
Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. We note that Tata Chemicals Limited (NSE:TATACHEM) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Tata Chemicals
How Much Debt Does Tata Chemicals Carry?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of September 2020 Tata Chemicals had ₹69.7b of debt, an increase on ₹36.2b, over one year. However, it does have ₹31.7b in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about ₹38.0b.
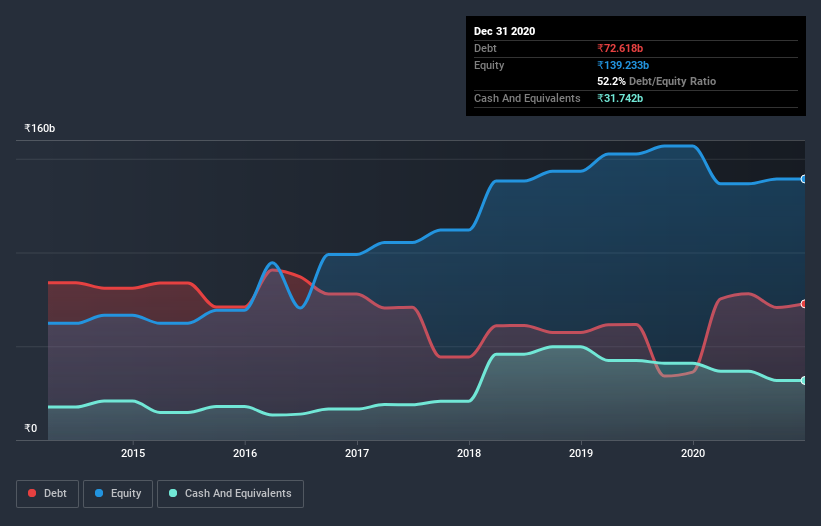
How Healthy Is Tata Chemicals' Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Tata Chemicals had liabilities of ₹31.5b due within 12 months, and liabilities of ₹98.3b due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of ₹31.7b and ₹13.2b worth of receivables due within a year. So it has liabilities totalling ₹84.8b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Tata Chemicals has a market capitalization of ₹194.6b, so it could very likely raise cash to ameliorate its balance sheet, if the need arose. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Tata Chemicals has a debt to EBITDA ratio of 2.5 and its EBIT covered its interest expense 4.3 times. Taken together this implies that, while we wouldn't want to see debt levels rise, we think it can handle its current leverage. Shareholders should be aware that Tata Chemicals's EBIT was down 46% last year. If that earnings trend continues then paying off its debt will be about as easy as herding cats on to a roller coaster. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Tata Chemicals can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. During the last three years, Tata Chemicals produced sturdy free cash flow equating to 51% of its EBIT, about what we'd expect. This free cash flow puts the company in a good position to pay down debt, when appropriate.
Our View
Mulling over Tata Chemicals's attempt at (not) growing its EBIT, we're certainly not enthusiastic. Having said that, its ability to convert EBIT to free cash flow isn't such a worry. Once we consider all the factors above, together, it seems to us that Tata Chemicals's debt is making it a bit risky. That's not necessarily a bad thing, but we'd generally feel more comfortable with less leverage. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. To that end, you should be aware of the 4 warning signs we've spotted with Tata Chemicals .
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
If you decide to trade Tata Chemicals, use the lowest-cost* platform that is rated #1 Overall by Barron’s, Interactive Brokers. Trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds on 135 markets, all from a single integrated account. Promoted
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Tata Chemicals might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About NSEI:TATACHEM
Tata Chemicals
Manufactures, markets, sells, and distributes basic chemistry and specialty products in India, Europe, Africa, America, rest of Asia, and internationally.
Adequate balance sheet average dividend payer.

