
Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. As with many other companies CGG (EPA:CGG) makes use of debt. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for CGG
What Is CGG's Debt?
As you can see below, at the end of September 2023, CGG had US$1.20b of debt, up from US$1.11b a year ago. Click the image for more detail. However, it also had US$275.1m in cash, and so its net debt is US$921.5m.
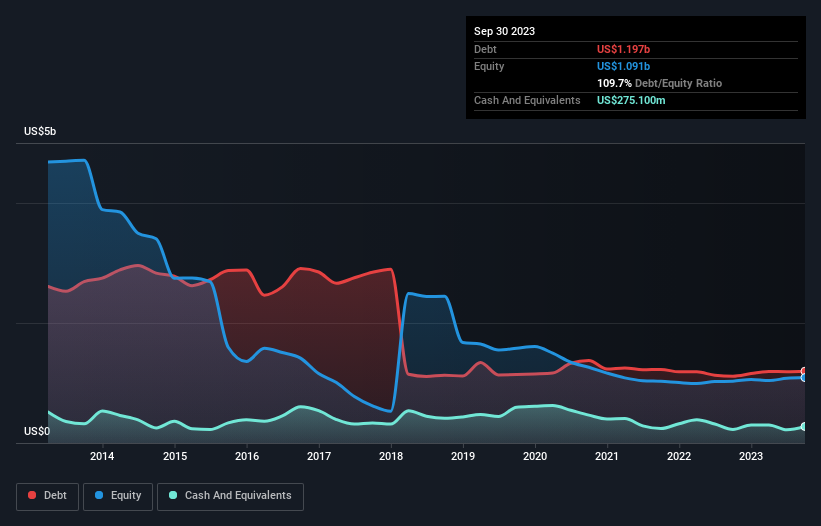
A Look At CGG's Liabilities
The latest balance sheet data shows that CGG had liabilities of US$565.6m due within a year, and liabilities of US$1.26b falling due after that. Offsetting this, it had US$275.1m in cash and US$327.6m in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling US$1.22b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
This deficit casts a shadow over the US$294.5m company, like a colossus towering over mere mortals. So we'd watch its balance sheet closely, without a doubt. At the end of the day, CGG would probably need a major re-capitalization if its creditors were to demand repayment.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
While CGG's debt to EBITDA ratio (2.7) suggests that it uses some debt, its interest cover is very weak, at 1.9, suggesting high leverage. It seems clear that the cost of borrowing money is negatively impacting returns for shareholders, of late. Investors should also be troubled by the fact that CGG saw its EBIT drop by 12% over the last twelve months. If things keep going like that, handling the debt will about as easy as bundling an angry house cat into its travel box. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if CGG can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. During the last two years, CGG produced sturdy free cash flow equating to 53% of its EBIT, about what we'd expect. This cold hard cash means it can reduce its debt when it wants to.
Our View
To be frank both CGG's interest cover and its track record of staying on top of its total liabilities make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But at least it's pretty decent at converting EBIT to free cash flow; that's encouraging. We're quite clear that we consider CGG to be really rather risky, as a result of its balance sheet health. So we're almost as wary of this stock as a hungry kitten is about falling into its owner's fish pond: once bitten, twice shy, as they say. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. Case in point: We've spotted 2 warning signs for CGG you should be aware of, and 1 of them is a bit unpleasant.
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About ENXTPA:VIRI
Viridien Société anonyme
Engages in the provision of data, products, services, and solutions in Earth science, data science, sensing, and monitoring in North America, Latin America, the Central and South Americas, Europe, Africa, the Middle East, and the Asia Pacific.
Undervalued with moderate growth potential.

