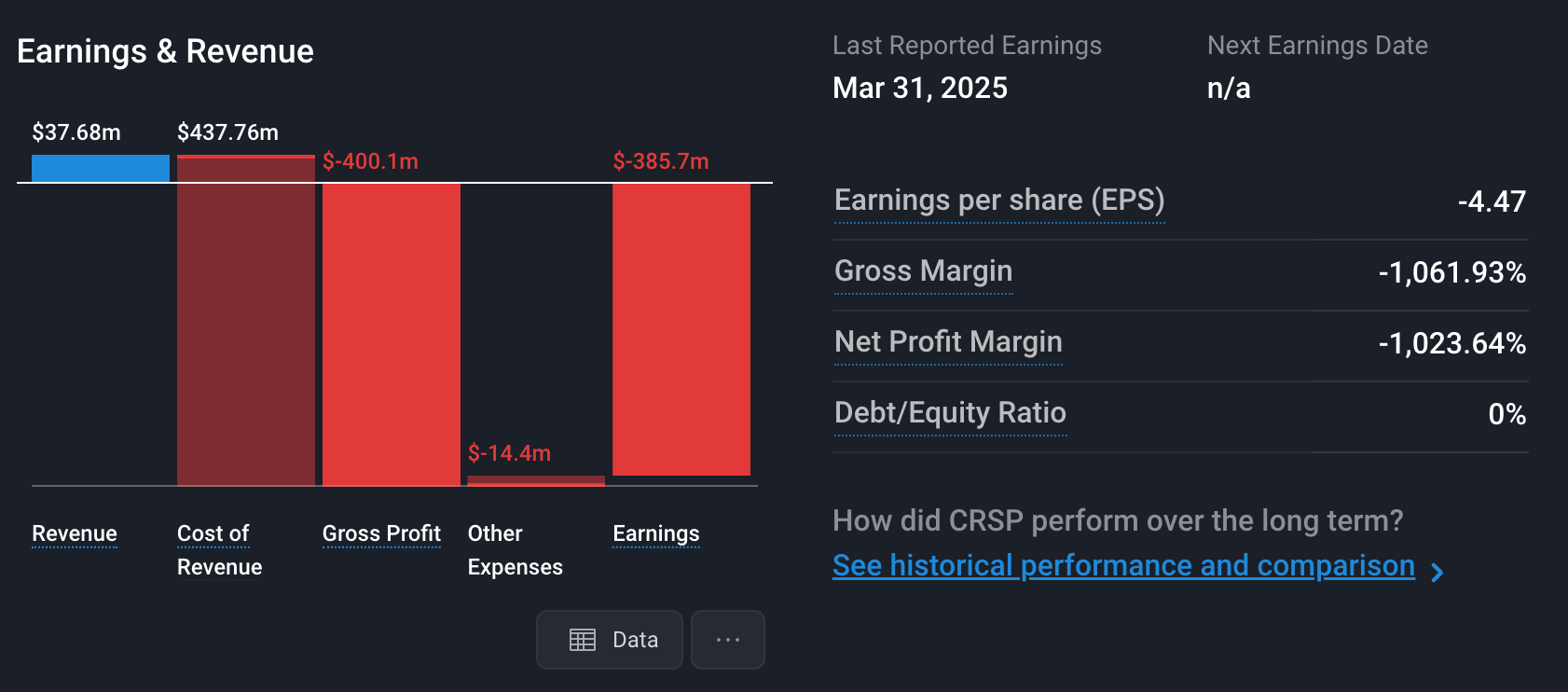
CRISPR Therapeutics Revenue vs Costs and Expenses - Simply Wall St
⛏️ NGS Technology Companies
Firms that develop and sell the sequencing machines, reagents, and software that are fundamental to genomic research.
These companies can be considered the ‘picks and shovels’ of the industry, but they are doing revolutionary work in their own right.
Examples include:
These companies are essential to the R&D process, and therefore further along the path to profitability.
🔭 AI-First Drug Discovery Companies
A newer breed of company that uses AI as the core of their drug discovery platform, often partnering with larger pharma companies.
- Recursion Pharmaceuticals
- Exscientia (owned by Recursion)
- Moderna
Beyond the drug developers themselves, consider companies that provide essential tools and services to the entire ecosystem.
This includes Contract Research Organizations (CROs) with specialized expertise in genomics or AI-driven trials, software providers for data analysis and management, and manufacturers of specialized lab equipment.
Enabling Technologies and Services
Possibly the fastest-growing part of the ecosystem includes the companies developing AI and data analysis software, and diagnostic equipment.
TempusAI, which sells diagnostic equipment and software, has grown revenue 10-fold to $800 million over the last five years.
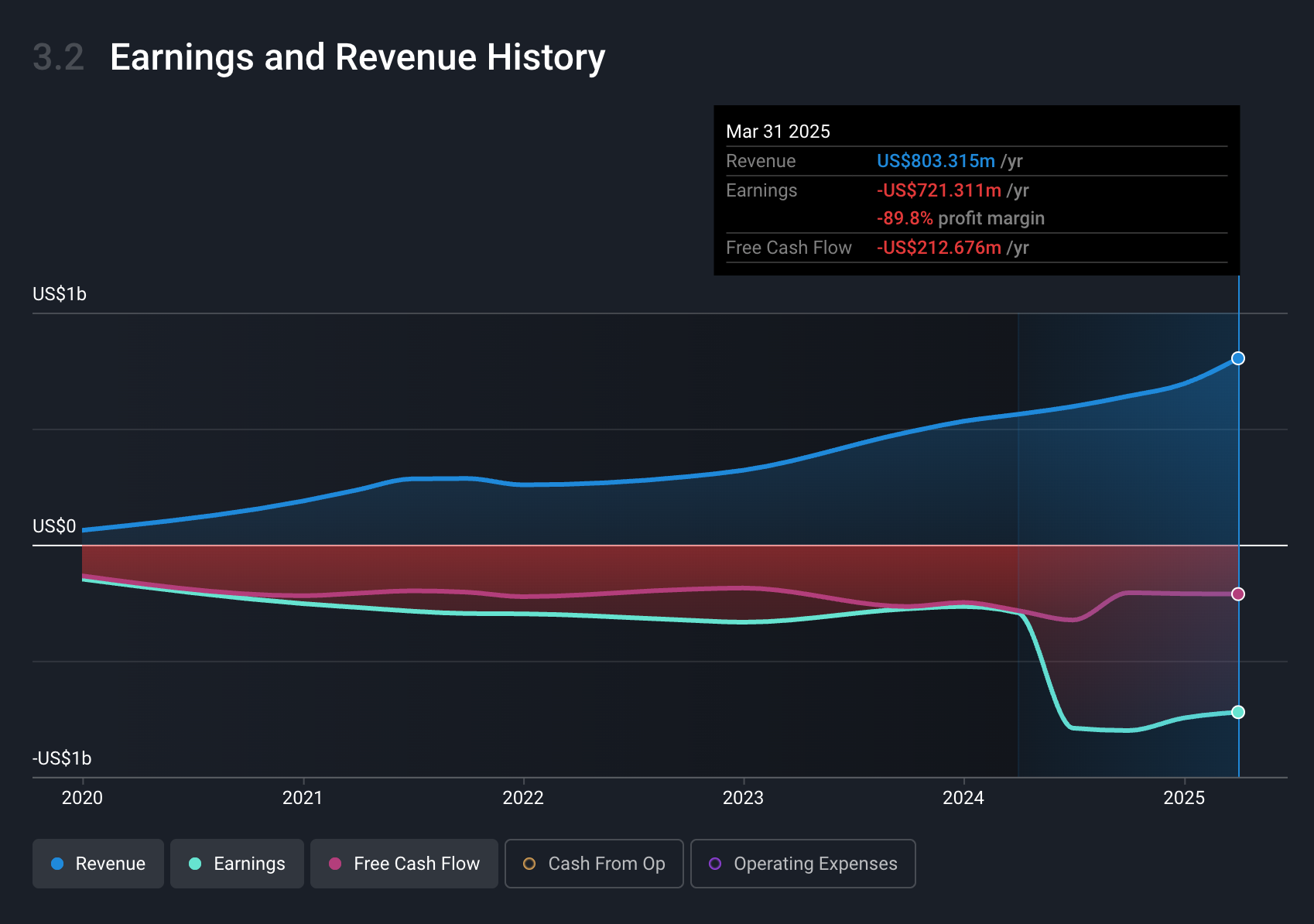
TempusAI Revenue, Earnings and Cash Flow - Simply Wall St
🔍 Liquid Biopsy & Advanced Diagnostics Firms
These companies are developing and commercializing tests for early disease detection and monitoring, and include the likes of:
🏢 Big Pharma and Biotech’s Pivot
The more established pharmaceutical and biotech companies are ramping up investments in genomics, too.
Some, like Novartis , Regeneron , and Alnylam Pharmaceuticals , are already established gene therapy providers.
Regeneron recently announced that it is buying genetics testing company 23andMe out of bankruptcy.
✨ Big pharma is actively seeking partnerships and acquisitions of smaller, innovative biotech and AI firms to access new technologies and drug candidates.
📊 Genomic Medicine ETFs
There’s no shortage of ETFs that focus on the industry. Most are actively managed, which makes sense in such a dynamic space.
For such a specialized industry, ETFs do make sense - but there is a risk to keep in mind!
If another bubble (like the one in 2020/2021) develops and bursts, ETFs facing redemptions could become forced sellers, driving down the prices of their own holdings. This applies to most thematic ETFs.
Some of the popular genomic medicine funds include:
- ARK Genomic Revolution ETF ( ARKG )
- Franklin Genomic Advancements ETF ( HELX )
- iShares Genomics Immunology and Healthcare ETF ( IDNA )
Alternatively, there are even more that have a broader scope, investing in the entire health-teach ecosystem:
- Global X HealthTech ETF ( HEAL )
- ROBO Global Healthcare Technology and Innovation ETF ( HTEC )
💡 The Insight: Long-Duration Assets Require Patience and a Plan
Growth stocks are long-duration assets. That means investors are paying for cash flows that won’t occur for 5 to 10 years or even longer. This is particularly true for companies that are years away from breakeven.
There are a few things to keep in mind when investing in long-duration assets:
⚖️ Risk and Return
If your investment is going to be at risk for a long time, you need to compensate for the additional risk. Longer-dated bonds have higher yields than short-dated bonds for the same reason.
- You can account for this by using a higher discount rate in your valuation.
🧑🧑🧒🧒 People
When you invest in companies attempting to solve very hard problems, you are really investing in a group of people. You’ll want to make sure the leadership team are in it for the long haul, and not chasing the next hot sector attracting investor attention.
Employees need to be incentivized to stick around, and stock-based compensation (SBC) is one way to do that. SBC often accounts for the difference between net income (earnings) and free cash flow.
You can check this by referring to Section 3.3 of the company report: Free Cash Flow vs Earnings Analysis.
Here’s that analysis for TempusAI:
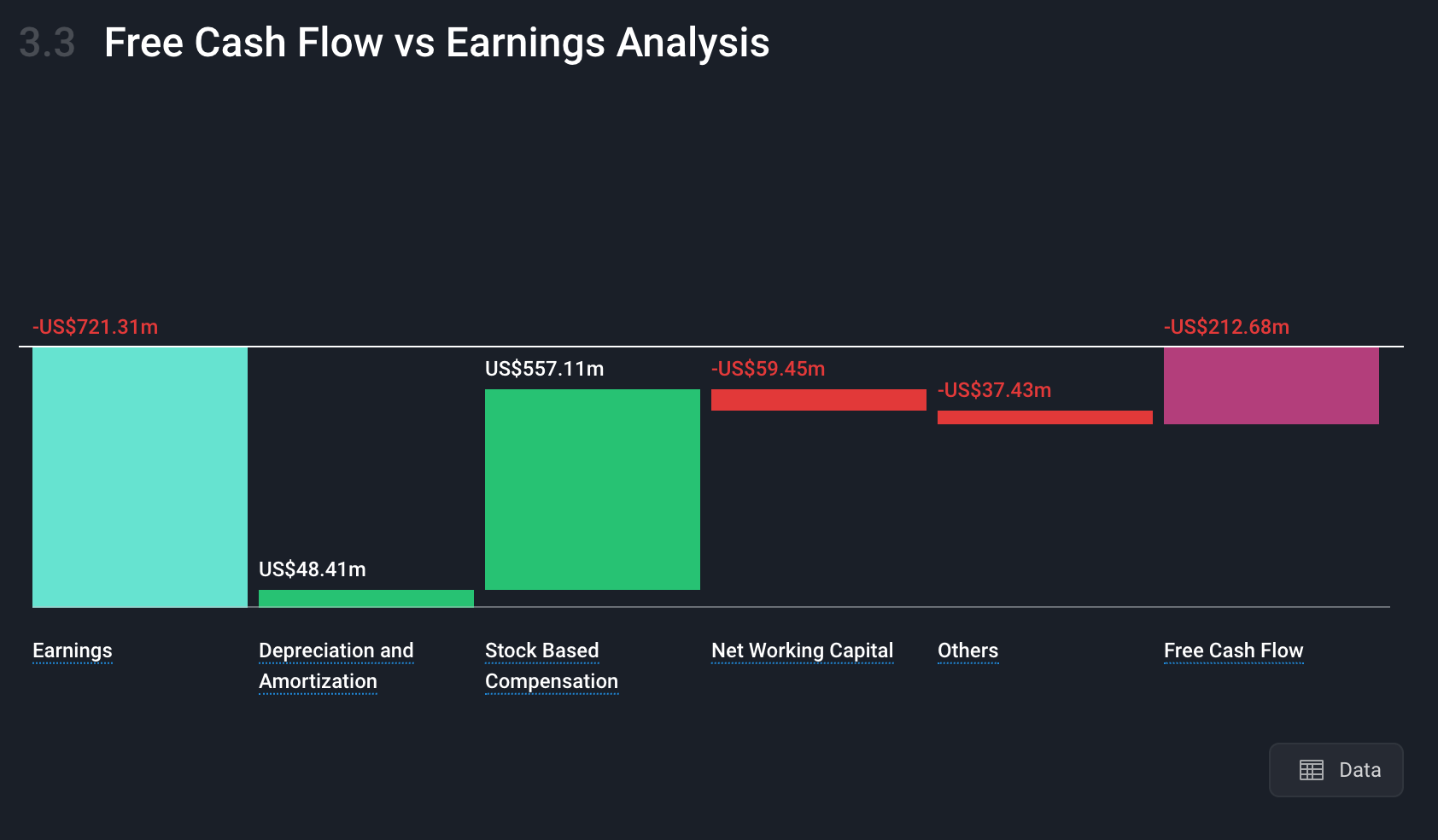
Tempus AI Earnings vs Cash Flow- Simply Wall St
You can also find out who the leadership team is, and how much stock they own by checking:
- Section 6.3: Leadership Team, and
- Section 7: Ownership
SBC means your ownership will be diluted, so this is something to anticipate.
💰 Funding
Early-stage growth companies will usually have to raise fresh capital along the way to reaching profitability.
This also means your stake will be diluted. But the ability of the company to raise capital when it needs to is a bigger issue.
Section 4 of the company report will give you an overview of the company’s financial health. Section 4.4: Cash Runway Analysis will show you how long the company can keep operating with its current cash balance.

The key question then becomes: is the company clearing enough milestones to raise more capital when it needs to?
⌛ Patience
If you are investing for the long haul, you shouldn’t expect returns in a hurry. Even if the company is successful, there are likely to be rallies and declines along the way.
Typically, whenever there’s a new breakthrough or a regulatory approval, interest spikes, and then when the market runs out of patience, the share price drifts lower until the next positive catalyst.
The opportunities occur when everyone else loses patience. So develop your narrative around a business, estimate a fair value, wait patiently, and move when the time is right.
Key Events During the Next Week
Monday
It’s Memorial Day in the US and the Spring Bank Holiday in the UK, so those markets are closed.
Tuesday
🇺🇸 Durable Goods orders
- 📊 Previous: 7.5%. Forecast ↘️ -6.5%
- ➡️ Why it matters: A sharp drop signals weakening business investment and possible economic slowdown.
🇺🇸 CB Consumer Confidence
- 📊 Previous: 86. Forecast: ↘️ 84
- ➡️ Why it matters: Falling confidence means Americans may reduce spending, dragging on growth.
Thursday
🇺🇸 FOMC minutes
- ➡️ Why it matters: Investors will be hunting for any commentary that hints at future rate moves.
🇯🇵 Consumer Confidence
- 📊Previous: 31.2. Forecast ↗️ 32.8
- ➡️ Why it matters: Rising sentiment could support domestic spending and lift Japan’s sluggish recovery.
Friday
🇨🇦 GDP growth rate (annualised)
- Previous: 2.6%. Forecast ↘️ 0.6%
- ➡️ Why it matters: A big slowdown could revive rate cut bets and weaken the Canadian dollar.
🇺🇸 Personal Spending MoM
- 📊 Previous: 0.7%. Forecast ↘️ 0.1%
- ➡️ Why it matters: Flatlining spending would dent hopes for a resilient US consumer.
Stocks reporting this week:
- Nvidia
- Costco
- Salesforce
- PDD
- Synopsys
- Dell
- Marvell Technology
- Lululemon
- ZScaler
- Veeva Systems
- Agilent Technologies
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com
Simply Wall St analyst Richard Bowman and Simply Wall St have no position in any of the companies mentioned. This article is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.

Richard Bowman
Richard is an analyst, writer and investor based in Cape Town, South Africa. He has written for several online investment publications and continues to do so. Richard is fascinated by economics, financial markets and behavioral finance. He is also passionate about tools and content that make investing accessible to everyone.
