- Hong Kong
- /
- Semiconductors
- /
- SEHK:968
Here's Why Xinyi Solar Holdings (HKG:968) Has A Meaningful Debt Burden

Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. We can see that Xinyi Solar Holdings Limited (HKG:968) does use debt in its business. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. Of course, debt can be an important tool in businesses, particularly capital heavy businesses. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Xinyi Solar Holdings
What Is Xinyi Solar Holdings's Net Debt?
As you can see below, at the end of June 2023, Xinyi Solar Holdings had HK$8.45b of debt, up from HK$6.98b a year ago. Click the image for more detail. However, it does have HK$4.26b in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about HK$4.19b.
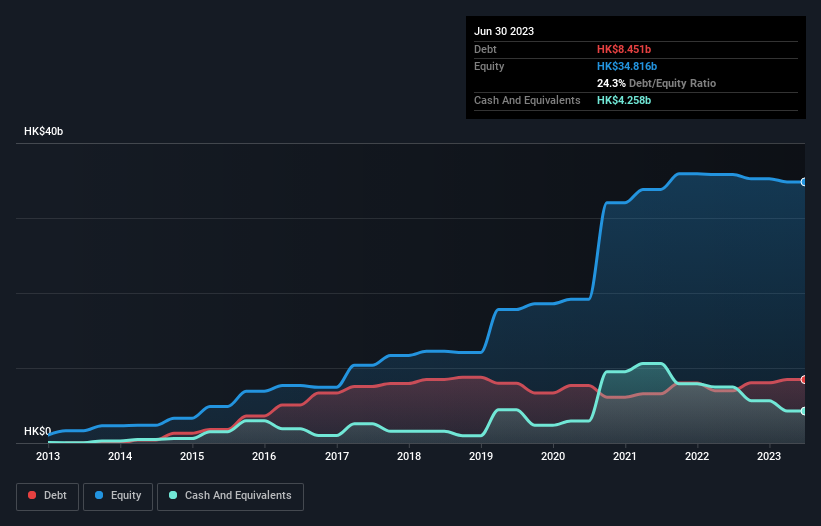
How Healthy Is Xinyi Solar Holdings' Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Xinyi Solar Holdings had liabilities of HK$14.2b due within 12 months, and liabilities of HK$4.00b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of HK$4.26b as well as receivables valued at HK$12.0b due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling HK$1.96b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Since publicly traded Xinyi Solar Holdings shares are worth a total of HK$38.9b, it seems unlikely that this level of liabilities would be a major threat. Having said that, it's clear that we should continue to monitor its balance sheet, lest it change for the worse.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Xinyi Solar Holdings's net debt is only 0.66 times its EBITDA. And its EBIT easily covers its interest expense, being 15.5 times the size. So you could argue it is no more threatened by its debt than an elephant is by a mouse. On the other hand, Xinyi Solar Holdings saw its EBIT drop by 9.5% in the last twelve months. If earnings continue to decline at that rate the company may have increasing difficulty managing its debt load. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Xinyi Solar Holdings can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. Considering the last three years, Xinyi Solar Holdings actually recorded a cash outflow, overall. Debt is far more risky for companies with unreliable free cash flow, so shareholders should be hoping that the past expenditure will produce free cash flow in the future.
Our View
Neither Xinyi Solar Holdings's ability to convert EBIT to free cash flow nor its EBIT growth rate gave us confidence in its ability to take on more debt. But its interest cover tells a very different story, and suggests some resilience. We think that Xinyi Solar Holdings's debt does make it a bit risky, after considering the aforementioned data points together. That's not necessarily a bad thing, since leverage can boost returns on equity, but it is something to be aware of. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For instance, we've identified 2 warning signs for Xinyi Solar Holdings that you should be aware of.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About SEHK:968
Xinyi Solar Holdings
An investment holding company, produces and sells solar glass products in the People’s Republic of China, rest of Asia, North America, Europe, and internationally.
Undervalued with excellent balance sheet.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



