- Hong Kong
- /
- Oil and Gas
- /
- SEHK:956
These 4 Measures Indicate That China Suntien Green Energy (HKG:956) Is Using Debt In A Risky Way

Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. Importantly, China Suntien Green Energy Corporation Limited (HKG:956) does carry debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
View our latest analysis for China Suntien Green Energy
What Is China Suntien Green Energy's Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at September 2020 China Suntien Green Energy had debt of CN¥26.2b, up from CN¥19.9b in one year. However, because it has a cash reserve of CN¥2.33b, its net debt is less, at about CN¥23.9b.
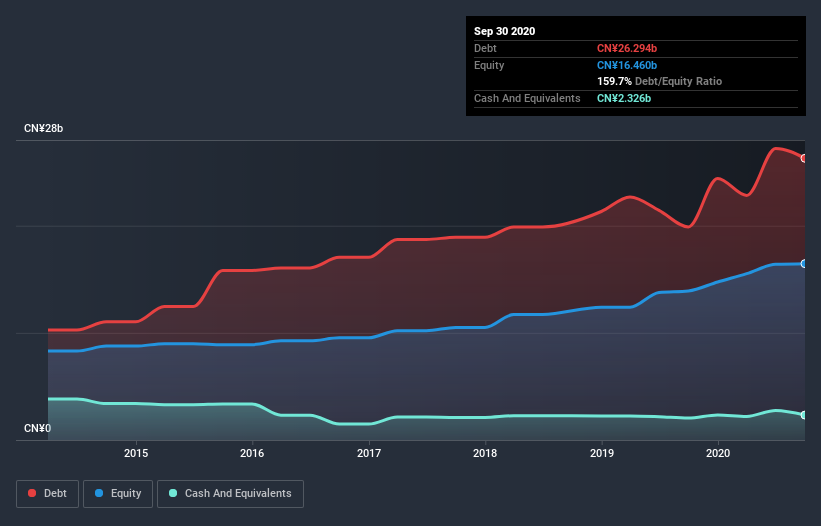
A Look At China Suntien Green Energy's Liabilities
According to the last reported balance sheet, China Suntien Green Energy had liabilities of CN¥10.7b due within 12 months, and liabilities of CN¥26.3b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting this, it had CN¥2.33b in cash and CN¥4.99b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by CN¥29.7b.
This deficit casts a shadow over the CN¥19.5b company, like a colossus towering over mere mortals. So we'd watch its balance sheet closely, without a doubt. At the end of the day, China Suntien Green Energy would probably need a major re-capitalization if its creditors were to demand repayment.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
With a net debt to EBITDA ratio of 5.8, it's fair to say China Suntien Green Energy does have a significant amount of debt. But the good news is that it boasts fairly comforting interest cover of 3.1 times, suggesting it can responsibly service its obligations. The good news is that China Suntien Green Energy improved its EBIT by 5.6% over the last twelve months, thus gradually reducing its debt levels relative to its earnings. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine China Suntien Green Energy's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. During the last three years, China Suntien Green Energy burned a lot of cash. While that may be a result of expenditure for growth, it does make the debt far more risky.
Our View
On the face of it, China Suntien Green Energy's net debt to EBITDA left us tentative about the stock, and its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. Having said that, its ability to grow its EBIT isn't such a worry. Taking into account all the aforementioned factors, it looks like China Suntien Green Energy has too much debt. That sort of riskiness is ok for some, but it certainly doesn't float our boat. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For example, we've discovered 3 warning signs for China Suntien Green Energy (1 makes us a bit uncomfortable!) that you should be aware of before investing here.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
When trading China Suntien Green Energy or any other investment, use the platform considered by many to be the Professional's Gateway to the Worlds Market, Interactive Brokers. You get the lowest-cost* trading on stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About SEHK:956
China Suntien Green Energy
Develops and utilizes clean energy in Mainland China.
Fair value second-rate dividend payer.
Market Insights
Community Narratives