Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. Importantly, Brickworks Limited (ASX:BKW) does carry debt. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
See our latest analysis for Brickworks
What Is Brickworks's Net Debt?
As you can see below, Brickworks had AU$594.7m of debt at July 2022, down from AU$662.3m a year prior. On the flip side, it has AU$106.1m in cash leading to net debt of about AU$488.6m.
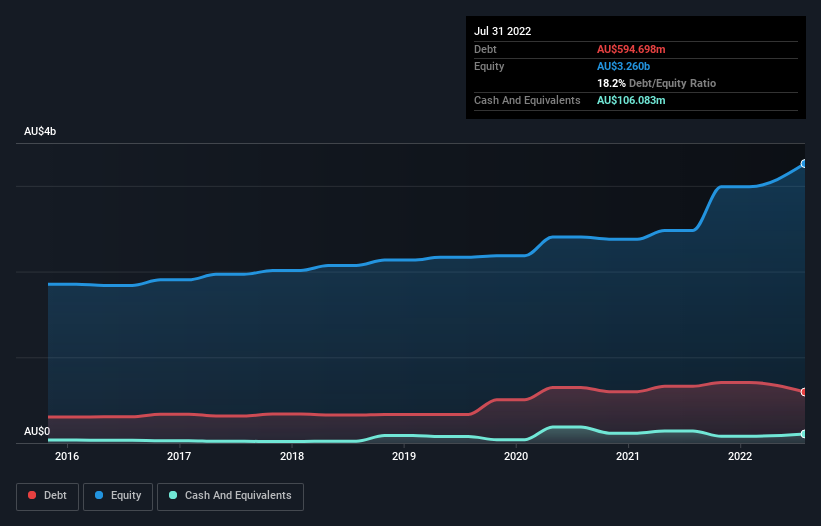
A Look At Brickworks' Liabilities
According to the last reported balance sheet, Brickworks had liabilities of AU$325.7m due within 12 months, and liabilities of AU$1.99b due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of AU$106.1m and AU$157.3m worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities total AU$2.05b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
This is a mountain of leverage relative to its market capitalization of AU$3.34b. Should its lenders demand that it shore up the balance sheet, shareholders would likely face severe dilution.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Brickworks shareholders face the double whammy of a high net debt to EBITDA ratio (5.2), and fairly weak interest coverage, since EBIT is just 1.6 times the interest expense. The debt burden here is substantial. However, it should be some comfort for shareholders to recall that Brickworks actually grew its EBIT by a hefty 154%, over the last 12 months. If that earnings trend continues it will make its debt load much more manageable in the future. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Brickworks can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. Considering the last three years, Brickworks actually recorded a cash outflow, overall. Debt is far more risky for companies with unreliable free cash flow, so shareholders should be hoping that the past expenditure will produce free cash flow in the future.
Our View
On the face of it, Brickworks's interest cover left us tentative about the stock, and its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. But on the bright side, its EBIT growth rate is a good sign, and makes us more optimistic. Looking at the balance sheet and taking into account all these factors, we do believe that debt is making Brickworks stock a bit risky. That's not necessarily a bad thing, but we'd generally feel more comfortable with less leverage. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. To that end, you should learn about the 3 warning signs we've spotted with Brickworks (including 2 which can't be ignored) .
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
Mobile Infrastructure for Defense and Disaster
The next wave in robotics isn't humanoid. Its fully autonomous towers delivering 5G, ISR, and radar in under 30 minutes, anywhere.
Get the investor briefing before the next round of contracts
Sponsored On Behalf of CiTechValuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Brickworks might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About ASX:BKW
Brickworks
Engages in the manufacture, sale, and distribution of building products for the residential and commercial markets in Australia and North America.
Reasonable growth potential with imperfect balance sheet.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

Early mover in a fast growing industry. Likely to experience share price volatility as they scale


A case for CA$31.80 (undiluted), aka 8,616% upside from CA$0.37 (an 86 bagger!).


Moderation and Stabilisation: HOLD: Fair Price based on a 4-year Cycle is $12.08
Recently Updated Narratives

Amazon: Why the World’s Biggest Platform Still Runs on Invisible Economics

Sunrun Stock: When the Energy Transition Collides With the Cost of Capital

Salesforce Stock: AI-Fueled Growth Is Real — But Can Margins Stay This Strong?
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)






