
Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. We can see that Lindsay Australia Limited (ASX:LAU) does use debt in its business. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
Check out our latest analysis for Lindsay Australia
What Is Lindsay Australia's Debt?
As you can see below, at the end of June 2020, Lindsay Australia had AU$25.1m of debt, up from AU$20.1m a year ago. Click the image for more detail. However, it does have AU$17.9m in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about AU$7.21m.
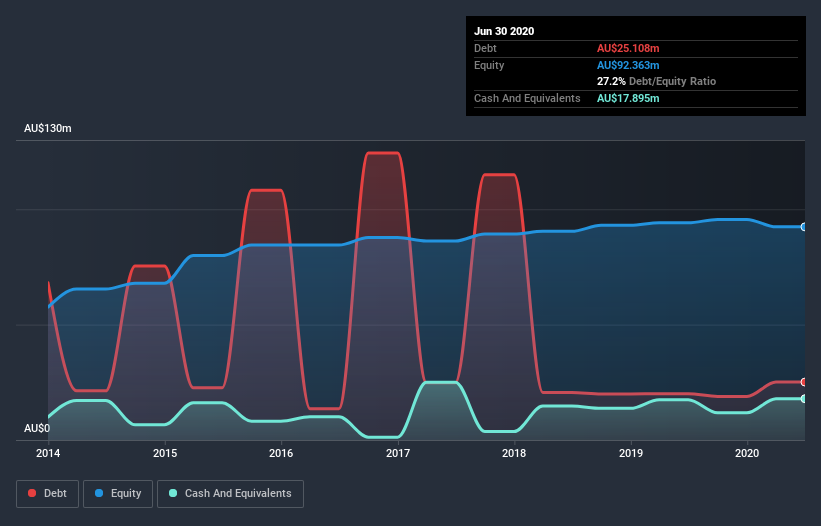
A Look At Lindsay Australia's Liabilities
The latest balance sheet data shows that Lindsay Australia had liabilities of AU$91.5m due within a year, and liabilities of AU$177.7m falling due after that. On the other hand, it had cash of AU$17.9m and AU$51.8m worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities total AU$199.5m more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
This deficit casts a shadow over the AU$98.8m company, like a colossus towering over mere mortals. So we definitely think shareholders need to watch this one closely. After all, Lindsay Australia would likely require a major re-capitalisation if it had to pay its creditors today.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Given net debt is only 0.35 times EBITDA, it is initially surprising to see that Lindsay Australia's EBIT has low interest coverage of 1.6 times. So while we're not necessarily alarmed we think that its debt is far from trivial. Importantly, Lindsay Australia's EBIT fell a jaw-dropping 21% in the last twelve months. If that decline continues then paying off debt will be harder than selling foie gras at a vegan convention. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Lindsay Australia's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Over the last three years, Lindsay Australia actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT. There's nothing better than incoming cash when it comes to staying in your lenders' good graces.
Our View
To be frank both Lindsay Australia's EBIT growth rate and its track record of staying on top of its total liabilities make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But at least it's pretty decent at converting EBIT to free cash flow; that's encouraging. We're quite clear that we consider Lindsay Australia to be really rather risky, as a result of its balance sheet health. For this reason we're pretty cautious about the stock, and we think shareholders should keep a close eye on its liquidity. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For instance, we've identified 4 warning signs for Lindsay Australia that you should be aware of.
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
If you’re looking to trade Lindsay Australia, open an account with the lowest-cost* platform trusted by professionals, Interactive Brokers. Their clients from over 200 countries and territories trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com.
About ASX:LAU
Lindsay Australia
Provides integrated transport, logistics, and rural supply services to the food processing, food services, fresh produce, and horticulture sectors in Australia.
Undervalued with excellent balance sheet and pays a dividend.
Market Insights
Community Narratives




