Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. Importantly, Petrofac Limited (LON:PFC) does carry debt. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
See our latest analysis for Petrofac
What Is Petrofac's Debt?
As you can see below, Petrofac had US$800.0m of debt at December 2020, down from US$1.01b a year prior. However, it also had US$684.0m in cash, and so its net debt is US$116.0m.
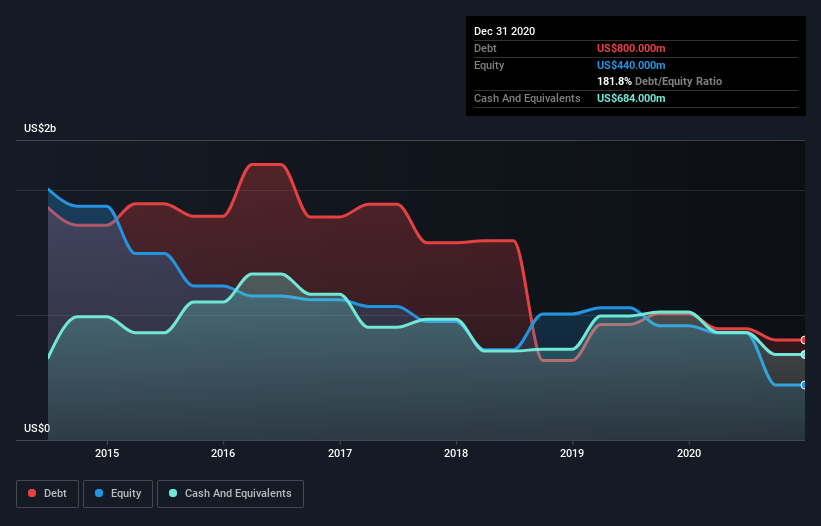
How Healthy Is Petrofac's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Petrofac had liabilities of US$3.34b due within 12 months, and liabilities of US$425.0m due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$684.0m as well as receivables valued at US$2.41b due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by US$671.0m.
When you consider that this deficiency exceeds the company's US$603.7m market capitalization, you might well be inclined to review the balance sheet intently. Hypothetically, extremely heavy dilution would be required if the company were forced to pay down its liabilities by raising capital at the current share price.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
While Petrofac's low debt to EBITDA ratio of 0.53 suggests only modest use of debt, the fact that EBIT only covered the interest expense by 3.6 times last year does give us pause. So we'd recommend keeping a close eye on the impact financing costs are having on the business. Shareholders should be aware that Petrofac's EBIT was down 71% last year. If that earnings trend continues then paying off its debt will be about as easy as herding cats on to a roller coaster. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Petrofac's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. During the last three years, Petrofac produced sturdy free cash flow equating to 51% of its EBIT, about what we'd expect. This cold hard cash means it can reduce its debt when it wants to.
Our View
We'd go so far as to say Petrofac's EBIT growth rate was disappointing. But on the bright side, its net debt to EBITDA is a good sign, and makes us more optimistic. Looking at the bigger picture, it seems clear to us that Petrofac's use of debt is creating risks for the company. If everything goes well that may pay off but the downside of this debt is a greater risk of permanent losses. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For example - Petrofac has 1 warning sign we think you should be aware of.
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
When trading Petrofac or any other investment, use the platform considered by many to be the Professional's Gateway to the Worlds Market, Interactive Brokers. You get the lowest-cost* trading on stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About LSE:PFC
Petrofac
Designs, builds, manages, maintains, and decommissions infrastructure for the energy industries in the United Kingdom, Algeria, Lithuania, Malaysia, the United States, Thailand, Oman, Australia, Bahrain, Kuwait, Iraq, Libya, India, the United Arab Emirates, the Netherlands, Ivory Coast, and internationally.
Undervalued with high growth potential.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)


Fiducian: Compliance Clouds or Value Opportunity?

Willamette Valley Vineyards (WVVI): Not-So-Great Value
Recently Updated Narratives


The "Molecular Pencil": Why Beam's Technology is Built to Win

PRME remains a long shot but publication in the New England Journal of Medicine helps.

This one is all about the tax benefits
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026




