Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We can see that Barry Callebaut AG (VTX:BARN) does use debt in its business. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Having said that, the most common situation is where a company manages its debt reasonably well - and to its own advantage. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Barry Callebaut
How Much Debt Does Barry Callebaut Carry?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of February 2024 Barry Callebaut had CHF2.74b of debt, an increase on CHF1.95b, over one year. However, it does have CHF428.0m in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about CHF2.31b.
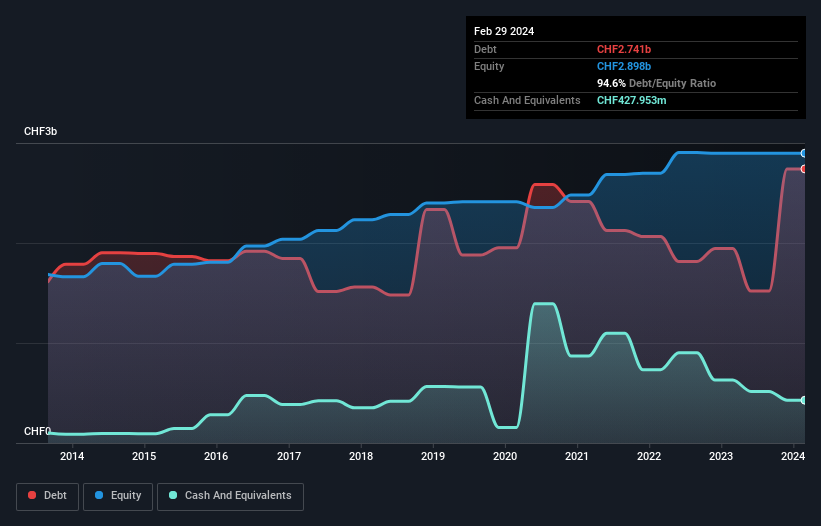
How Healthy Is Barry Callebaut's Balance Sheet?
The latest balance sheet data shows that Barry Callebaut had liabilities of CHF8.19b due within a year, and liabilities of CHF2.24b falling due after that. On the other hand, it had cash of CHF428.0m and CHF2.18b worth of receivables due within a year. So it has liabilities totalling CHF7.82b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
When you consider that this deficiency exceeds the company's CHF7.49b market capitalization, you might well be inclined to review the balance sheet intently. Hypothetically, extremely heavy dilution would be required if the company were forced to pay down its liabilities by raising capital at the current share price.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Barry Callebaut's debt is 2.8 times its EBITDA, and its EBIT cover its interest expense 5.4 times over. Taken together this implies that, while we wouldn't want to see debt levels rise, we think it can handle its current leverage. Notably Barry Callebaut's EBIT was pretty flat over the last year. We would prefer to see some earnings growth, because that always helps diminish debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Barry Callebaut's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. Considering the last three years, Barry Callebaut actually recorded a cash outflow, overall. Debt is far more risky for companies with unreliable free cash flow, so shareholders should be hoping that the past expenditure will produce free cash flow in the future.
Our View
Mulling over Barry Callebaut's attempt at converting EBIT to free cash flow, we're certainly not enthusiastic. Having said that, its ability to cover its interest expense with its EBIT isn't such a worry. Overall, it seems to us that Barry Callebaut's balance sheet is really quite a risk to the business. So we're almost as wary of this stock as a hungry kitten is about falling into its owner's fish pond: once bitten, twice shy, as they say. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. For example, we've discovered 3 warning signs for Barry Callebaut (2 are significant!) that you should be aware of before investing here.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Barry Callebaut might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About SWX:BARN
Barry Callebaut
Engages in the manufacture and sale of chocolate and cocoa products.
Moderate risk with moderate growth potential.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives





