These 4 Measures Indicate That Tupy (BVMF:TUPY3) Is Using Debt Reasonably Well

Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. We can see that Tupy S.A. (BVMF:TUPY3) does use debt in its business. But should shareholders be worried about its use of debt?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for Tupy
What Is Tupy's Net Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at March 2020 Tupy had debt of R$2.64b, up from R$1.44b in one year. On the flip side, it has R$1.36b in cash leading to net debt of about R$1.28b.
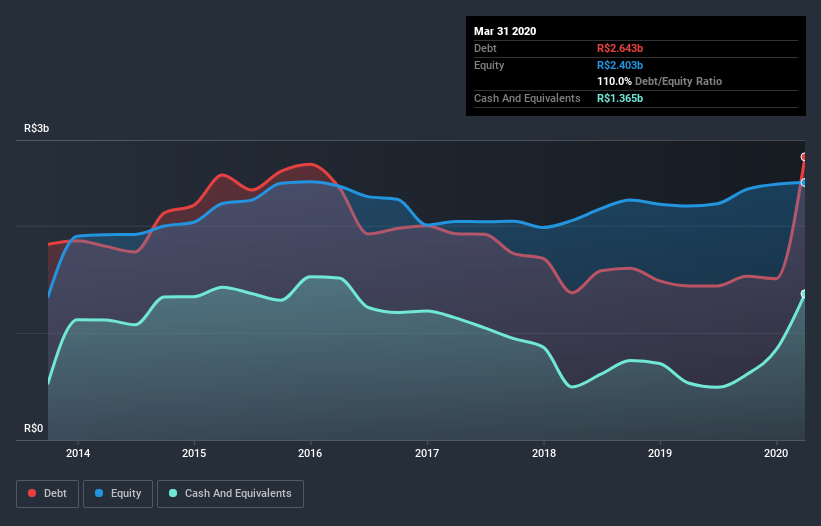
How Healthy Is Tupy's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Tupy had liabilities of R$1.78b due within 12 months, and liabilities of R$2.14b due beyond 12 months. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of R$1.36b as well as receivables valued at R$1.10b due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by R$1.4b.
Tupy has a market capitalization of R$2.66b, so it could very likely raise cash to ameliorate its balance sheet, if the need arose. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Tupy has net debt worth 1.6 times EBITDA, which isn't too much, but its interest cover looks a bit on the low side, with EBIT at only 5.4 times the interest expense. While these numbers do not alarm us, it's worth noting that the cost of the company's debt is having a real impact. It is well worth noting that Tupy's EBIT shot up like bamboo after rain, gaining 41% in the last twelve months. That'll make it easier to manage its debt. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Tupy can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. During the last three years, Tupy produced sturdy free cash flow equating to 71% of its EBIT, about what we'd expect. This cold hard cash means it can reduce its debt when it wants to.
Our View
Happily, Tupy's impressive EBIT growth rate implies it has the upper hand on its debt. But, on a more sombre note, we are a little concerned by its level of total liabilities. All these things considered, it appears that Tupy can comfortably handle its current debt levels. On the plus side, this leverage can boost shareholder returns, but the potential downside is more risk of loss, so it's worth monitoring the balance sheet. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. Like risks, for instance. Every company has them, and we've spotted 3 warning signs for Tupy (of which 1 doesn't sit too well with us!) you should know about.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
If you’re looking to trade Tupy, open an account with the lowest-cost* platform trusted by professionals, Interactive Brokers. Their clients from over 200 countries and territories trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds worldwide from a single integrated account. Promoted
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Tupy might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisThis article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com.
About BOVESPA:TUPY3
Tupy
Engages in the development, manufacture, and sale of cast and compacted graphite iron structural components in North America, South and Central Americas, Europe, Asia, Africa, Oceania, and internationally.
Undervalued with adequate balance sheet.
Market Insights
Community Narratives



