- Hong Kong
- /
- Telecom Services and Carriers
- /
- SEHK:1310
HKBN (HKG:1310) Has A Somewhat Strained Balance Sheet

The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. We note that HKBN Ltd. (HKG:1310) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
View our latest analysis for HKBN
How Much Debt Does HKBN Carry?
As you can see below, at the end of February 2021, HKBN had HK$11.3b of debt, up from HK$10.5b a year ago. Click the image for more detail. On the flip side, it has HK$1.23b in cash leading to net debt of about HK$10.1b.
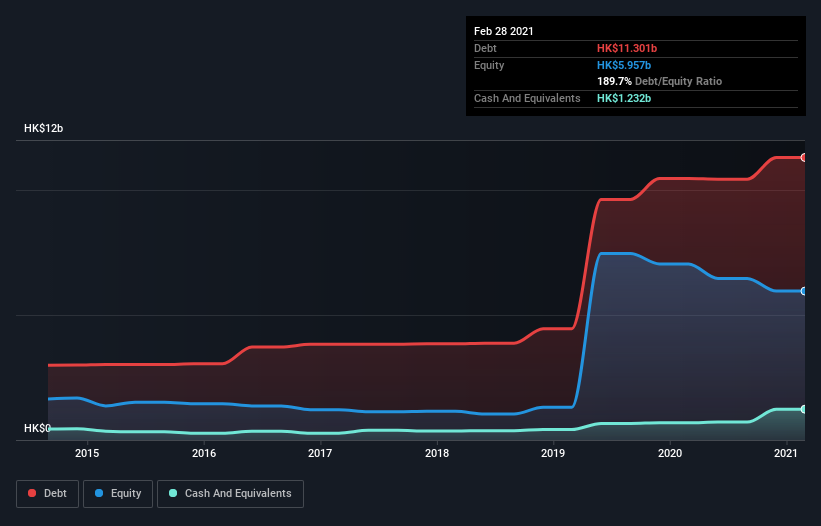
A Look At HKBN's Liabilities
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that HKBN had liabilities of HK$4.44b due within 12 months and liabilities of HK$11.6b due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of HK$1.23b as well as receivables valued at HK$1.98b due within 12 months. So its liabilities total HK$12.8b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
This is a mountain of leverage relative to its market capitalization of HK$13.2b. Should its lenders demand that it shore up the balance sheet, shareholders would likely face severe dilution.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
While HKBN's debt to EBITDA ratio (4.9) suggests that it uses some debt, its interest cover is very weak, at 1.6, suggesting high leverage. It seems that the business incurs large depreciation and amortisation charges, so maybe its debt load is heavier than it would first appear, since EBITDA is arguably a generous measure of earnings. It seems clear that the cost of borrowing money is negatively impacting returns for shareholders, of late. Given the debt load, it's hardly ideal that HKBN's EBIT was pretty flat over the last twelve months. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if HKBN can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. Happily for any shareholders, HKBN actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT over the last three years. There's nothing better than incoming cash when it comes to staying in your lenders' good graces.
Our View
Neither HKBN's ability to cover its interest expense with its EBIT nor its net debt to EBITDA gave us confidence in its ability to take on more debt. But its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow tells a very different story, and suggests some resilience. When we consider all the factors discussed, it seems to us that HKBN is taking some risks with its use of debt. So while that leverage does boost returns on equity, we wouldn't really want to see it increase from here. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For instance, we've identified 4 warning signs for HKBN (2 make us uncomfortable) you should be aware of.
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
When trading stocks or any other investment, use the platform considered by many to be the Professional's Gateway to the Worlds Market, Interactive Brokers. You get the lowest-cost* trading on stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if HKBN might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About SEHK:1310
HKBN
An investment holding company, provides fixed telecommunications network, international telecommunications, and mobile services to residential and enterprise customers in Hong Kong, Mainland China, and Macao.
Undervalued with reasonable growth potential.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives




