- United States
- /
- IT
- /
- NYSE:IBM
Does International Business Machines (NYSE:IBM) Have A Healthy Balance Sheet?

Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. As with many other companies International Business Machines Corporation (NYSE:IBM) makes use of debt. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for International Business Machines
What Is International Business Machines's Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of September 2023 International Business Machines had US$54.9b of debt, an increase on US$50.7b, over one year. On the flip side, it has US$11.0b in cash leading to net debt of about US$44.0b.
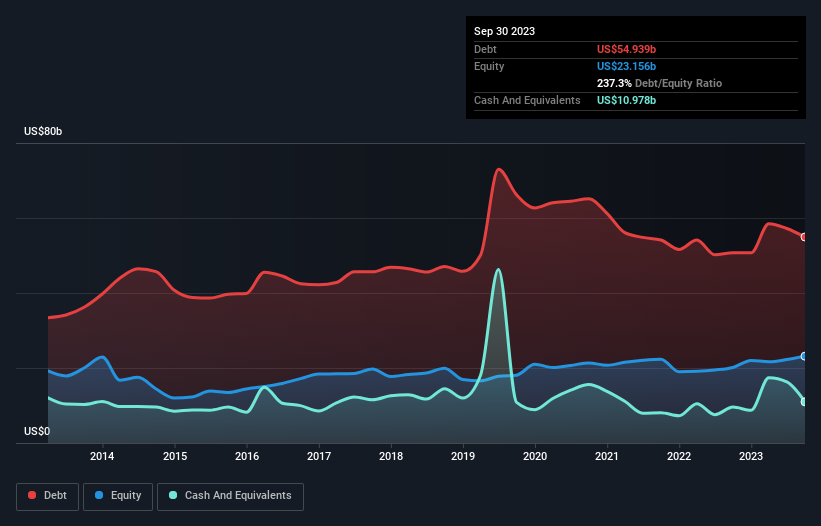
How Strong Is International Business Machines' Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that International Business Machines had liabilities of US$30.6b due within 12 months and liabilities of US$75.6b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had US$11.0b in cash and US$6.51b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling US$88.7b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
While this might seem like a lot, it is not so bad since International Business Machines has a huge market capitalization of US$152.3b, and so it could probably strengthen its balance sheet by raising capital if it needed to. However, it is still worthwhile taking a close look at its ability to pay off debt.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
International Business Machines has a debt to EBITDA ratio of 3.2, which signals significant debt, but is still pretty reasonable for most types of business. But its EBIT was about 10.0 times its interest expense, implying the company isn't really paying a high cost to maintain that level of debt. Even were the low cost to prove unsustainable, that is a good sign. It is well worth noting that International Business Machines's EBIT shot up like bamboo after rain, gaining 33% in the last twelve months. That'll make it easier to manage its debt. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if International Business Machines can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, International Business Machines actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last three years. There's nothing better than incoming cash when it comes to staying in your lenders' good graces.
Our View
International Business Machines's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow suggests it can handle its debt as easily as Cristiano Ronaldo could score a goal against an under 14's goalkeeper. But truth be told we feel its net debt to EBITDA does undermine this impression a bit. When we consider the range of factors above, it looks like International Business Machines is pretty sensible with its use of debt. That means they are taking on a bit more risk, in the hope of boosting shareholder returns. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. Be aware that International Business Machines is showing 1 warning sign in our investment analysis , you should know about...
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NYSE:IBM
International Business Machines
Provides integrated solutions and services in the Americas, Europe, the Middle East, Africa, and the Asia Pacific.
Adequate balance sheet average dividend payer.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



