
Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. Importantly, Tarmat Limited (NSE:TARMAT) does carry debt. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. Of course, debt can be an important tool in businesses, particularly capital heavy businesses. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Tarmat
How Much Debt Does Tarmat Carry?
As you can see below, Tarmat had ₹946.0m of debt at September 2020, down from ₹1.10b a year prior. However, it does have ₹150.7m in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about ₹795.2m.
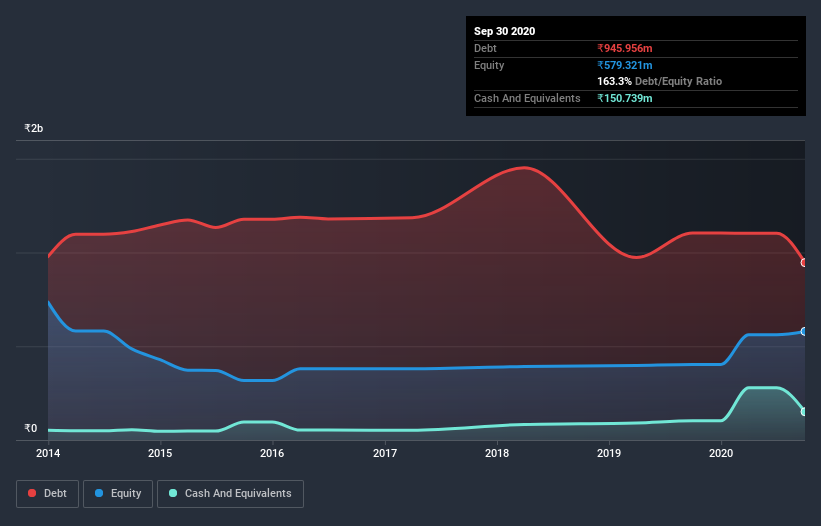
How Strong Is Tarmat's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Tarmat had liabilities of ₹820.3m due within 12 months, and liabilities of ₹956.9m due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of ₹150.7m and ₹992.4m worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by ₹634.1m.
This is a mountain of leverage relative to its market capitalization of ₹741.2m. This suggests shareholders would be heavily diluted if the company needed to shore up its balance sheet in a hurry.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
With a net debt to EBITDA ratio of 6.2, it's fair to say Tarmat does have a significant amount of debt. But the good news is that it boasts fairly comforting interest cover of 6.2 times, suggesting it can responsibly service its obligations. Notably, Tarmat's EBIT launched higher than Elon Musk, gaining a whopping 731% on last year. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But you can't view debt in total isolation; since Tarmat will need earnings to service that debt. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. During the last two years, Tarmat burned a lot of cash. While investors are no doubt expecting a reversal of that situation in due course, it clearly does mean its use of debt is more risky.
Our View
On the face of it, Tarmat's net debt to EBITDA left us tentative about the stock, and its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. But at least it's pretty decent at growing its EBIT; that's encouraging. Looking at the balance sheet and taking into account all these factors, we do believe that debt is making Tarmat stock a bit risky. That's not necessarily a bad thing, but we'd generally feel more comfortable with less leverage. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. Consider for instance, the ever-present spectre of investment risk. We've identified 3 warning signs with Tarmat (at least 1 which doesn't sit too well with us) , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
If you decide to trade Tarmat, use the lowest-cost* platform that is rated #1 Overall by Barron’s, Interactive Brokers. Trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds on 135 markets, all from a single integrated account. Promoted
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Tarmat might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About NSEI:TARMAT
Adequate balance sheet and slightly overvalued.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives




