- Japan
- /
- Electronic Equipment and Components
- /
- TSE:7111
INEST (TSE:7111) Has A Somewhat Strained Balance Sheet
Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. As with many other companies INEST, Inc. (TSE:7111) makes use of debt. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
What Is INEST's Debt?
As you can see below, INEST had JP¥2.85b of debt at March 2025, down from JP¥3.24b a year prior. However, it also had JP¥1.67b in cash, and so its net debt is JP¥1.18b.
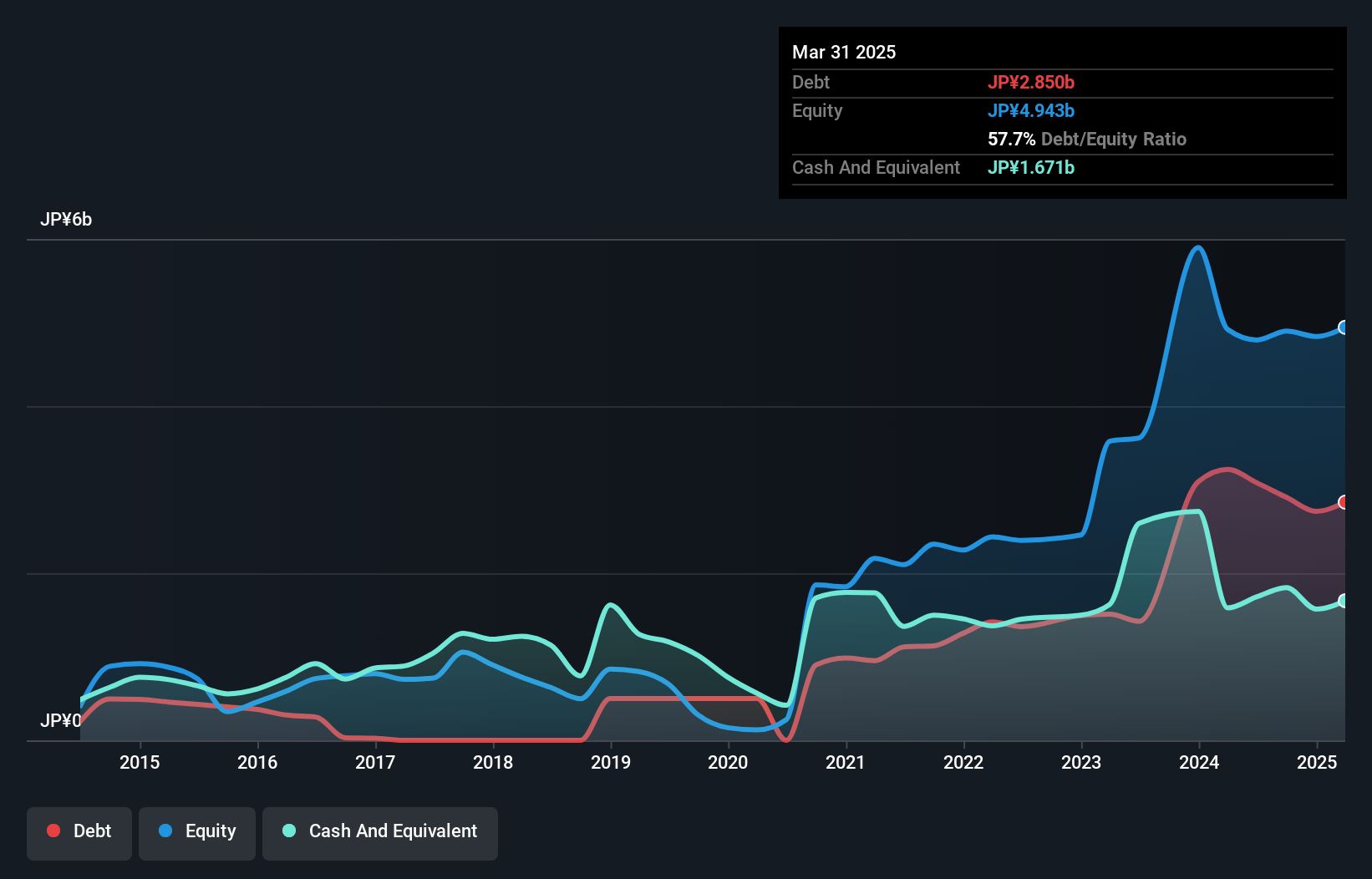
A Look At INEST's Liabilities
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that INEST had liabilities of JP¥4.59b due within 12 months and liabilities of JP¥4.14b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had JP¥1.67b in cash and JP¥2.57b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling JP¥4.48b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
INEST has a market capitalization of JP¥8.00b, so it could very likely raise cash to ameliorate its balance sheet, if the need arose. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
Check out our latest analysis for INEST
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Even though INEST's debt is only 1.7, its interest cover is really very low at 1.9. The main reason for this is that it has such high depreciation and amortisation. These charges may be non-cash, so they could be excluded when it comes to paying down debt. But the accounting charges are there for a reason -- some assets are seen to be losing value. In any case, it's safe to say the company has meaningful debt. Unfortunately, INEST saw its EBIT slide 9.1% in the last twelve months. If earnings continue on that decline then managing that debt will be difficult like delivering hot soup on a unicycle. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is INEST's earnings that will influence how the balance sheet holds up in the future. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, INEST actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last three years. That sort of strong cash conversion gets us as excited as the crowd when the beat drops at a Daft Punk concert.
Our View
Neither INEST's ability to cover its interest expense with its EBIT nor its EBIT growth rate gave us confidence in its ability to take on more debt. But its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow tells a very different story, and suggests some resilience. We think that INEST's debt does make it a bit risky, after considering the aforementioned data points together. That's not necessarily a bad thing, since leverage can boost returns on equity, but it is something to be aware of. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For example INEST has 2 warning signs (and 1 which is significant) we think you should know about.
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About TSE:7111
INEST
Engages in the marketing and solutions support business for corporate enterprises and individual consumers.
Flawless balance sheet and slightly overvalued.
Market Insights
Weekly Picks


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)


Fiducian: Compliance Clouds or Value Opportunity?

Willamette Valley Vineyards (WVVI): Not-So-Great Value
Recently Updated Narratives


ADNOC Gas future shines with a 21.4% revenue surge

Watch Pulse Seismic Outperform with 13.6% Revenue Growth in the Coming Years

Significantly undervalued gold explorer in Timmins, finally getting traction
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026





