
Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. Importantly, The Home Depot, Inc. (NYSE:HD) does carry debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Home Depot
What Is Home Depot's Debt?
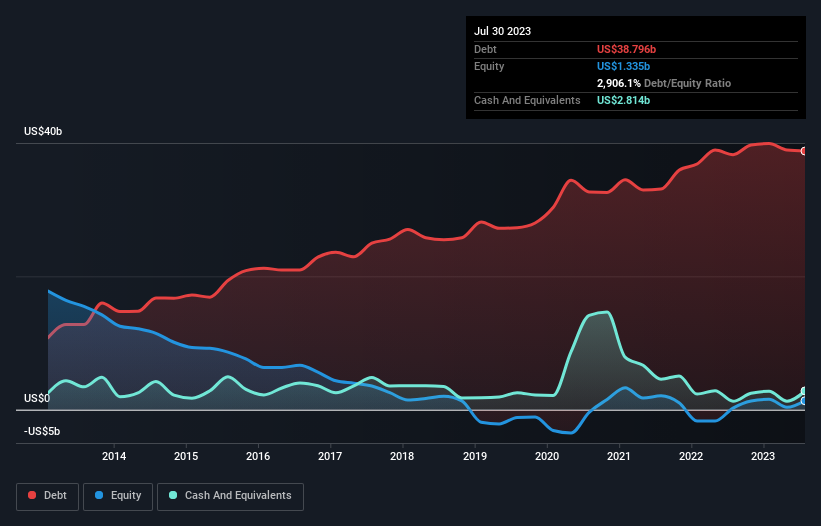
The chart below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Home Depot had US$38.8b in debt in July 2023; about the same as the year before. However, it also had US$2.81b in cash, and so its net debt is US$36.0b.
How Healthy Is Home Depot's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Home Depot had liabilities of US$24.2b due within 12 months, and liabilities of US$50.8b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$2.81b as well as receivables valued at US$3.84b due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by US$68.4b.
This deficit isn't so bad because Home Depot is worth a massive US$295.6b, and thus could probably raise enough capital to shore up its balance sheet, if the need arose. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Home Depot's net debt is only 1.4 times its EBITDA. And its EBIT easily covers its interest expense, being 13.7 times the size. So you could argue it is no more threatened by its debt than an elephant is by a mouse. But the other side of the story is that Home Depot saw its EBIT decline by 3.0% over the last year. That sort of decline, if sustained, will obviously make debt harder to handle. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Home Depot's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Over the most recent three years, Home Depot recorded free cash flow worth 56% of its EBIT, which is around normal, given free cash flow excludes interest and tax. This free cash flow puts the company in a good position to pay down debt, when appropriate.
Our View
When it comes to the balance sheet, the standout positive for Home Depot was the fact that it seems able to cover its interest expense with its EBIT confidently. But the other factors we noted above weren't so encouraging. For instance it seems like it has to struggle a bit to grow its EBIT. When we consider all the elements mentioned above, it seems to us that Home Depot is managing its debt quite well. But a word of caution: we think debt levels are high enough to justify ongoing monitoring. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. Case in point: We've spotted 2 warning signs for Home Depot you should be aware of.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Home Depot might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NYSE:HD
Home Depot
Operates as a home improvement retailer in the United States and internationally.
Established dividend payer with adequate balance sheet.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



