- South Korea
- /
- Electronic Equipment and Components
- /
- KOSDAQ:A042600
Here's Why Seronics (KOSDAQ:042600) Has A Meaningful Debt Burden
Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. As with many other companies Seronics Co., Ltd. (KOSDAQ:042600) makes use of debt. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Seronics
What Is Seronics's Debt?
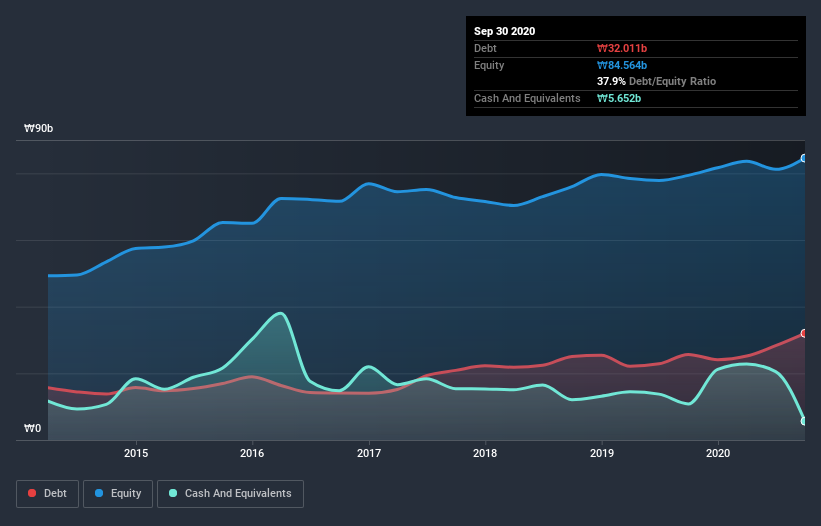
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of September 2020 Seronics had ₩32.0b of debt, an increase on ₩25.7b, over one year. However, it also had ₩5.65b in cash, and so its net debt is ₩26.4b.
How Healthy Is Seronics' Balance Sheet?
We can see from the most recent balance sheet that Seronics had liabilities of ₩43.1b falling due within a year, and liabilities of ₩20.0b due beyond that. On the other hand, it had cash of ₩5.65b and ₩33.8b worth of receivables due within a year. So it has liabilities totalling ₩23.7b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Of course, Seronics has a market capitalization of ₩160.2b, so these liabilities are probably manageable. But there are sufficient liabilities that we would certainly recommend shareholders continue to monitor the balance sheet, going forward.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
Seronics has a debt to EBITDA ratio of 3.9 and its EBIT covered its interest expense 4.3 times. Taken together this implies that, while we wouldn't want to see debt levels rise, we think it can handle its current leverage. Even worse, Seronics saw its EBIT tank 23% over the last 12 months. If earnings continue to follow that trajectory, paying off that debt load will be harder than convincing us to run a marathon in the rain. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is Seronics's earnings that will influence how the balance sheet holds up in the future. So when considering debt, it's definitely worth looking at the earnings trend. Click here for an interactive snapshot.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. During the last three years, Seronics burned a lot of cash. While that may be a result of expenditure for growth, it does make the debt far more risky.
Our View
On the face of it, Seronics's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow left us tentative about the stock, and its EBIT growth rate was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. Having said that, its ability to handle its total liabilities isn't such a worry. We're quite clear that we consider Seronics to be really rather risky, as a result of its balance sheet health. For this reason we're pretty cautious about the stock, and we think shareholders should keep a close eye on its liquidity. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For example, we've discovered 3 warning signs for Seronics (1 is concerning!) that you should be aware of before investing here.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
When trading Seronics or any other investment, use the platform considered by many to be the Professional's Gateway to the Worlds Market, Interactive Brokers. You get the lowest-cost* trading on stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
The New Payments ETF Is Live on NASDAQ:
Money is moving to real-time rails, and a newly listed ETF now gives investors direct exposure. Fast settlement. Institutional custody. Simple access.
Explore how this launch could reshape portfolios
Sponsored ContentNew: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About KOSDAQ:A042600
Seronics
Manufactures and sells electronic components in Korea and North America.
Low risk with worrying balance sheet.
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

THE KINGDOM OF BROWN GOODS: WHY MGPI IS BEING CRUSHED BY INVENTORY & PRIMED FOR RESURRECTION


Why Vertical Aerospace (NYSE: EVTL) is Worth Possibly Over 13x its Current Price

The Quiet Giant That Became AI’s Power Grid
Recently Updated Narratives

Agfa-Gevaert is a digital and materials turnaround opportunity, with growth potential in ZIRFON, but carrying legacy risks.

Hitit Bilgisayar Hizmetleri will achieve a 19.7% revenue boost in the next five years


MINISO's fair value is projected at 26.69 with an anticipated PE ratio shift of 20x
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)





