Three Things You Should Check Before Buying Myotoku Ltd. (TYO:6265) For Its Dividend

Could Myotoku Ltd. (TYO:6265) be an attractive dividend share to own for the long haul? Investors are often drawn to strong companies with the idea of reinvesting the dividends. Unfortunately, it's common for investors to be enticed in by the seemingly attractive yield, and lose money when the company has to cut its dividend payments.
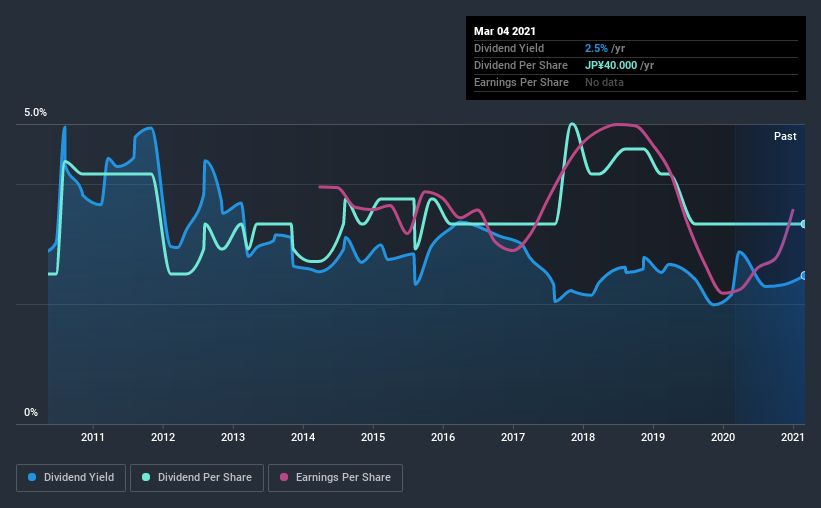
While Myotoku's 2.5% dividend yield is not the highest, we think its lengthy payment history is quite interesting. Some simple analysis can reduce the risk of holding Myotoku for its dividend, and we'll focus on the most important aspects below.
Explore this interactive chart for our latest analysis on Myotoku!
Payout ratios
Companies (usually) pay dividends out of their earnings. If a company is paying more than it earns, the dividend might have to be cut. Comparing dividend payments to a company's net profit after tax is a simple way of reality-checking whether a dividend is sustainable. In the last year, Myotoku paid out 26% of its profit as dividends. This is a medium payout level that leaves enough capital in the business to fund opportunities that might arise, while also rewarding shareholders. Besides, if reinvestment opportunities dry up, the company has room to increase the dividend.
We also measure dividends paid against a company's levered free cash flow, to see if enough cash was generated to cover the dividend. Myotoku's cash payout ratio last year was 20%. Cash flows are typically lumpy, but this looks like an appropriately conservative payout. It's encouraging to see that the dividend is covered by both profit and cash flow. This generally suggests the dividend is sustainable, as long as earnings don't drop precipitously.
While the above analysis focuses on dividends relative to a company's earnings, we do note Myotoku's strong net cash position, which will let it pay larger dividends for a time, should it choose.
We update our data on Myotoku every 24 hours, so you can always get our latest analysis of its financial health, here.
Dividend Volatility
From the perspective of an income investor who wants to earn dividends for many years, there is not much point buying a stock if its dividend is regularly cut or is not reliable. For the purpose of this article, we only scrutinise the last decade of Myotoku's dividend payments. Its dividend payments have declined on at least one occasion over the past 10 years. During the past 10-year period, the first annual payment was JP¥30.0 in 2011, compared to JP¥40.0 last year. This works out to be a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 2.9% a year over that time. The growth in dividends has not been linear, but the CAGR is a decent approximation of the rate of change over this time frame.
Modest growth in the dividend is good to see, but we think this is offset by historical cuts to the payments. It is hard to live on a dividend income if the company's earnings are not consistent.
Dividend Growth Potential
Given that the dividend has been cut in the past, we need to check if earnings are growing and if that might lead to stronger dividends in the future. While there may be fluctuations in the past , Myotoku's earnings per share have basically not grown from where they were five years ago. Flat earnings per share are acceptable for a time, but over the long term, the purchasing power of the company's dividends could be eroded by inflation.
We'd also point out that Myotoku issued a meaningful number of new shares in the past year. Regularly issuing new shares can be detrimental - it's hard to grow dividends per share when new shares are regularly being created.
Conclusion
When we look at a dividend stock, we need to form a judgement on whether the dividend will grow, if the company is able to maintain it in a wide range of economic circumstances, and if the dividend payout is sustainable. It's great to see that Myotoku is paying out a low percentage of its earnings and cash flow. Second, earnings per share have been in decline, and its dividend has been cut at least once in the past. Ultimately, Myotoku comes up short on our dividend analysis. It's not that we think it is a bad company - just that there are likely more appealing dividend prospects out there on this analysis.
Companies possessing a stable dividend policy will likely enjoy greater investor interest than those suffering from a more inconsistent approach. Still, investors need to consider a host of other factors, apart from dividend payments, when analysing a company. To that end, Myotoku has 3 warning signs (and 1 which is significant) we think you should know about.
We have also put together a list of global stocks with a market capitalisation above $1bn and yielding more 3%.
If you decide to trade Myotoku, use the lowest-cost* platform that is rated #1 Overall by Barron’s, Interactive Brokers. Trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds on 135 markets, all from a single integrated account. Promoted
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About TSE:6265
CONVUM
Engages in the manufacture and sale of pneumatic equipment in Japan and internationally.
Flawless balance sheet average dividend payer.
Market Insights
Community Narratives




