We Think São Martinho (BVMF:SMTO3) Can Stay On Top Of Its Debt

Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. We note that São Martinho S.A. (BVMF:SMTO3) does have debt on its balance sheet. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. Part and parcel of capitalism is the process of 'creative destruction' where failed businesses are mercilessly liquidated by their bankers. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for São Martinho
How Much Debt Does São Martinho Carry?
As you can see below, São Martinho had R$3.98b of debt at June 2021, down from R$4.68b a year prior. However, it also had R$1.33b in cash, and so its net debt is R$2.65b.
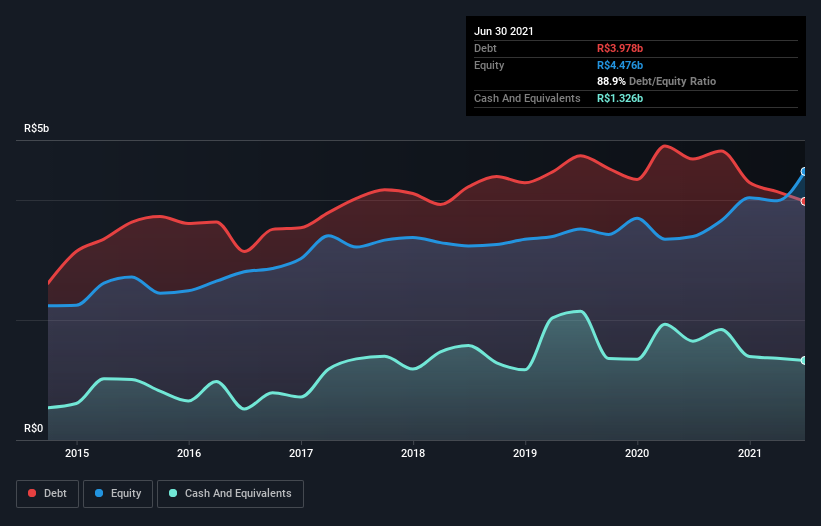
A Look At São Martinho's Liabilities
According to the last reported balance sheet, São Martinho had liabilities of R$1.80b due within 12 months, and liabilities of R$6.84b due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of R$1.33b and R$345.7m worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by R$6.96b.
This deficit is considerable relative to its market capitalization of R$11.6b, so it does suggest shareholders should keep an eye on São Martinho's use of debt. Should its lenders demand that it shore up the balance sheet, shareholders would likely face severe dilution.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
São Martinho has net debt of just 1.00 times EBITDA, indicating that it is certainly not a reckless borrower. And this view is supported by the solid interest coverage, with EBIT coming in at 8.9 times the interest expense over the last year. The good news is that São Martinho has increased its EBIT by 3.0% over twelve months, which should ease any concerns about debt repayment. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if São Martinho can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. During the last three years, São Martinho produced sturdy free cash flow equating to 62% of its EBIT, about what we'd expect. This cold hard cash means it can reduce its debt when it wants to.
Our View
Both São Martinho's ability to to cover its interest expense with its EBIT and its net debt to EBITDA gave us comfort that it can handle its debt. On the other hand, its level of total liabilities makes us a little less comfortable about its debt. Considering this range of data points, we think São Martinho is in a good position to manage its debt levels. But a word of caution: we think debt levels are high enough to justify ongoing monitoring. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. These risks can be hard to spot. Every company has them, and we've spotted 4 warning signs for São Martinho you should know about.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
When trading stocks or any other investment, use the platform considered by many to be the Professional's Gateway to the Worlds Market, Interactive Brokers. You get the lowest-cost* trading on stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
If you're looking to trade São Martinho, open an account with the lowest-cost platform trusted by professionals, Interactive Brokers.
With clients in over 200 countries and territories, and access to 160 markets, IBKR lets you trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds from a single integrated account.
Enjoy no hidden fees, no account minimums, and FX conversion rates as low as 0.03%, far better than what most brokers offer.
Sponsored ContentNew: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About BOVESPA:SMTO3
São Martinho
Engages in the production and sale of sugar, ethanol, and other sugarcane byproducts in Brazil.
Very undervalued average dividend payer.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives