- United States
- /
- Life Sciences
- /
- NYSE:AVTR
These 4 Measures Indicate That Avantor (NYSE:AVTR) Is Using Debt Extensively
David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. As with many other companies Avantor, Inc. (NYSE:AVTR) makes use of debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for Avantor
What Is Avantor's Debt?
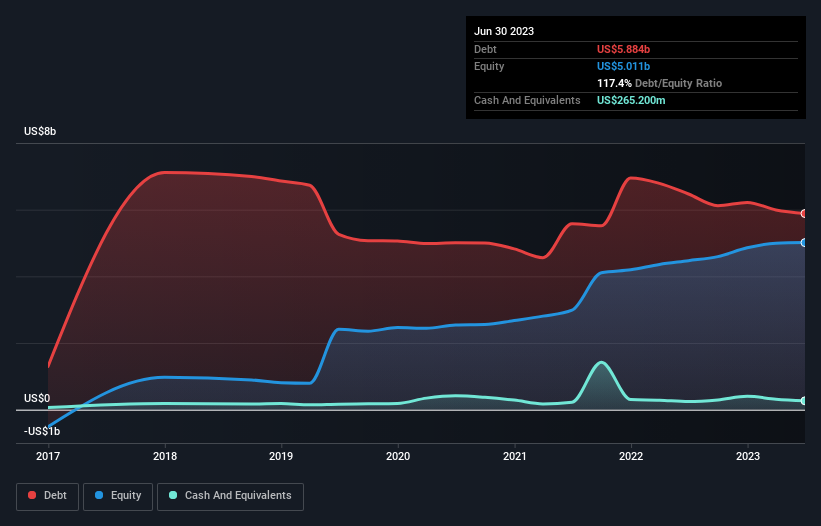
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that Avantor had US$5.88b of debt in June 2023, down from US$6.47b, one year before. However, it also had US$265.2m in cash, and so its net debt is US$5.62b.
A Look At Avantor's Liabilities
The latest balance sheet data shows that Avantor had liabilities of US$1.55b due within a year, and liabilities of US$6.50b falling due after that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$265.2m as well as receivables valued at US$1.22b due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling US$6.57b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Avantor has a very large market capitalization of US$13.9b, so it could very likely raise cash to ameliorate its balance sheet, if the need arose. However, it is still worthwhile taking a close look at its ability to pay off debt.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Avantor has a debt to EBITDA ratio of 4.0 and its EBIT covered its interest expense 3.6 times. This suggests that while the debt levels are significant, we'd stop short of calling them problematic. Another concern for investors might be that Avantor's EBIT fell 13% in the last year. If things keep going like that, handling the debt will about as easy as bundling an angry house cat into its travel box. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Avantor can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. During the last three years, Avantor produced sturdy free cash flow equating to 78% of its EBIT, about what we'd expect. This free cash flow puts the company in a good position to pay down debt, when appropriate.
Our View
Neither Avantor's ability to grow its EBIT nor its net debt to EBITDA gave us confidence in its ability to take on more debt. But its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow tells a very different story, and suggests some resilience. We think that Avantor's debt does make it a bit risky, after considering the aforementioned data points together. That's not necessarily a bad thing, since leverage can boost returns on equity, but it is something to be aware of. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. We've identified 3 warning signs with Avantor (at least 1 which is a bit concerning) , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NYSE:AVTR
Avantor
Engages in the provision of mission-critical products and services to customers in the biopharma, healthcare, education and government, advanced technologies, and applied materials industries in the Americas, Europe, Asia, the Middle East, and Africa.
Very undervalued with proven track record.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives




