Here's Why Cydsa. de (BMV:CYDSASAA) Is Weighed Down By Its Debt Load
David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. As with many other companies Cydsa, S.A.B. de C.V. (BMV:CYDSASAA) makes use of debt. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. Part and parcel of capitalism is the process of 'creative destruction' where failed businesses are mercilessly liquidated by their bankers. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, debt can be an important tool in businesses, particularly capital heavy businesses. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Cydsa. de
How Much Debt Does Cydsa. de Carry?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at December 2020 Cydsa. de had debt of Mex$14.0b, up from Mex$11.1b in one year. On the flip side, it has Mex$5.56b in cash leading to net debt of about Mex$8.48b.
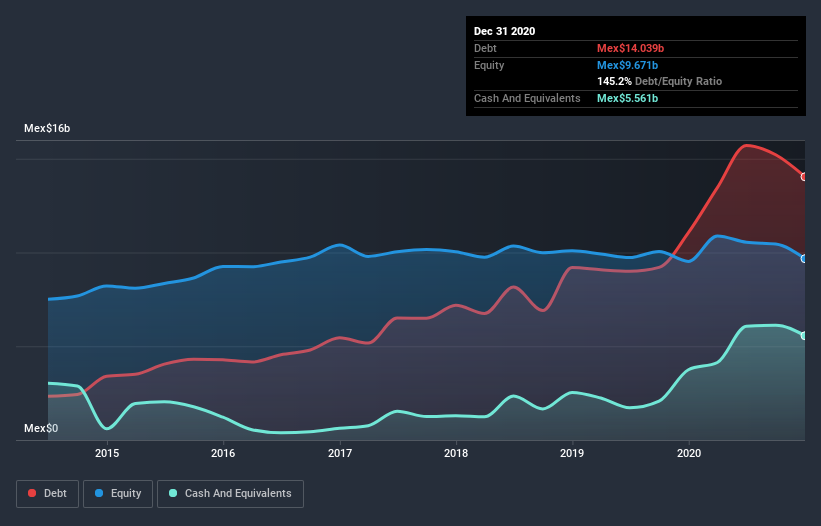
How Strong Is Cydsa. de's Balance Sheet?
We can see from the most recent balance sheet that Cydsa. de had liabilities of Mex$2.95b falling due within a year, and liabilities of Mex$16.4b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had Mex$5.56b in cash and Mex$2.31b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by Mex$11.5b.
When you consider that this deficiency exceeds the company's Mex$8.11b market capitalization, you might well be inclined to review the balance sheet intently. In the scenario where the company had to clean up its balance sheet quickly, it seems likely shareholders would suffer extensive dilution.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
While Cydsa. de's debt to EBITDA ratio (3.3) suggests that it uses some debt, its interest cover is very weak, at 1.7, suggesting high leverage. It seems clear that the cost of borrowing money is negatively impacting returns for shareholders, of late. Another concern for investors might be that Cydsa. de's EBIT fell 20% in the last year. If that's the way things keep going handling the debt load will be like delivering hot coffees on a pogo stick. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Cydsa. de can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Looking at the most recent three years, Cydsa. de recorded free cash flow of 40% of its EBIT, which is weaker than we'd expect. That's not great, when it comes to paying down debt.
Our View
To be frank both Cydsa. de's interest cover and its track record of (not) growing its EBIT make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. Having said that, its ability to convert EBIT to free cash flow isn't such a worry. After considering the datapoints discussed, we think Cydsa. de has too much debt. While some investors love that sort of risky play, it's certainly not our cup of tea. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. We've identified 5 warning signs with Cydsa. de (at least 1 which is significant) , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
When trading Cydsa. de or any other investment, use the platform considered by many to be the Professional's Gateway to the Worlds Market, Interactive Brokers. You get the lowest-cost* trading on stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About BMV:CYDSASA A
Cydsa. de
Together its subsidiaries, produces and markets salt, chlorine, caustic soda, and refrigerant gases, electricity and steam cogeneration, and underground storage of hydrocarbons in Mexico, the United States, Canada, Central and South America, Asia, and Europe.
Reasonable growth potential with adequate balance sheet.
Market Insights
Community Narratives




