Warren Buffett famously said, 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' When we think about how risky a company is, we always like to look at its use of debt, since debt overload can lead to ruin. As with many other companies Ted Baker Plc (LON:TED) makes use of debt. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
When Is Debt A Problem?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. Part and parcel of capitalism is the process of 'creative destruction' where failed businesses are mercilessly liquidated by their bankers. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
Check out our latest analysis for Ted Baker
What Is Ted Baker's Debt?
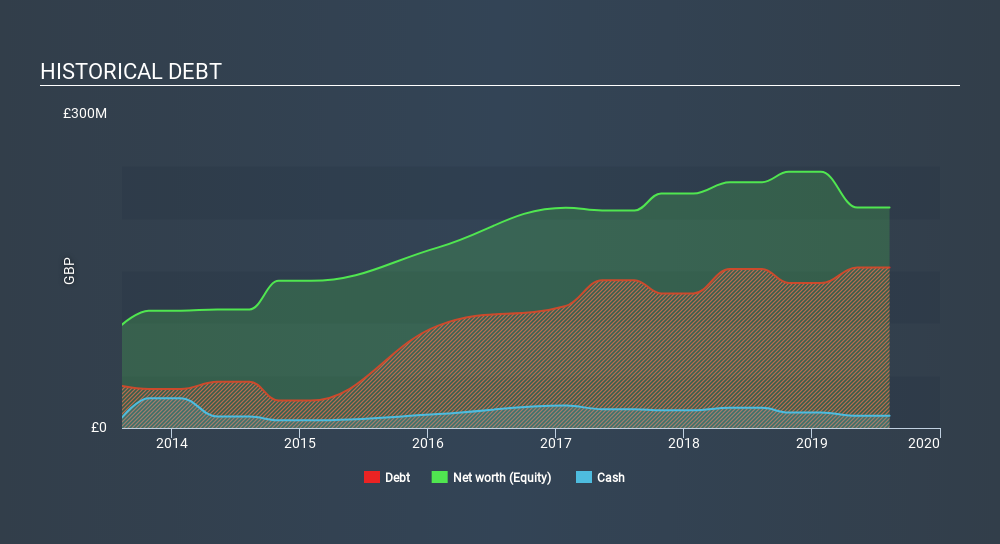
The chart below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Ted Baker had UK£153.2m in debt in August 2019; about the same as the year before. However, because it has a cash reserve of UK£11.7m, its net debt is less, at about UK£141.5m.
How Healthy Is Ted Baker's Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Ted Baker had liabilities of UK£263.6m due within 12 months and liabilities of UK£188.7m due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had UK£11.7m in cash and UK£71.1m in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling UK£369.5m more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
The deficiency here weighs heavily on the UK£73.4m company itself, as if a child were struggling under the weight of an enormous back-pack full of books, his sports gear, and a trumpet. So we'd watch its balance sheet closely, without a doubt. At the end of the day, Ted Baker would probably need a major re-capitalization if its creditors were to demand repayment.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
Ted Baker has net debt worth 2.2 times EBITDA, which isn't too much, but its interest cover looks a bit on the low side, with EBIT at only 4.6 times the interest expense. While that doesn't worry us too much, it does suggest the interest payments are somewhat of a burden. Shareholders should be aware that Ted Baker's EBIT was down 48% last year. If that earnings trend continues then paying off its debt will be about as easy as herding cats on to a roller coaster. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Ted Baker's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So the logical step is to look at the proportion of that EBIT that is matched by actual free cash flow. In the last three years, Ted Baker created free cash flow amounting to 17% of its EBIT, an uninspiring performance. For us, cash conversion that low sparks a little paranoia about is ability to extinguish debt.
Our View
On the face of it, Ted Baker's EBIT growth rate left us tentative about the stock, and its level of total liabilities was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. Having said that, its ability handle its debt, based on its EBITDA, isn't such a worry. After considering the datapoints discussed, we think Ted Baker has too much debt. While some investors love that sort of risky play, it's certainly not our cup of tea. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. Case in point: We've spotted 6 warning signs for Ted Baker you should be aware of, and 1 of them makes us a bit uncomfortable.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
Love or hate this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned. Thank you for reading.
About LSE:TED
Ted Baker
Ted Baker plc engages in the design, wholesale, and retail of menswear, womenswear, and accessories under the Ted Baker brand in the United States, the United Kingdom, rest of Europe, Canada, and South Africa.
Adequate balance sheet and fair value.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives





