The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. As with many other companies Lear Corporation (NYSE:LEA) makes use of debt. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, the upside of debt is that it often represents cheap capital, especially when it replaces dilution in a company with the ability to reinvest at high rates of return. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for Lear
What Is Lear's Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at December 2023 Lear had debt of US$2.77b, up from US$2.61b in one year. However, it does have US$1.20b in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about US$1.57b.
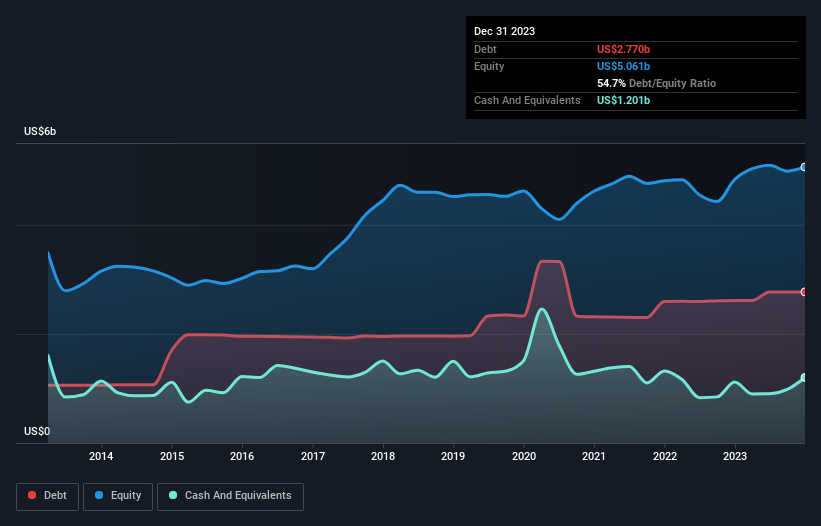
A Look At Lear's Liabilities
The latest balance sheet data shows that Lear had liabilities of US$5.67b due within a year, and liabilities of US$3.97b falling due after that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of US$1.20b as well as receivables valued at US$3.90b due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by US$4.53b.
While this might seem like a lot, it is not so bad since Lear has a market capitalization of US$7.74b, and so it could probably strengthen its balance sheet by raising capital if it needed to. But we definitely want to keep our eyes open to indications that its debt is bringing too much risk.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Lear has a low net debt to EBITDA ratio of only 0.95. And its EBIT covers its interest expense a whopping 10.4 times over. So we're pretty relaxed about its super-conservative use of debt. On top of that, Lear grew its EBIT by 31% over the last twelve months, and that growth will make it easier to handle its debt. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Lear can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Looking at the most recent three years, Lear recorded free cash flow of 41% of its EBIT, which is weaker than we'd expect. That weak cash conversion makes it more difficult to handle indebtedness.
Our View
The good news is that Lear's demonstrated ability to grow its EBIT delights us like a fluffy puppy does a toddler. But, on a more sombre note, we are a little concerned by its level of total liabilities. Looking at all the aforementioned factors together, it strikes us that Lear can handle its debt fairly comfortably. On the plus side, this leverage can boost shareholder returns, but the potential downside is more risk of loss, so it's worth monitoring the balance sheet. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For example, we've discovered 1 warning sign for Lear that you should be aware of before investing here.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
The New Payments ETF Is Live on NASDAQ:
Money is moving to real-time rails, and a newly listed ETF now gives investors direct exposure. Fast settlement. Institutional custody. Simple access.
Explore how this launch could reshape portfolios
Sponsored ContentNew: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NYSE:LEA
Lear
Designs, develops, engineers, manufactures, assembles, and supplies automotive seating, and electrical distribution systems and related components for automotive original equipment manufacturers in North America, Europe, Africa, Asia, and South America.
Flawless balance sheet, good value and pays a dividend.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

Early mover in a fast growing industry. Likely to experience share price volatility as they scale


A case for CA$31.80 (undiluted), aka 8,616% upside from CA$0.37 (an 86 bagger!).


Moderation and Stabilisation: HOLD: Fair Price based on a 4-year Cycle is $12.08
Recently Updated Narratives

Airbnb Stock: Platform Growth in a World of Saturation and Scrutiny

Clarivate Stock: When Data Becomes the Backbone of Innovation and Law

Adobe Stock: AI-Fueled ARR Growth Pushes Guidance Higher, But Cost Pressures Loom
Popular Narratives


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success
Trending Discussion


