Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. Importantly, Reliance Power Limited (NSE:RPOWER) does carry debt. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Of course, debt can be an important tool in businesses, particularly capital heavy businesses. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Reliance Power
How Much Debt Does Reliance Power Carry?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Reliance Power had debt of ₹220.5b at the end of September 2020, a reduction from ₹252.4b over a year. However, it also had ₹17.0b in cash, and so its net debt is ₹203.5b.
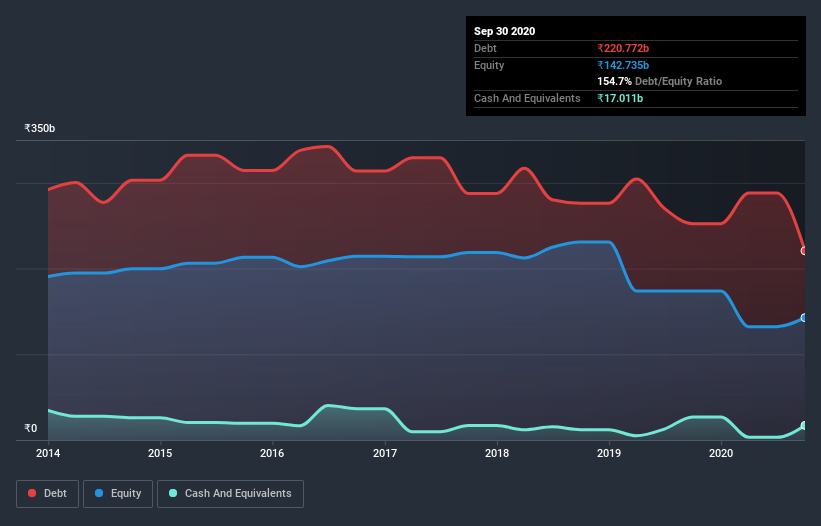
How Strong Is Reliance Power's Balance Sheet?
We can see from the most recent balance sheet that Reliance Power had liabilities of ₹169.1b falling due within a year, and liabilities of ₹225.7b due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of ₹17.0b as well as receivables valued at ₹34.6b due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by ₹343.2b.
The deficiency here weighs heavily on the ₹9.82b company itself, as if a child were struggling under the weight of an enormous back-pack full of books, his sports gear, and a trumpet. So we'd watch its balance sheet closely, without a doubt. After all, Reliance Power would likely require a major re-capitalisation if it had to pay its creditors today.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Reliance Power shareholders face the double whammy of a high net debt to EBITDA ratio (6.0), and fairly weak interest coverage, since EBIT is just 0.87 times the interest expense. This means we'd consider it to have a heavy debt load. Worse, Reliance Power's EBIT was down 22% over the last year. If earnings continue to follow that trajectory, paying off that debt load will be harder than convincing us to run a marathon in the rain. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is Reliance Power's earnings that will influence how the balance sheet holds up in the future. So when considering debt, it's definitely worth looking at the earnings trend. Click here for an interactive snapshot.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, Reliance Power actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last three years. That sort of strong cash conversion gets us as excited as the crowd when the beat drops at a Daft Punk concert.
Our View
To be frank both Reliance Power's EBIT growth rate and its track record of staying on top of its total liabilities make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But at least it's pretty decent at converting EBIT to free cash flow; that's encouraging. Overall, it seems to us that Reliance Power's balance sheet is really quite a risk to the business. So we're almost as wary of this stock as a hungry kitten is about falling into its owner's fish pond: once bitten, twice shy, as they say. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. Take risks, for example - Reliance Power has 2 warning signs (and 1 which is potentially serious) we think you should know about.
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
If you decide to trade Reliance Power, use the lowest-cost* platform that is rated #1 Overall by Barron’s, Interactive Brokers. Trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds on 135 markets, all from a single integrated account. Promoted
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About NSEI:RPOWER
Reliance Power
Engages in the development, construction, and operation of power projects in India and internationally.
Low risk with poor track record.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

Solutions by stc: 34% Upside in Saudi's Digital Transformation Leader


The AI Infrastructure Giant Grows Into Its Valuation
Recently Updated Narratives
Many trends acting at the same time


Engineered for Stability. Positioned for Growth.


Staggered by dilution; positions for growth
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026



