
Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. As with many other companies Oil India Limited (NSE:OIL) makes use of debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for Oil India
How Much Debt Does Oil India Carry?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at March 2024 Oil India had debt of ₹236.4b, up from ₹185.5b in one year. However, because it has a cash reserve of ₹69.0b, its net debt is less, at about ₹167.4b.
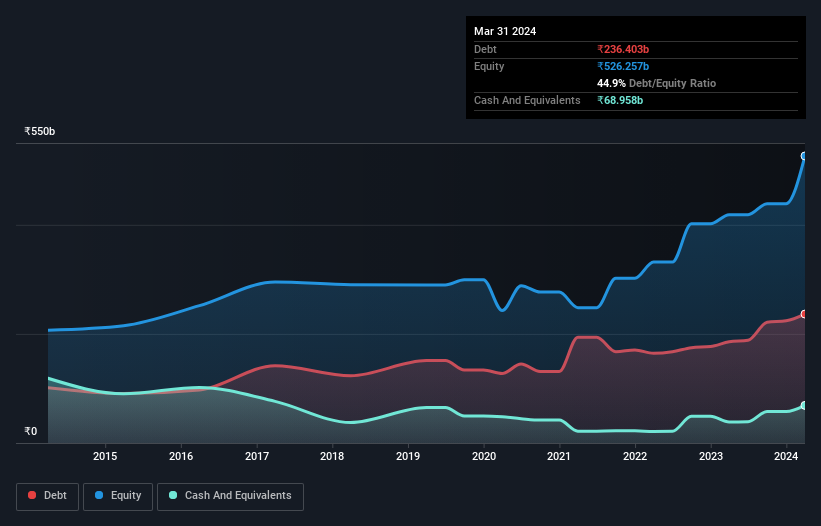
A Look At Oil India's Liabilities
We can see from the most recent balance sheet that Oil India had liabilities of ₹143.6b falling due within a year, and liabilities of ₹251.7b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had ₹69.0b in cash and ₹33.9b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by ₹292.4b.
Oil India has a very large market capitalization of ₹999.5b, so it could very likely raise cash to ameliorate its balance sheet, if the need arose. But it's clear that we should definitely closely examine whether it can manage its debt without dilution.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Oil India has net debt of just 1.3 times EBITDA, suggesting it could ramp leverage without breaking a sweat. But the really cool thing is that it actually managed to receive more interest than it paid, over the last year. So it's fair to say it can handle debt like a hotshot teppanyaki chef handles cooking. The modesty of its debt load may become crucial for Oil India if management cannot prevent a repeat of the 28% cut to EBIT over the last year. When it comes to paying off debt, falling earnings are no more useful than sugary sodas are for your health. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Oil India can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Over the last three years, Oil India reported free cash flow worth 15% of its EBIT, which is really quite low. For us, cash conversion that low sparks a little paranoia about is ability to extinguish debt.
Our View
Oil India's EBIT growth rate and conversion of EBIT to free cash flow definitely weigh on it, in our esteem. But the good news is it seems to be able to cover its interest expense with its EBIT with ease. Taking the abovementioned factors together we do think Oil India's debt poses some risks to the business. So while that leverage does boost returns on equity, we wouldn't really want to see it increase from here. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For instance, we've identified 2 warning signs for Oil India that you should be aware of.
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com
About NSEI:OIL
Oil India
Engages in the exploration, development, and production of crude oil and natural gas in India.
Undervalued with solid track record and pays a dividend.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



