
Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. Importantly, PTC India Limited (NSE:PTC) does carry debt. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for India
How Much Debt Does India Carry?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that India had ₹112.6b of debt in September 2020, down from ₹130.0b, one year before. On the flip side, it has ₹30.0b in cash leading to net debt of about ₹82.6b.
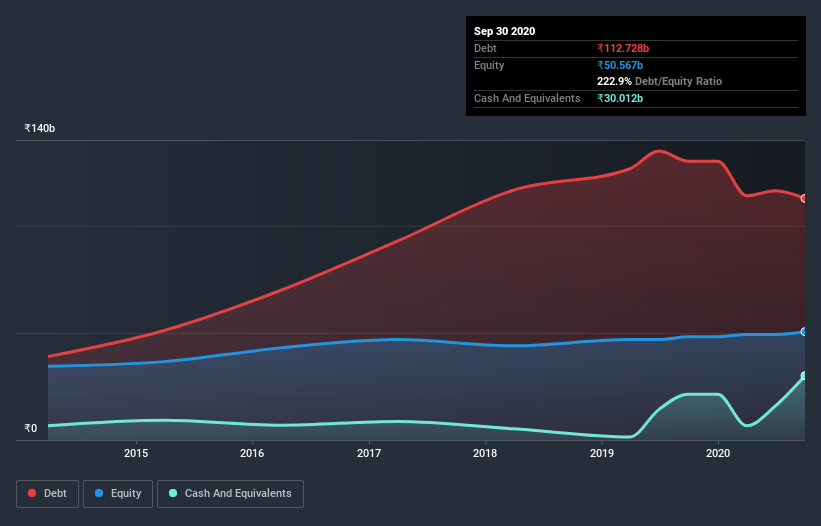
How Strong Is India's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, India had liabilities of ₹97.5b due within 12 months, and liabilities of ₹81.9b due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of ₹30.0b and ₹83.9b worth of receivables due within a year. So it has liabilities totalling ₹65.5b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
The deficiency here weighs heavily on the ₹17.9b company itself, as if a child were struggling under the weight of an enormous back-pack full of books, his sports gear, and a trumpet. So we definitely think shareholders need to watch this one closely. At the end of the day, India would probably need a major re-capitalization if its creditors were to demand repayment.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
While we wouldn't worry about India's net debt to EBITDA ratio of 4.4, we think its super-low interest cover of 1.8 times is a sign of high leverage. So shareholders should probably be aware that interest expenses appear to have really impacted the business lately. More concerning, India saw its EBIT drop by 3.3% in the last twelve months. If that earnings trend continues the company will face an uphill battle to pay off its debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But it is India's earnings that will influence how the balance sheet holds up in the future. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Over the last three years, India recorded free cash flow worth a fulsome 85% of its EBIT, which is stronger than we'd usually expect. That puts it in a very strong position to pay down debt.
Our View
To be frank both India's interest cover and its track record of staying on top of its total liabilities make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But on the bright side, its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow is a good sign, and makes us more optimistic. Overall, we think it's fair to say that India has enough debt that there are some real risks around the balance sheet. If everything goes well that may pay off but the downside of this debt is a greater risk of permanent losses. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. To that end, you should learn about the 3 warning signs we've spotted with India (including 1 which is a bit unpleasant) .
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
If you’re looking to trade India, open an account with the lowest-cost* platform trusted by professionals, Interactive Brokers. Their clients from over 200 countries and territories trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About NSEI:PTC
PTC India
Engages in the trading of power in India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
Flawless balance sheet established dividend payer.


