What Type Of Shareholders Make Up SAS AB (publ)'s (STO:SAS) Share Registry?

The big shareholder groups in SAS AB (publ) (STO:SAS) have power over the company. Institutions often own shares in more established companies, while it's not unusual to see insiders own a fair bit of smaller companies. Companies that have been privatized tend to have low insider ownership.
With a market capitalization of kr12b, SAS is a decent size, so it is probably on the radar of institutional investors. Taking a look at our data on the ownership groups (below), it seems that institutions are noticeable on the share registry. Let's take a closer look to see what the different types of shareholders can tell us about SAS.
View our latest analysis for SAS
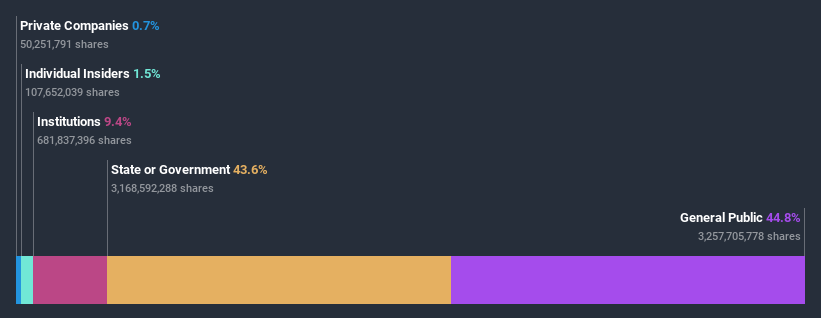
What Does The Institutional Ownership Tell Us About SAS?
Institutions typically measure themselves against a benchmark when reporting to their own investors, so they often become more enthusiastic about a stock once it's included in a major index. We would expect most companies to have some institutions on the register, especially if they are growing.
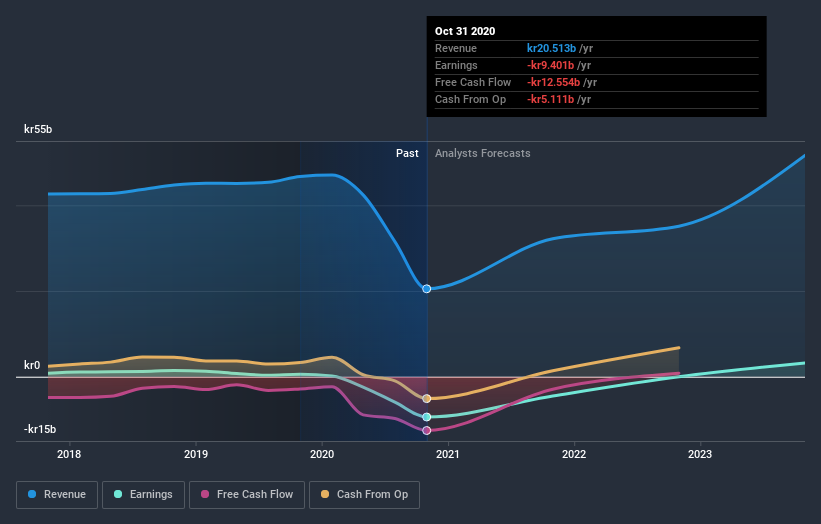
We can see that SAS does have institutional investors; and they hold a good portion of the company's stock. This suggests some credibility amongst professional investors. But we can't rely on that fact alone since institutions make bad investments sometimes, just like everyone does. When multiple institutions own a stock, there's always a risk that they are in a 'crowded trade'. When such a trade goes wrong, multiple parties may compete to sell stock fast. This risk is higher in a company without a history of growth. You can see SAS' historic earnings and revenue below, but keep in mind there's always more to the story.
SAS is not owned by hedge funds. Looking at our data, we can see that the largest shareholder is Denmark with 22% of shares outstanding. For context, the second largest shareholder holds about 22% of the shares outstanding, followed by an ownership of 3.4% by the third-largest shareholder.
To make our study more interesting, we found that the top 5 shareholders control more than half of the company which implies that this group has considerable sway over the company's decision-making.
Researching institutional ownership is a good way to gauge and filter a stock's expected performance. The same can be achieved by studying analyst sentiments. Quite a few analysts cover the stock, so you could look into forecast growth quite easily.
Insider Ownership Of SAS
The definition of company insiders can be subjective and does vary between jurisdictions. Our data reflects individual insiders, capturing board members at the very least. Management ultimately answers to the board. However, it is not uncommon for managers to be executive board members, especially if they are a founder or the CEO.
Most consider insider ownership a positive because it can indicate the board is well aligned with other shareholders. However, on some occasions too much power is concentrated within this group.
I can report that insiders do own shares in SAS AB (publ). It is a pretty big company, so it is generally a positive to see some potentially meaningful alignment. In this case, they own around kr181m worth of shares (at current prices). It is good to see this level of investment by insiders. You can check here to see if those insiders have been buying recently.
General Public Ownership
With a 45% ownership, the general public have some degree of sway over SAS. This size of ownership, while considerable, may not be enough to change company policy if the decision is not in sync with other large shareholders.
Next Steps:
It's always worth thinking about the different groups who own shares in a company. But to understand SAS better, we need to consider many other factors. For example, we've discovered 2 warning signs for SAS (1 is a bit concerning!) that you should be aware of before investing here.
But ultimately it is the future, not the past, that will determine how well the owners of this business will do. Therefore we think it advisable to take a look at this free report showing whether analysts are predicting a brighter future.
NB: Figures in this article are calculated using data from the last twelve months, which refer to the 12-month period ending on the last date of the month the financial statement is dated. This may not be consistent with full year annual report figures.
If you decide to trade SAS, use the lowest-cost* platform that is rated #1 Overall by Barron’s, Interactive Brokers. Trade stocks, options, futures, forex, bonds and funds on 135 markets, all from a single integrated account. Promoted
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
*Interactive Brokers Rated Lowest Cost Broker by StockBrokers.com Annual Online Review 2020
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
About OM:SAS
SAS
Provides passenger flight transportation services in the Nordic and international route network.
Slight and slightly overvalued.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives



