Key Takeaways
- Building its own cloud platform to take advantage of the best features of each public cloud provider
- The partnership with Symbotic could help automate around 60% of store operations
- Average unit costs to reduce up to 20% due to automation
- Expanding its use of automated delivery methods to deliver products to customers
- Targeting two key markets in its international strategy: China and India
Catalysts
A Great Business And Disciplined Cost Structure Should Keep Growth Consistent
Walmart is a budget retailer with over 10,500 stores worldwide and their strong business performance is due to a number of factors, including:
- Walmart’s large and efficient supply chain - a vast network of stores and distribution centers, which allows it to deliver products to customers efficiently.
- Innovation at scale - Walmart is constantly investing in new technologies, such as automation of its supply chain, self-checkout and online grocery delivery. Even small efficiency improvements make a difference for value in a $631B revenue company.
- The company's incessant focus on low prices.
What we can see is that Walmart is producing strong growth in all of its segments with a 3-year CAGR of 5.2%, including the U.S., international, and e-commerce businesses. The company is also managing its costs effectively, which will lead to higher margins.
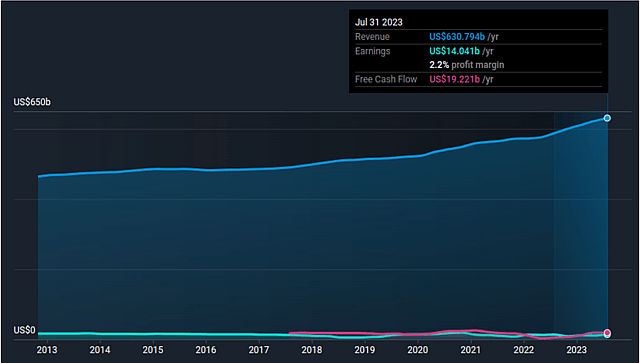
Walmart’s historical performance
I also find that Walmart has a long history of disciplined cost management and operational efficiency. This has helped the company consistently deliver strong financial results.
Walmart is also generating strong cash flows ($19.2bn), which it is using to return capital to shareholders through dividends and share repurchases. The cash flows are frequently above their earnings (of $14bn), which is due to their efficient working capital management.
Sales and Earnings Growth Potential Are Not Priced-In By The Market
Walmart is one of the largest revenue generating companies, but as a retailer it has relatively low margins, with a gross margin of 24.2% and a profit margin of 2.2%.
By producing slight improvements of its margins, the effect on its cash flows will be considerable, but the market is currently expecting a stabilization and possibly minor improvements. Per management’s guidance, Walmart affirms its commitment of 4% sales growth and 4%+ operating income growth over the next 3-5 years.
However, the innovation in which Walmart is investing scales efficiently and can have lasting effects on the cost structure, which is why there is a possibility for the company to become closer to a 4% net profit business by executing on its automation and e-commerce. Conversely, Walmart has been experiencing inflation impacts in the last 2 years, which have grabbed much of the market’s attention, while the potential upside has been neglected.
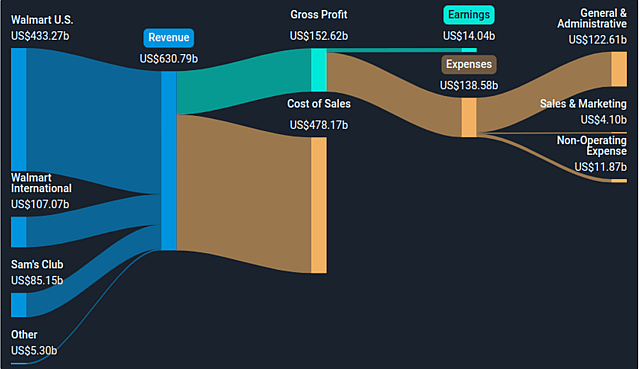
Automation Will Lower Costs And Decrease Complexity: Walmart Partners With Symbotic
Walmart is partnering with Symbotic to automate its regional distribution centers. This is a major move for the retail giant, and could have an impact on the way Walmart gets products to stores.
Walmart is intent on leveraging automation to cut its cost structure. The company estimates that roughly 65% of stores will be serviced by automation, 55% of fulfillment center volumes will move via automated facilities, and unit cost averages could be improved by 20%, all by roughly 2026. I think that this statement alone has significant upside potential and believe that management will surprise on the upside as it starts showing benefits in margins. But these improvements will come at a cost (albeit affordably for WMT), and I expand on that further down when discussing continuous reinvestment.
It seems that management chose a high return path for the company, and by using automation they will lower costs and improve the bottom line, having a large impact on its valuation. Further, by reducing operating complexity with automation, the company will become easier to manage, opening up the path to stronger e-commerce growth.
Their partner in automation, Symbotic, uses an algorithm to store cases like puzzle pieces using high-speed mobile bots. This allows for more efficient storage and retrieval of inventory, which can lead to faster order fulfillment. The system also uses dense modular storage to expand building capacity and high-speed palletizing robotics to organize and optimize freight.
There are specific benefits, that I expect Walmart to see from this partnership:
- Faster order fulfillment: Move products on shelves even faster.
- Increased efficiency: The new technology will help Walmart to improve its efficiency and reduce costs.
- Reduced headcount: Besides driving down operational complexity, the technology can allow fulfillment centers to operate with higher efficiency.
Overall, this partnership is a positive development for Walmart and its customers. It is a sign of the company's commitment to innovation and its willingness to invest in new technologies that can help it to improve its operations.
Walmart’s Digital Infrastructure Is Not To Be Underestimated
The company is investing in new technologies, such as artificial intelligence and robotics, to improve the customer experience.
For example, Walmart is using artificial intelligence to recommend products to customers and to optimize its inventory. This is partly driven via the Google partnership aimed to use artificial intelligence for improving retail processes. Walmart is also a Google Cloud customer and leverages their infrastructure and capabilities to produce innovation.
However, the company is wisely minimizing cloud vendor lock-in. Walmart has developed a multi-cloud approach which managed to cut down IT spend between 10% to 18%.
By building its own cloud platform, called the Walmart Cloud Native Platform, the company manages to run workloads on three different public clouds: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). This allows them to take advantage of the best features of each public cloud provider.
For example, Walmart uses AWS for its machine learning capabilities, Azure for its analytics capabilities, and GCP for its containerization capabilities. By using services from multiple cloud vendors as well as their own native platform, the company leverages bargaining power and is able to convince vendors to cater to its specific cloud infrastructure needs. For example, Microsoft and Google have allowed Walmart to run some of their respective software on any of the three clouds.
Walmart is also experimenting with cutting-edge technology which has a large potential opportunity to cut costs. The company is expanding its use of drones and self-driving vehicles to deliver groceries to customers. I believe these initiatives will help increase operating margins, and as for the delivery side, they could potentially help generate additional sales.
Walmart Is Gaining Experience In International Retail Which Will Help Grow Its Presence In Emerging Markets
The company is teaming up with big local players and targeting emerging markets for its international strategy, which is yielding considerable success as the segment now represents 17% of total revenue.
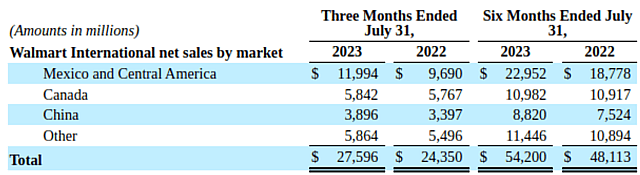
Walmart’s international segment revenues
Of Walmart International's total net sales, approximately $5.8 billion in the last quarter and $4.6 billion in the same period a year ago were related to e-commerce, which grew 26% YoY, and represents 21% of international sales.
Besides Central America where Walmart has a direct presence, there are two key markets on the international scene, China and India; and Walmart is using a similar strategy to capture their market share. I believe expansion in these areas will be the biggest contributors to revenue growth going forward.
The Smart Way To Do Business With China: Cooperation & Minority Stakes
The company is present in the Chinese market primarily with its 9.2% stake in , which should help the company grow its business in China.
is a major player in the Chinese e-commerce market, and the partnership gives Walmart access to their customers and infrastructure.
The two partners have integrated logistics and Sam’s club is also available in JD’s stores giving customers access to the membership retail model. This means that the companies are actively collaborating and sharing their infrastructure to their combined customer base in China and internationally.
Sales growth in China was solid in the second quarter, but it's important to note that this was due to the low base of comparison from last year, when there were strict COVID-19 lockdowns.
In the last 12 months JD made $147 billion (converted from CNY), and has a profit margin of 2%, equating to about $3 billion. With Walmart’s minority stake, the company has a claim of $278 million on JD’s earnings. Analysts expect JD’s revenues and profits to continue growing, and this will benefit WMT’s bottom line.
The Indian Retail Market Will Grow From $40 Billion To $200 Billion And Walmart Is Gaining Share
The 2018 Walmart-Flipkart deal for a 77% stake is a major development in the global e-commerce landscape and it seems that the company is executing well on its $16 billion bet.
Walmart increased its stake in Flipkart in 2023 by $1.4B at a $35 billion valuation, amounting to a 4% increase. They also bought Accel's remaining 1% stake in the retailer. In total, the company likely now has more than an 80% stake in Flipkart which is the main entry avenue to the Indian market.
Walmart is capitalizing on India's e-commerce market, which is currently worth $38 billion, and expected to grow to $200 billion by 2027. While Flipkart isn’t expected to become profitable for a while, the deal is also a way for Walmart to compete with Amazon, which is the dominant player in the Indian e-commerce market.
Both Walmart and Flipkart are drawing from their strengths as Flipkart has access to Walmart's expertise in online grocery and a strong food supply chain, while Walmart has better access to sourcing food from India.
Sam’s Club And Costco To Remain In Tight Competition
Sam's Club is a membership-only warehouse owned by Walmart. It has over 600 stores in the United States, Puerto Rico, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, China, and India.
Sam's Club offers a wide variety of products and services. The brand is primarily targeting business owners and families. While its membership model allows members to save money on bulk purchases.
Sam's Club is a major competitor to Costco, another membership-only warehouse club. The two companies are constantly vying for market share, and they offer similar products and services. However, there are some key differences between the two companies. For example, Sam's Club has a wider selection of groceries, while Costco has a wider selection of electronics. Sam's Club also offers a wider variety of services, such as optical and tire and battery centers.
I don’t see an obvious advantage of Sam’s Club over Costco, and estimate that the two companies will be in tight competition for the foreseeable future. Conversely, Costco also has an e-commerce solution which makes up some 10% of its sales, and while it’s lagging behind Walmart and Amazon, it seems to be offering a lower selection of goods which may be tailored for higher returns on capital instead of capturing market share.
Continuous Reinvestment Into The Business
Walmart invested $9.2 billion in the first half of FY’24, 23% more than the same period last year. Management has noted that most of the investments are geared towards technology and supply chain projects - 56%, and has also noted that they expect capital expenditures to be flat compared with last year.
This indicates that the company is focused on leveraging its existing stores and improving their efficiency in order to drive up margins. Which is why I think that this will show up as bottom line growth as opposed to high revenue growth.

Management’s estimates for CapEx of around $16.7 billion is roughly what I expect to see the company investing annually in the future. However, barring any major technological surprises, I see these investments targeted towards efficiency (as opposed to growth). Therefore, I estimate that the need for this level of CapEx will decline in five years, when the company will start reaping the profitability improvements and increase the returns to its shareholders.
Stock Repurchases to Continue, Reducing The Number Of Shares Outstanding
Walmart has repurchased an average of 2.1% of its outstanding shares per year in the last two years. I expect the company to continue reducing its share count by roughly the same amount, and estimate a share count of 7.26 billion in 2028, down by 10% from the current 8.07 billion.
Assumptions
Revenue To Keep Growing At A Stable Rate
I assume Walmart to grow roughly in-line with the market growth rate in the next five years, and estimate revenues of $782 billion growing by 4.4% p.a. to 2028.
Margins Are The Largest Value Driver For Walmart
I expect that the investments in automation and eCommerce will result in an increase of net margins to 4% in five years and continue at the same level moving forward. This produces a net income of $31.3 billion in 2028, up by 124% from the current $14 billion.
Part of this growth is attributed to the unlocked value from the cost-cutting produced by automation efforts, and the higher-margin e-commerce business which will become a growing portion of the company’s income. While the other part is attributable to the working capital normalization expected to happen in the next two years as inventory levels normalize and consumer spending picks up.
Why I Chose 22x As Walmart’s Future Price to Earnings Ratio
In 2028 I expect Walmart to be a high-return company that re-rates as a mature stock at a 22x PE as the efficiency boost experiences its limit.
My estimated PE is a function of 1/(discount rate (9%) - (4.4%) growth in perpetuity).
The 9% discount rate comes from my levered regression beta of 0.927 * 5.07% risk in the regions where Walmart operates + the current risk free rate (10-Year T.Bond) of 4.27%.
I assume that for a company with a long history of operations, a regression beta is appropriate and even reveals competitive (dis)advantages present in the company. As Walmart increases their presence in emerging markets, their risk will increase, and reflect in a higher beta.
Risks
The rising cost of labor could put downwards pressure on margins
Walmart is a labor-intensive company, and the rising cost of labor could hurt its margins.
The Chinese economy may not see a lasting rebound
Per an analysis from Ruchir Sharma, the Chinese property market is contracting, which is a major driver of the economy. Local government debt has more than doubled in 10 years and is now nearly half of China's total debt. Beijing is partly immobilized by these debts and cannot use easy monetary policy to prop up the property market without triggering an outflow of capital and a crash in the yuan. This may impact the Chinese market growth, and JD’s revenue as Walmart’s partner. We should also note that the article is first published by the FT - a Japanese owned company, that may be adversarial towards China.
Walmart faces increasing competition from other retailers and could lose its competitive advantages
Walmart is not the only retailer that is investing in automation and e-commerce. Other major retailers, such as Amazon and Target, are also making significant investments in these areas. This could make it more difficult for Walmart to maintain its competitive advantage.
The success of Walmart's automation strategy is uncertain and failure could be costly
The company is investing heavily in automation, but it is not yet clear how successful this strategy will be. There are a number of challenges that Walmart will need to overcome, such as the high cost of automation and the need to integrate new technologies into its existing operations.
Walmart's international expansion may contribute to a higher beta (risk)
Walmart has been expanding its international operations in recent years, but this could be a risky move. The company faces a number of challenges in international markets, such as different cultures, regulations, and currencies.
Walmart's supply chain is complex and vulnerable to disruption
Walmart's supply chain is one of its most important assets, but it is also one of its most vulnerable areas. The company relies on a complex network of suppliers and distributors, and any disruption to this network could have a significant impact on Walmart's operations.
Insiders have been selling stock in the last 12 months
When this happens on multiple occasions, there may be underlying reasons why shareholders are pessimistic on the company.
Have other thoughts on Walmart?
Create your own narrative on this stock, and estimate its Fair Value using our Valuator tool.
Create NarrativeHow well do narratives help inform your perspective?
Disclaimer
Simply Wall St analyst Goran_Damchevski holds no position in NasdaqGS:WMT. Simply Wall St has no position in the company(s) mentioned. Simply Wall St may provide the securities issuer or related entities with website advertising services for a fee, on an arm's length basis. These relationships have no impact on the way we conduct our business, the content we host, or how our content is served to users. This narrative is general in nature and explores scenarios and estimates created by the author. The narrative does not reflect the opinions of Simply Wall St, and the views expressed are the opinion of the author alone, acting on their own behalf. These scenarios are not indicative of the company's future performance and are exploratory in the ideas they cover. The fair value estimate's are estimations only, and does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and they do not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. Note that the author's analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material.





