Does Techtronic Industries (HKG:669) Have A Healthy Balance Sheet?

The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. As with many other companies Techtronic Industries Company Limited (HKG:669) makes use of debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Techtronic Industries
What Is Techtronic Industries's Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that Techtronic Industries had US$3.15b of debt in December 2022, down from US$3.29b, one year before. However, it also had US$1.67b in cash, and so its net debt is US$1.48b.
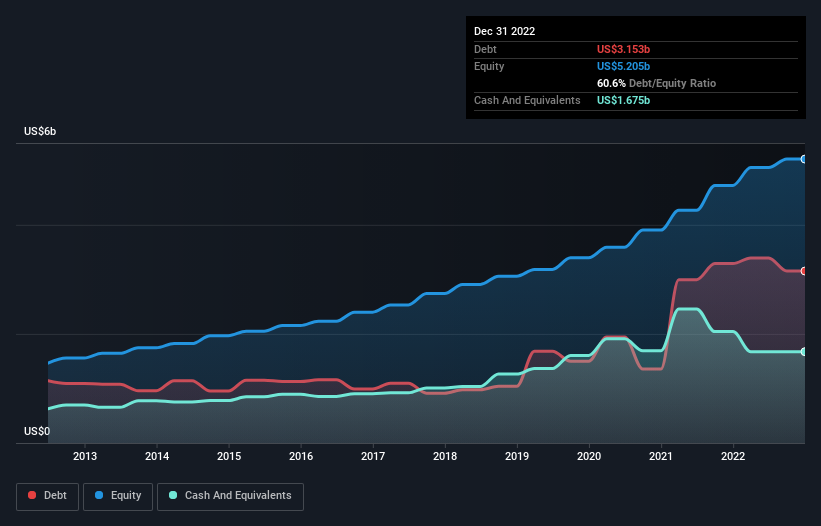
A Look At Techtronic Industries' Liabilities
According to the last reported balance sheet, Techtronic Industries had liabilities of US$6.22b due within 12 months, and liabilities of US$1.89b due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of US$1.67b and US$1.69b worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by US$4.75b.
Techtronic Industries has a very large market capitalization of US$19.7b, so it could very likely raise cash to ameliorate its balance sheet, if the need arose. But it's clear that we should definitely closely examine whether it can manage its debt without dilution.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Techtronic Industries has a low net debt to EBITDA ratio of only 1.0. And its EBIT easily covers its interest expense, being 27.0 times the size. So we're pretty relaxed about its super-conservative use of debt. While Techtronic Industries doesn't seem to have gained much on the EBIT line, at least earnings remain stable for now. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Techtronic Industries's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. Considering the last three years, Techtronic Industries actually recorded a cash outflow, overall. Debt is far more risky for companies with unreliable free cash flow, so shareholders should be hoping that the past expenditure will produce free cash flow in the future.
Our View
On our analysis Techtronic Industries's interest cover should signal that it won't have too much trouble with its debt. However, our other observations weren't so heartening. In particular, conversion of EBIT to free cash flow gives us cold feet. When we consider all the factors mentioned above, we do feel a bit cautious about Techtronic Industries's use of debt. While debt does have its upside in higher potential returns, we think shareholders should definitely consider how debt levels might make the stock more risky. Of course, we wouldn't say no to the extra confidence that we'd gain if we knew that Techtronic Industries insiders have been buying shares: if you're on the same wavelength, you can find out if insiders are buying by clicking this link.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Techtronic Industries might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About SEHK:669
Techtronic Industries
Engages in designing, manufacturing, and marketing of power tools, outdoor power equipment, and floorcare and cleaning products in the North America, Europe, and internationally.
Flawless balance sheet with solid track record and pays a dividend.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



