Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it might be obvious that you need to consider debt, when you think about how risky any given stock is, because too much debt can sink a company. We can see that CBI Co., Ltd. (KOSDAQ:013720) does use debt in its business. But is this debt a concern to shareholders?
When Is Debt A Problem?
Generally speaking, debt only becomes a real problem when a company can't easily pay it off, either by raising capital or with its own cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, debt can be an important tool in businesses, particularly capital heavy businesses. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
Check out our latest analysis for CBI
What Is CBI's Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that CBI had debt of ₩18.7b at the end of June 2024, a reduction from ₩29.6b over a year. However, it does have ₩10.3b in cash offsetting this, leading to net debt of about ₩8.45b.
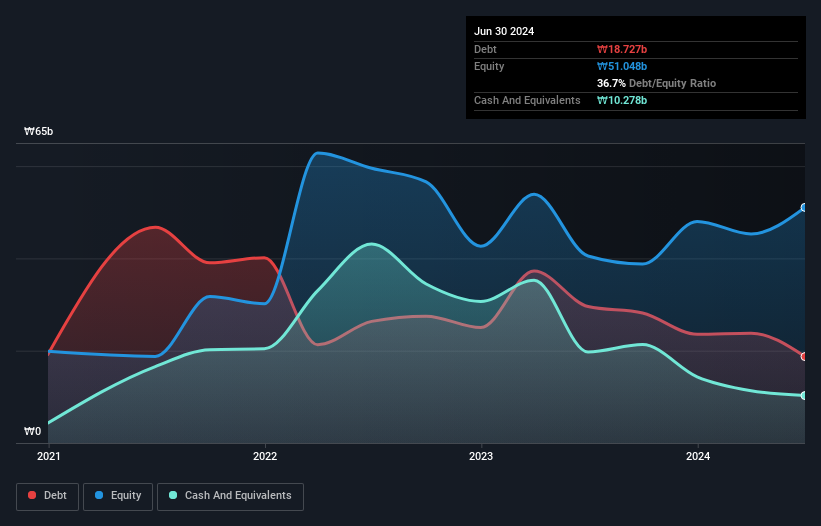
How Healthy Is CBI's Balance Sheet?
We can see from the most recent balance sheet that CBI had liabilities of ₩20.6b falling due within a year, and liabilities of ₩3.95b due beyond that. Offsetting this, it had ₩10.3b in cash and ₩8.29b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So it has liabilities totalling ₩5.96b more than its cash and near-term receivables, combined.
Since publicly traded CBI shares are worth a total of ₩42.8b, it seems unlikely that this level of liabilities would be a major threat. However, we do think it is worth keeping an eye on its balance sheet strength, as it may change over time.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
While CBI's debt to EBITDA ratio (2.9) suggests that it uses some debt, its interest cover is very weak, at 1.1, suggesting high leverage. It seems that the business incurs large depreciation and amortisation charges, so maybe its debt load is heavier than it would first appear, since EBITDA is arguably a generous measure of earnings. So shareholders should probably be aware that interest expenses appear to have really impacted the business lately. One redeeming factor for CBI is that it turned last year's EBIT loss into a gain of ₩1.2b, over the last twelve months. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But you can't view debt in total isolation; since CBI will need earnings to service that debt. So if you're keen to discover more about its earnings, it might be worth checking out this graph of its long term earnings trend.
But our final consideration is also important, because a company cannot pay debt with paper profits; it needs cold hard cash. So it is important to check how much of its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) converts to actual free cash flow. Over the last year, CBI actually produced more free cash flow than EBIT. That sort of strong cash conversion gets us as excited as the crowd when the beat drops at a Daft Punk concert.
Our View
CBI's interest cover was a real negative on this analysis, although the other factors we considered were considerably better. In particular, we are dazzled with its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow. When we consider all the elements mentioned above, it seems to us that CBI is managing its debt quite well. Having said that, the load is sufficiently heavy that we would recommend any shareholders keep a close eye on it. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. We've identified 3 warning signs with CBI (at least 1 which makes us a bit uncomfortable) , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
If you're interested in investing in businesses that can grow profits without the burden of debt, then check out this free list of growing businesses that have net cash on the balance sheet.
New: AI Stock Screener & Alerts
Our new AI Stock Screener scans the market every day to uncover opportunities.
• Dividend Powerhouses (3%+ Yield)
• Undervalued Small Caps with Insider Buying
• High growth Tech and AI Companies
Or build your own from over 50 metrics.
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About KOSDAQ:A013720
Cube &
Manufactures and sells motor vehicles parts and accessories in South Korea, rest of Asia, the United States, Europe, and internationally.
Excellent balance sheet with low risk.
Market Insights
Weekly Picks

Solutions by stc: 34% Upside in Saudi's Digital Transformation Leader


The AI Infrastructure Giant Grows Into Its Valuation
Recently Updated Narratives


The "Sleeping Giant" Wakes Up – Efficiency & Monetization


The "Rate Cut" Supercycle Winner – Profitable & Accelerating


The Industrialist of the Skies – Scaling with "Automotive DNA
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026



