
Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. As with many other companies LG Chem, Ltd. (KRX:051910) makes use of debt. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. Part and parcel of capitalism is the process of 'creative destruction' where failed businesses are mercilessly liquidated by their bankers. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for LG Chem
How Much Debt Does LG Chem Carry?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at March 2024 LG Chem had debt of ₩24t, up from ₩17t in one year. However, because it has a cash reserve of ₩9.29t, its net debt is less, at about ₩15t.
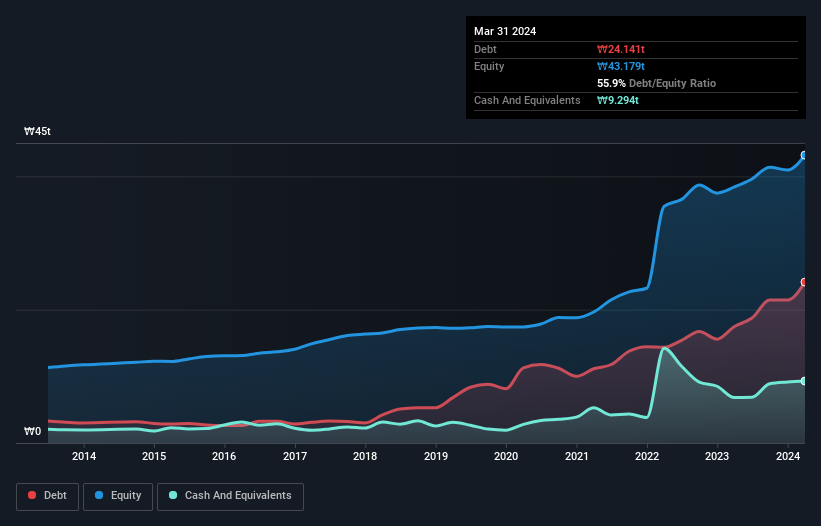
How Strong Is LG Chem's Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that LG Chem had liabilities of ₩19t due within 12 months and liabilities of ₩20t due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of ₩9.29t as well as receivables valued at ₩9.00t due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by ₩21t.
This deficit is considerable relative to its very significant market capitalization of ₩27t, so it does suggest shareholders should keep an eye on LG Chem's use of debt. Should its lenders demand that it shore up the balance sheet, shareholders would likely face severe dilution.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
LG Chem has net debt worth 2.5 times EBITDA, which isn't too much, but its interest cover looks a bit on the low side, with EBIT at only 5.3 times the interest expense. In large part that's due to the company's significant depreciation and amortisation charges, which arguably mean its EBITDA is a very generous measure of earnings, and its debt may be more of a burden than it first appears. Importantly, LG Chem's EBIT fell a jaw-dropping 28% in the last twelve months. If that decline continues then paying off debt will be harder than selling foie gras at a vegan convention. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine LG Chem's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. During the last three years, LG Chem burned a lot of cash. While that may be a result of expenditure for growth, it does make the debt far more risky.
Our View
On the face of it, LG Chem's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow left us tentative about the stock, and its EBIT growth rate was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. But at least its interest cover is not so bad. We're quite clear that we consider LG Chem to be really rather risky, as a result of its balance sheet health. So we're almost as wary of this stock as a hungry kitten is about falling into its owner's fish pond: once bitten, twice shy, as they say. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. Case in point: We've spotted 1 warning sign for LG Chem you should be aware of.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com
About KOSE:A051910
LG Chem
Engages in the petrochemicals, energy, advanced materials, and life science businesses in Korea, China, Asia/Oceania, the United States, Europe, and internationally.
Very undervalued with reasonable growth potential.


