
David Iben put it well when he said, 'Volatility is not a risk we care about. What we care about is avoiding the permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We note that Collins Co., Ltd. (TPE:2906) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
What Risk Does Debt Bring?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. In the worst case scenario, a company can go bankrupt if it cannot pay its creditors. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Collins
How Much Debt Does Collins Carry?
You can click the graphic below for the historical numbers, but it shows that as of September 2020 Collins had NT$1.62b of debt, an increase on NT$1.41b, over one year. However, because it has a cash reserve of NT$1.08b, its net debt is less, at about NT$543.2m.
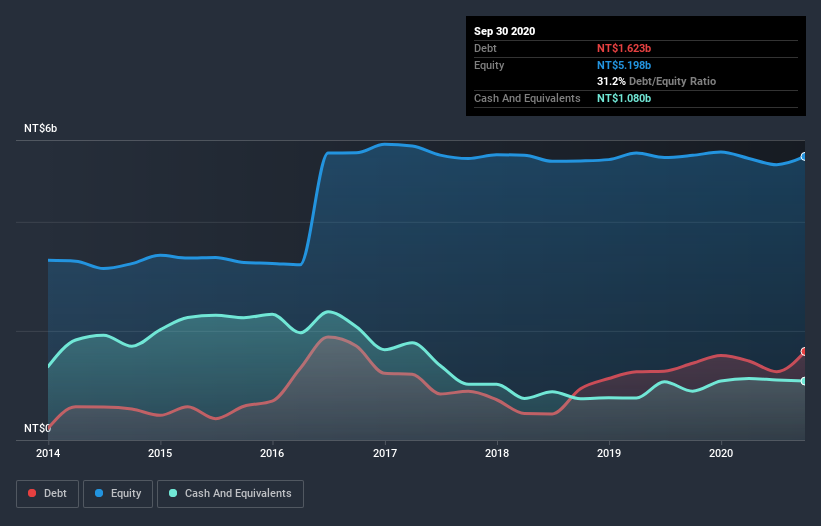
How Strong Is Collins's Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Collins had liabilities of NT$2.65b due within 12 months, and liabilities of NT$1.25b due beyond 12 months. On the other hand, it had cash of NT$1.08b and NT$1.64b worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities total NT$1.19b more than the combination of its cash and short-term receivables.
This deficit isn't so bad because Collins is worth NT$3.08b, and thus could probably raise enough capital to shore up its balance sheet, if the need arose. But it's clear that we should definitely closely examine whether it can manage its debt without dilution.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
Collins has net debt of just 1.2 times EBITDA, suggesting it could ramp leverage without breaking a sweat. And remarkably, despite having net debt, it actually received more in interest over the last twelve months than it had to pay. So it's fair to say it can handle debt like a hotshot teppanyaki chef handles cooking. Fortunately, Collins grew its EBIT by 6.2% in the last year, making that debt load look even more manageable. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But you can't view debt in total isolation; since Collins will need earnings to service that debt. So when considering debt, it's definitely worth looking at the earnings trend. Click here for an interactive snapshot.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. In the last three years, Collins's free cash flow amounted to 49% of its EBIT, less than we'd expect. That's not great, when it comes to paying down debt.
Our View
When it comes to the balance sheet, the standout positive for Collins was the fact that it seems able to cover its interest expense with its EBIT confidently. However, our other observations weren't so heartening. For instance it seems like it has to struggle a bit to handle its total liabilities. When we consider all the elements mentioned above, it seems to us that Collins is managing its debt quite well. Having said that, the load is sufficiently heavy that we would recommend any shareholders keep a close eye on it. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. Like risks, for instance. Every company has them, and we've spotted 2 warning signs for Collins (of which 1 is significant!) you should know about.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
If you decide to trade Collins, use the lowest-cost* platform that is rated #1 Overall by Barron’s, Interactive Brokers. Trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds on 135 markets, all from a single integrated account. Promoted
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team@simplywallst.com.
About TWSE:2906
Collins
Engages in the export of household consumer products and garments in Taiwan, the United States, Canada, and internationally.
Adequate balance sheet with questionable track record.
Market Insights
Community Narratives




