Stock Analysis

Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. As with many other companies Parsons Corporation (NYSE:PSN) makes use of debt. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, debt can be an important tool in businesses, particularly capital heavy businesses. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
Our analysis indicates that PSN is potentially undervalued!
How Much Debt Does Parsons Carry?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at June 2022 Parsons had debt of US$793.0m, up from US$640.9m in one year. However, it does have US$126.0m in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about US$667.0m.
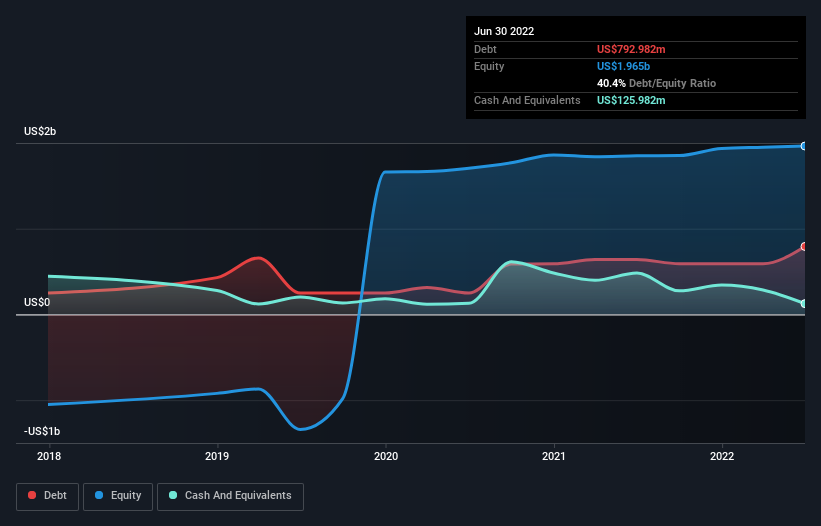
A Look At Parsons' Liabilities
The latest balance sheet data shows that Parsons had liabilities of US$1.10b due within a year, and liabilities of US$1.05b falling due after that. Offsetting this, it had US$126.0m in cash and US$1.34b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities total US$682.3m more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
Of course, Parsons has a market capitalization of US$4.20b, so these liabilities are probably manageable. But there are sufficient liabilities that we would certainly recommend shareholders continue to monitor the balance sheet, going forward.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
With a debt to EBITDA ratio of 2.5, Parsons uses debt artfully but responsibly. And the alluring interest cover (EBIT of 8.1 times interest expense) certainly does not do anything to dispel this impression. One way Parsons could vanquish its debt would be if it stops borrowing more but continues to grow EBIT at around 12%, as it did over the last year. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Parsons can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Over the last three years, Parsons actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT. That sort of strong cash conversion gets us as excited as the crowd when the beat drops at a Daft Punk concert.
Our View
The good news is that Parsons's demonstrated ability to convert EBIT to free cash flow delights us like a fluffy puppy does a toddler. But truth be told we feel its net debt to EBITDA does undermine this impression a bit. Taking all this data into account, it seems to us that Parsons takes a pretty sensible approach to debt. That means they are taking on a bit more risk, in the hope of boosting shareholder returns. Of course, we wouldn't say no to the extra confidence that we'd gain if we knew that Parsons insiders have been buying shares: if you're on the same wavelength, you can find out if insiders are buying by clicking this link.
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
Valuation is complex, but we're helping make it simple.
Find out whether Parsons is potentially over or undervalued by checking out our comprehensive analysis, which includes fair value estimates, risks and warnings, dividends, insider transactions and financial health.
View the Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NYSE:PSN
Parsons
Provides integrated solutions and services in the defense, intelligence, and critical infrastructure markets in North America, the Middle East, and internationally.
Flawless balance sheet and good value.

