- France
- /
- Telecom Services and Carriers
- /
- ENXTPA:ORA
Orange (EPA:ORA) Takes On Some Risk With Its Use Of Debt
The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. We can see that Orange S.A. (EPA:ORA) does use debt in its business. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Orange
What Is Orange's Debt?
The chart below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Orange had €37.8b in debt in June 2023; about the same as the year before. However, it also had €12.7b in cash, and so its net debt is €25.1b.
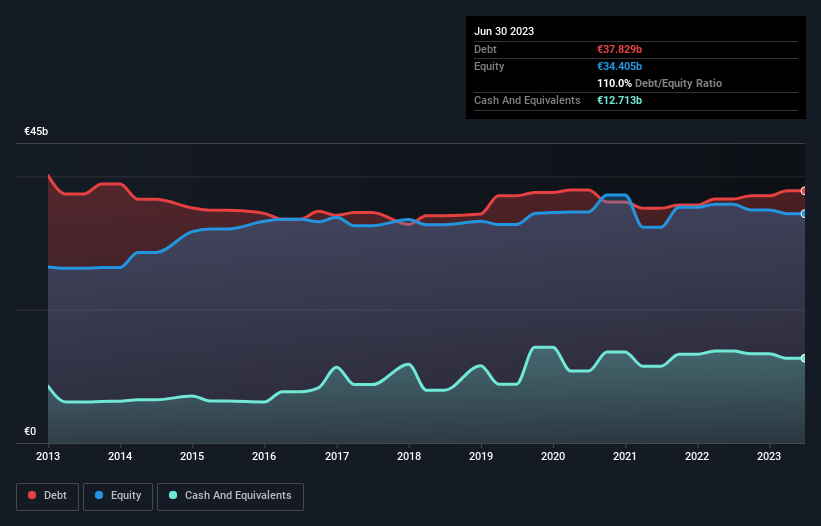
How Healthy Is Orange's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Orange had liabilities of €30.9b due within 12 months, and liabilities of €45.7b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting this, it had €12.7b in cash and €9.29b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by €54.6b.
This deficit casts a shadow over the €28.9b company, like a colossus towering over mere mortals. So we'd watch its balance sheet closely, without a doubt. At the end of the day, Orange would probably need a major re-capitalization if its creditors were to demand repayment.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
Orange has net debt worth 2.0 times EBITDA, which isn't too much, but its interest cover looks a bit on the low side, with EBIT at only 3.8 times the interest expense. It seems that the business incurs large depreciation and amortisation charges, so maybe its debt load is heavier than it would first appear, since EBITDA is arguably a generous measure of earnings. If Orange can keep growing EBIT at last year's rate of 19% over the last year, then it will find its debt load easier to manage. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Orange can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. During the last three years, Orange produced sturdy free cash flow equating to 65% of its EBIT, about what we'd expect. This cold hard cash means it can reduce its debt when it wants to.
Our View
Orange's struggle to handle its total liabilities had us second guessing its balance sheet strength, but the other data-points we considered were relatively redeeming. In particular, its EBIT growth rate was re-invigorating. Taking the abovementioned factors together we do think Orange's debt poses some risks to the business. While that debt can boost returns, we think the company has enough leverage now. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For example, we've discovered 4 warning signs for Orange that you should be aware of before investing here.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
Mobile Infrastructure for Defense and Disaster
The next wave in robotics isn't humanoid. Its fully autonomous towers delivering 5G, ISR, and radar in under 30 minutes, anywhere.
Get the investor briefing before the next round of contracts
Sponsored On Behalf of CiTechNew: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About ENXTPA:ORA
Orange
Operates as a telecommunications operator in France and internationally.
Average dividend payer with moderate growth potential.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

Early mover in a fast growing industry. Likely to experience share price volatility as they scale


A case for CA$31.80 (undiluted), aka 8,616% upside from CA$0.37 (an 86 bagger!).


Moderation and Stabilisation: HOLD: Fair Price based on a 4-year Cycle is $12.08
Recently Updated Narratives


Title: Market Sentiment Is Dead Wrong — Here's Why PSEC Deserves a Second Look


An amazing opportunity to potentially get a 100 bagger

Amazon: Why the World’s Biggest Platform Still Runs on Invisible Economics
Popular Narratives


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026
Trending Discussion


