- Poland
- /
- Telecom Services and Carriers
- /
- WSE:KOR
Here's Why Korbank (WSE:KOR) Can Manage Its Debt Responsibly
The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. We can see that Korbank S.A. (WSE:KOR) does use debt in its business. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Korbank
What Is Korbank's Net Debt?
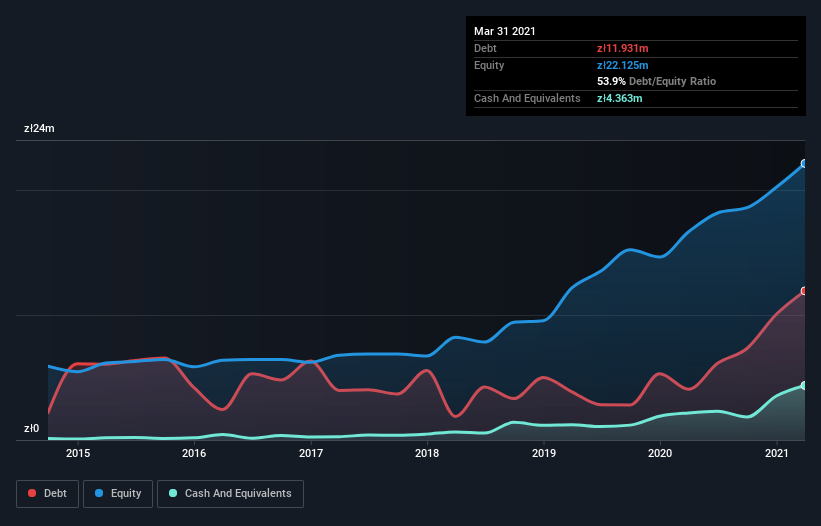
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at March 2021 Korbank had debt of zł11.7m, up from zł4.06m in one year. However, it does have zł4.36m in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about zł7.34m.
How Strong Is Korbank's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Korbank had liabilities of zł8.13m due within 12 months, and liabilities of zł14.3m due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of zł4.36m and zł8.43m worth of receivables due within a year. So it has liabilities totalling zł9.66m more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
This deficit isn't so bad because Korbank is worth zł47.9m, and thus could probably raise enough capital to shore up its balance sheet, if the need arose. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Korbank has a low net debt to EBITDA ratio of only 0.84. And its EBIT easily covers its interest expense, being 94.1 times the size. So you could argue it is no more threatened by its debt than an elephant is by a mouse. Another good sign is that Korbank has been able to increase its EBIT by 29% in twelve months, making it easier to pay down debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But it is Korbank's earnings that will influence how the balance sheet holds up in the future. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Considering the last three years, Korbank actually recorded a cash outflow, overall. Debt is far more risky for companies with unreliable free cash flow, so shareholders should be hoping that the past expenditure will produce free cash flow in the future.
Our View
The good news is that Korbank's demonstrated ability to cover its interest expense with its EBIT delights us like a fluffy puppy does a toddler. But we must concede we find its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow has the opposite effect. Looking at all the aforementioned factors together, it strikes us that Korbank can handle its debt fairly comfortably. On the plus side, this leverage can boost shareholder returns, but the potential downside is more risk of loss, so it's worth monitoring the balance sheet. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. We've identified 3 warning signs with Korbank (at least 1 which is potentially serious) , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
If you decide to trade Korbank, use the lowest-cost* platform that is rated #1 Overall by Barron’s, Interactive Brokers. Trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds on 135 markets, all from a single integrated account. Promoted
If you're looking to trade Korbank, open an account with the lowest-cost platform trusted by professionals, Interactive Brokers.
With clients in over 200 countries and territories, and access to 160 markets, IBKR lets you trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds from a single integrated account.
Enjoy no hidden fees, no account minimums, and FX conversion rates as low as 0.03%, far better than what most brokers offer.
Sponsored ContentValuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Korbank might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About WSE:KOR
Korbank
A telecommunications operator, provides various services to companies, institutions, and housing estates in Poland and internationally.
Good value slight.


