These 4 Measures Indicate That Telstra Group (ASX:TLS) Is Using Debt Reasonably Well

Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We can see that Telstra Group Limited (ASX:TLS) does use debt in its business. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Telstra Group
What Is Telstra Group's Net Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at December 2022 Telstra Group had debt of AU$12.8b, up from AU$12.0b in one year. However, because it has a cash reserve of AU$1.04b, its net debt is less, at about AU$11.8b.
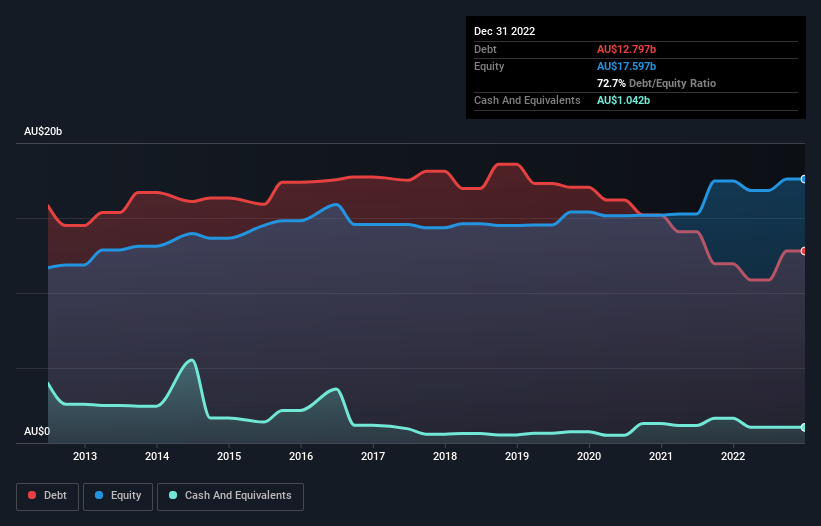
How Strong Is Telstra Group's Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Telstra Group had liabilities of AU$11.2b due within 12 months and liabilities of AU$15.9b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had AU$1.04b in cash and AU$4.11b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling AU$21.9b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
This deficit isn't so bad because Telstra Group is worth a massive AU$50.3b, and thus could probably raise enough capital to shore up its balance sheet, if the need arose. However, it is still worthwhile taking a close look at its ability to pay off debt.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Telstra Group's net debt is sitting at a very reasonable 2.0 times its EBITDA, while its EBIT covered its interest expense just 6.3 times last year. It seems that the business incurs large depreciation and amortisation charges, so maybe its debt load is heavier than it would first appear, since EBITDA is arguably a generous measure of earnings. It is well worth noting that Telstra Group's EBIT shot up like bamboo after rain, gaining 31% in the last twelve months. That'll make it easier to manage its debt. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Telstra Group's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, Telstra Group actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last three years. That sort of strong cash conversion gets us as excited as the crowd when the beat drops at a Daft Punk concert.
Our View
The good news is that Telstra Group's demonstrated ability to convert EBIT to free cash flow delights us like a fluffy puppy does a toddler. But, on a more sombre note, we are a little concerned by its level of total liabilities. Taking all this data into account, it seems to us that Telstra Group takes a pretty sensible approach to debt. While that brings some risk, it can also enhance returns for shareholders. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. Case in point: We've spotted 2 warning signs for Telstra Group you should be aware of.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
If you're looking to trade Telstra Group, open an account with the lowest-cost platform trusted by professionals, Interactive Brokers.
With clients in over 200 countries and territories, and access to 160 markets, IBKR lets you trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds from a single integrated account.
Enjoy no hidden fees, no account minimums, and FX conversion rates as low as 0.03%, far better than what most brokers offer.
Sponsored ContentValuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Telstra Group might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About ASX:TLS
Telstra Group
Engages in the provision of telecommunications and information services to businesses, government, and individuals in Australia and internationally.
Mediocre balance sheet low.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



