
Howard Marks put it nicely when he said that, rather than worrying about share price volatility, 'The possibility of permanent loss is the risk I worry about... and every practical investor I know worries about.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We can see that Avista Corporation (NYSE:AVA) does use debt in its business. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. If things get really bad, the lenders can take control of the business. However, a more common (but still painful) scenario is that it has to raise new equity capital at a low price, thus permanently diluting shareholders. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. The first thing to do when considering how much debt a business uses is to look at its cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for Avista
What Is Avista's Net Debt?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of March 2023 Avista had US$2.85b of debt, an increase on US$2.61b, over one year. And it doesn't have much cash, so its net debt is about the same.
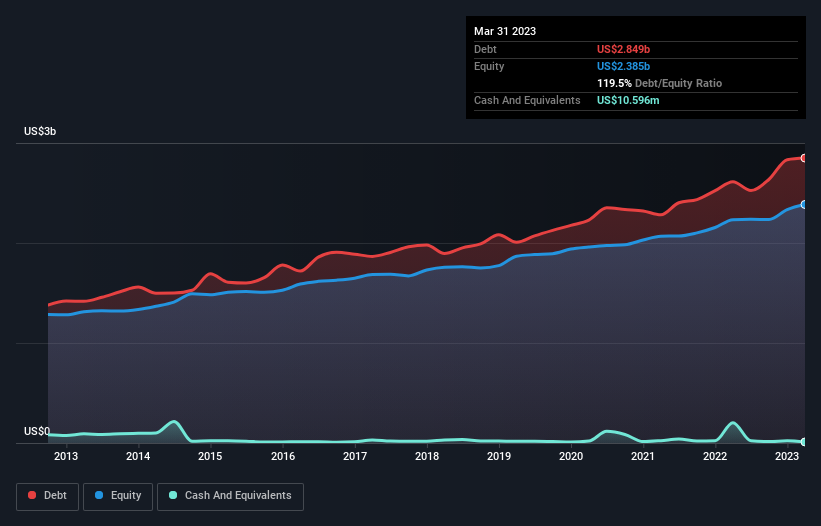
How Healthy Is Avista's Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Avista had liabilities of US$604.6m due within 12 months and liabilities of US$4.40b due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$10.6m as well as receivables valued at US$244.4m due within 12 months. So its liabilities total US$4.75b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
The deficiency here weighs heavily on the US$2.98b company itself, as if a child were struggling under the weight of an enormous back-pack full of books, his sports gear, and a trumpet. So we'd watch its balance sheet closely, without a doubt. At the end of the day, Avista would probably need a major re-capitalization if its creditors were to demand repayment.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Avista shareholders face the double whammy of a high net debt to EBITDA ratio (6.4), and fairly weak interest coverage, since EBIT is just 1.6 times the interest expense. This means we'd consider it to have a heavy debt load. Another concern for investors might be that Avista's EBIT fell 10% in the last year. If that's the way things keep going handling the debt load will be like delivering hot coffees on a pogo stick. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Avista's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, while the tax-man may adore accounting profits, lenders only accept cold hard cash. So we always check how much of that EBIT is translated into free cash flow. During the last three years, Avista burned a lot of cash. While investors are no doubt expecting a reversal of that situation in due course, it clearly does mean its use of debt is more risky.
Our View
On the face of it, Avista's net debt to EBITDA left us tentative about the stock, and its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. And furthermore, its interest cover also fails to instill confidence. It's also worth noting that Avista is in the Integrated Utilities industry, which is often considered to be quite defensive. Considering all the factors previously mentioned, we think that Avista really is carrying too much debt. To our minds, that means the stock is rather high risk, and probably one to avoid; but to each their own (investing) style. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For example, we've discovered 5 warning signs for Avista (2 are significant!) that you should be aware of before investing here.
When all is said and done, sometimes its easier to focus on companies that don't even need debt. Readers can access a list of growth stocks with zero net debt 100% free, right now.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NYSE:AVA
Avista
Operates as an electric and natural gas utility company in the United States.
Established dividend payer and fair value.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives




