- Australia
- /
- Specialty Stores
- /
- ASX:BBN
These 4 Measures Indicate That Baby Bunting Group (ASX:BBN) Is Using Debt Safely

Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. As with many other companies Baby Bunting Group Limited (ASX:BBN) makes use of debt. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Baby Bunting Group
What Is Baby Bunting Group's Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of December 2020 Baby Bunting Group had AU$29.2m of debt, an increase on AU$21.1m, over one year. On the flip side, it has AU$14.7m in cash leading to net debt of about AU$14.5m.
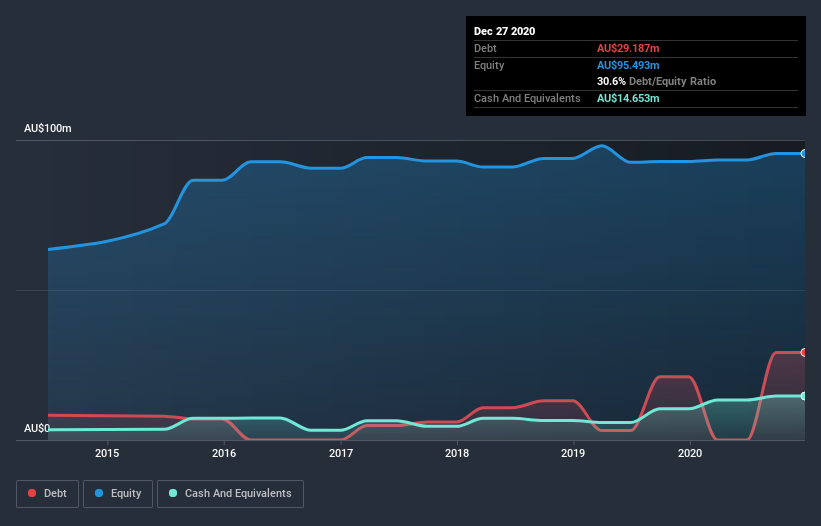
How Strong Is Baby Bunting Group's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Baby Bunting Group had liabilities of AU$89.7m due within 12 months, and liabilities of AU$111.0m due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of AU$14.7m and AU$8.48m worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by AU$177.6m.
While this might seem like a lot, it is not so bad since Baby Bunting Group has a market capitalization of AU$651.5m, and so it could probably strengthen its balance sheet by raising capital if it needed to. But it's clear that we should definitely closely examine whether it can manage its debt without dilution.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
While Baby Bunting Group's low debt to EBITDA ratio of 0.39 suggests only modest use of debt, the fact that EBIT only covered the interest expense by 5.8 times last year does give us pause. So we'd recommend keeping a close eye on the impact financing costs are having on the business. Importantly, Baby Bunting Group grew its EBIT by 35% over the last twelve months, and that growth will make it easier to handle its debt. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Baby Bunting Group can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Over the last three years, Baby Bunting Group recorded free cash flow worth a fulsome 88% of its EBIT, which is stronger than we'd usually expect. That positions it well to pay down debt if desirable to do so.
Our View
The good news is that Baby Bunting Group's demonstrated ability to convert EBIT to free cash flow delights us like a fluffy puppy does a toddler. And the good news does not stop there, as its EBIT growth rate also supports that impression! Looking at the bigger picture, we think Baby Bunting Group's use of debt seems quite reasonable and we're not concerned about it. After all, sensible leverage can boost returns on equity. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For instance, we've identified 2 warning signs for Baby Bunting Group that you should be aware of.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
When trading Baby Bunting Group or any other investment, use the platform considered by many to be the Professional's Gateway to the Worlds Market, Interactive Brokers. You get the lowest-cost* trading on stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Baby Bunting Group might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About ASX:BBN
Baby Bunting Group
Engages in the retail of maternity and baby goods in Australia and New Zealand.
Reasonable growth potential with adequate balance sheet.


