Legendary fund manager Li Lu (who Charlie Munger backed) once said, 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' It's only natural to consider a company's balance sheet when you examine how risky it is, since debt is often involved when a business collapses. We can see that Daicel Corporation (TSE:4202) does use debt in its business. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt and other liabilities become risky for a business when it cannot easily fulfill those obligations, either with free cash flow or by raising capital at an attractive price. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. By replacing dilution, though, debt can be an extremely good tool for businesses that need capital to invest in growth at high rates of return. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
View our latest analysis for Daicel
What Is Daicel's Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Daicel had debt of JP¥282.2b at the end of September 2024, a reduction from JP¥299.7b over a year. However, because it has a cash reserve of JP¥64.8b, its net debt is less, at about JP¥217.4b.
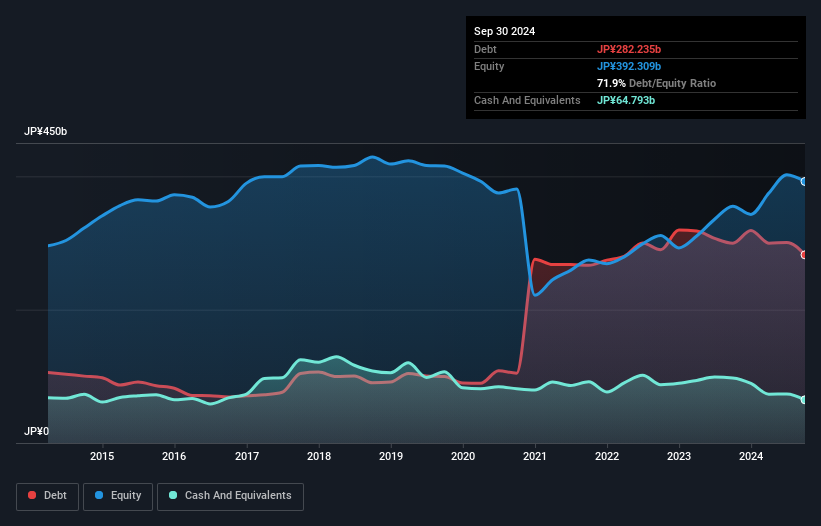
A Look At Daicel's Liabilities
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Daicel had liabilities of JP¥171.6b due within 12 months and liabilities of JP¥263.9b due beyond that. On the other hand, it had cash of JP¥64.8b and JP¥100.2b worth of receivables due within a year. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by JP¥270.5b.
This is a mountain of leverage relative to its market capitalization of JP¥367.6b. Should its lenders demand that it shore up the balance sheet, shareholders would likely face severe dilution.
In order to size up a company's debt relative to its earnings, we calculate its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) divided by its interest expense (its interest cover). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Daicel's net debt to EBITDA ratio of about 2.1 suggests only moderate use of debt. And its commanding EBIT of 1k times its interest expense, implies the debt load is as light as a peacock feather. It is well worth noting that Daicel's EBIT shot up like bamboo after rain, gaining 40% in the last twelve months. That'll make it easier to manage its debt. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Daicel's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you're focused on the future you can check out this free report showing analyst profit forecasts.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Over the last three years, Daicel recorded negative free cash flow, in total. Debt is far more risky for companies with unreliable free cash flow, so shareholders should be hoping that the past expenditure will produce free cash flow in the future.
Our View
While Daicel's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow has us nervous. To wit both its interest cover and EBIT growth rate were encouraging signs. We think that Daicel's debt does make it a bit risky, after considering the aforementioned data points together. Not all risk is bad, as it can boost share price returns if it pays off, but this debt risk is worth keeping in mind. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. We've identified 2 warning signs with Daicel , and understanding them should be part of your investment process.
At the end of the day, it's often better to focus on companies that are free from net debt. You can access our special list of such companies (all with a track record of profit growth). It's free.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About TSE:4202
Daicel
Engages in the materials, medical/healthcare, smart, safety, and engineering plastics businesses in Japan and internationally.
Undervalued established dividend payer.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives


Recently Updated Narratives

Astor Enerji will surge with a fair value of $140.43 in the next 3 years

Proximus: The State-Backed Backup Plan with 7% Gross Yield and 15% Currency Upside.


A case for for IMPACT Silver Corp (TSXV:IPT) to reach USD $4.52 (CAD $6.16) in 2026 (23 bagger in 1 year) and USD $5.76 (CAD $7.89) by 2030
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


The company that turned a verb into a global necessity and basically runs the modern internet, digital ads, smartphones, maps, and AI.



