David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. We can see that Accel, S.A.B. de C.V. (BMV:ACCELSAB) does use debt in its business. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Accel. de
What Is Accel. de's Net Debt?
As you can see below, at the end of September 2022, Accel. de had Mex$2.49b of debt, up from Mex$1.74b a year ago. Click the image for more detail. However, because it has a cash reserve of Mex$496.3m, its net debt is less, at about Mex$1.99b.
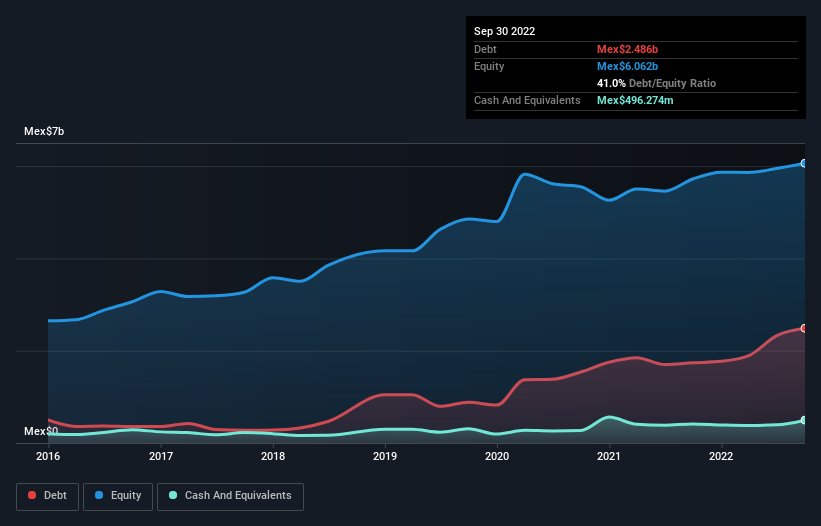
How Healthy Is Accel. de's Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Accel. de had liabilities of Mex$3.10b due within 12 months and liabilities of Mex$2.36b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had Mex$496.3m in cash and Mex$2.30b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by Mex$2.66b.
This is a mountain of leverage relative to its market capitalization of Mex$4.25b. Should its lenders demand that it shore up the balance sheet, shareholders would likely face severe dilution.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Accel. de's net debt of 1.8 times EBITDA suggests graceful use of debt. And the alluring interest cover (EBIT of 7.2 times interest expense) certainly does not do anything to dispel this impression. The bad news is that Accel. de saw its EBIT decline by 19% over the last year. If that sort of decline is not arrested, then the managing its debt will be harder than selling broccoli flavoured ice-cream for a premium. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But you can't view debt in total isolation; since Accel. de will need earnings to service that debt. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. Over the last three years, Accel. de recorded negative free cash flow, in total. Debt is usually more expensive, and almost always more risky in the hands of a company with negative free cash flow. Shareholders ought to hope for an improvement.
Our View
To be frank both Accel. de's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow and its track record of (not) growing its EBIT make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But at least it's pretty decent at covering its interest expense with its EBIT; that's encouraging. We're quite clear that we consider Accel. de to be really rather risky, as a result of its balance sheet health. So we're almost as wary of this stock as a hungry kitten is about falling into its owner's fish pond: once bitten, twice shy, as they say. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. These risks can be hard to spot. Every company has them, and we've spotted 3 warning signs for Accel. de (of which 2 are concerning!) you should know about.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About BMV:ACCELSA B
Accel. de
Provides manufacturing and logistics services in Mexico and the United States.
Mediocre balance sheet with poor track record.
Market Insights
Community Narratives




