David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. We can see that Uflex Limited (NSE:UFLEX) does use debt in its business. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. Part and parcel of capitalism is the process of 'creative destruction' where failed businesses are mercilessly liquidated by their bankers. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Uflex
What Is Uflex's Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of March 2022 Uflex had ₹45.6b of debt, an increase on ₹40.0b, over one year. However, it does have ₹5.88b in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about ₹39.7b.
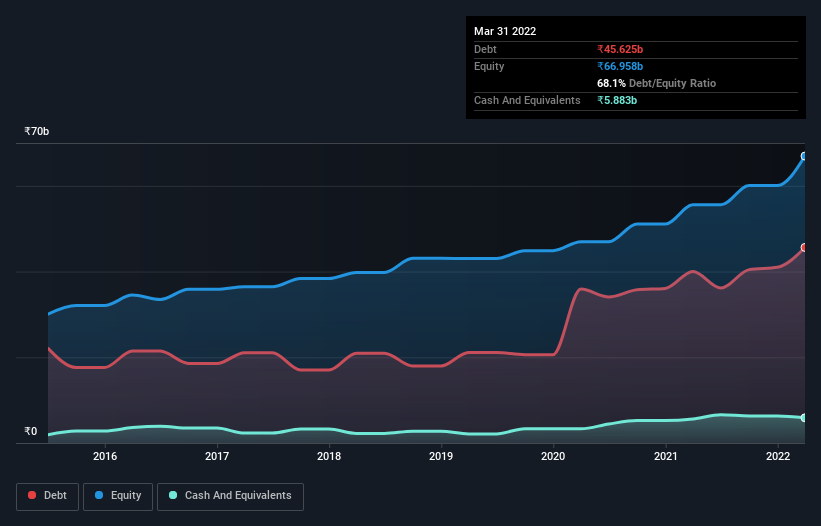
A Look At Uflex's Liabilities
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Uflex had liabilities of ₹40.8b due within 12 months and liabilities of ₹36.7b due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of ₹5.88b as well as receivables valued at ₹35.3b due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling ₹36.3b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
This deficit is considerable relative to its market capitalization of ₹44.5b, so it does suggest shareholders should keep an eye on Uflex's use of debt. This suggests shareholders would be heavily diluted if the company needed to shore up its balance sheet in a hurry.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Uflex's net debt is sitting at a very reasonable 1.8 times its EBITDA, while its EBIT covered its interest expense just 5.1 times last year. While these numbers do not alarm us, it's worth noting that the cost of the company's debt is having a real impact. We note that Uflex grew its EBIT by 24% in the last year, and that should make it easier to pay down debt, going forward. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But you can't view debt in total isolation; since Uflex will need earnings to service that debt. So when considering debt, it's definitely worth looking at the earnings trend. Click here for an interactive snapshot.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. Over the last three years, Uflex saw substantial negative free cash flow, in total. While that may be a result of expenditure for growth, it does make the debt far more risky.
Our View
Uflex's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow was a real negative on this analysis, although the other factors we considered cast it in a significantly better light. For example its EBIT growth rate was refreshing. Taking the abovementioned factors together we do think Uflex's debt poses some risks to the business. So while that leverage does boost returns on equity, we wouldn't really want to see it increase from here. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. Case in point: We've spotted 2 warning signs for Uflex you should be aware of, and 1 of them is significant.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NSEI:UFLEX
Uflex
Manufactures and sells flexible packaging materials and solutions in India, the United States, Canada, Egypt, Europe, and internationally.
Second-rate dividend payer with low risk.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives





