The external fund manager backed by Berkshire Hathaway's Charlie Munger, Li Lu, makes no bones about it when he says 'The biggest investment risk is not the volatility of prices, but whether you will suffer a permanent loss of capital.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. As with many other companies Teijin Limited (TSE:3401) makes use of debt. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
Why Does Debt Bring Risk?
Debt assists a business until the business has trouble paying it off, either with new capital or with free cash flow. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. While that is not too common, we often do see indebted companies permanently diluting shareholders because lenders force them to raise capital at a distressed price. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. The first step when considering a company's debt levels is to consider its cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Teijin
How Much Debt Does Teijin Carry?
The chart below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that Teijin had JP¥541.0b in debt in June 2024; about the same as the year before. However, because it has a cash reserve of JP¥141.0b, its net debt is less, at about JP¥399.9b.
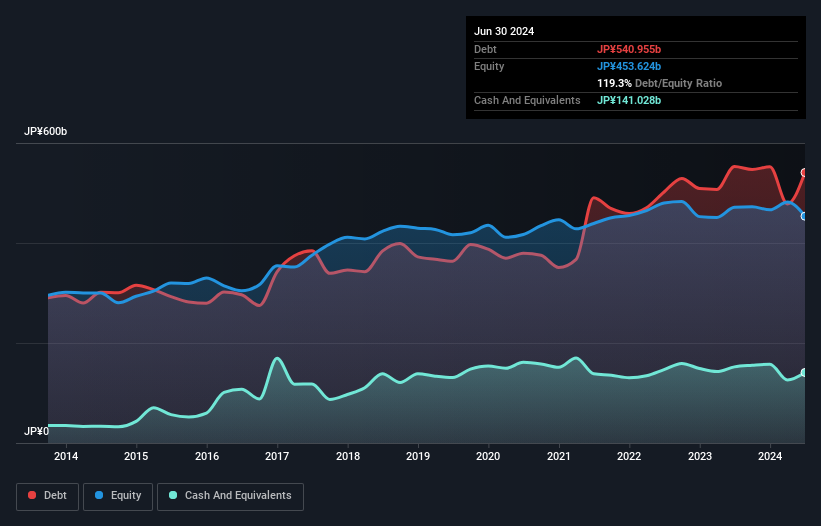
How Strong Is Teijin's Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Teijin had liabilities of JP¥481.8b due within 12 months and liabilities of JP¥353.8b due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of JP¥141.0b as well as receivables valued at JP¥210.5b due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by JP¥484.0b.
The deficiency here weighs heavily on the JP¥263.8b company itself, as if a child were struggling under the weight of an enormous back-pack full of books, his sports gear, and a trumpet. So we'd watch its balance sheet closely, without a doubt. After all, Teijin would likely require a major re-capitalisation if it had to pay its creditors today.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). This way, we consider both the absolute quantum of the debt, as well as the interest rates paid on it.
While Teijin's debt to EBITDA ratio (4.2) suggests that it uses some debt, its interest cover is very weak, at 1.8, suggesting high leverage. In large part that's due to the company's significant depreciation and amortisation charges, which arguably mean its EBITDA is a very generous measure of earnings, and its debt may be more of a burden than it first appears. It seems clear that the cost of borrowing money is negatively impacting returns for shareholders, of late. However, it should be some comfort for shareholders to recall that Teijin actually grew its EBIT by a hefty 169%, over the last 12 months. If it can keep walking that path it will be in a position to shed its debt with relative ease. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Teijin can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. During the last three years, Teijin burned a lot of cash. While investors are no doubt expecting a reversal of that situation in due course, it clearly does mean its use of debt is more risky.
Our View
To be frank both Teijin's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow and its track record of staying on top of its total liabilities make us rather uncomfortable with its debt levels. But at least it's pretty decent at growing its EBIT; that's encouraging. We're quite clear that we consider Teijin to be really rather risky, as a result of its balance sheet health. For this reason we're pretty cautious about the stock, and we think shareholders should keep a close eye on its liquidity. When analysing debt levels, the balance sheet is the obvious place to start. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. Case in point: We've spotted 4 warning signs for Teijin you should be aware of, and 2 of them are potentially serious.
If, after all that, you're more interested in a fast growing company with a rock-solid balance sheet, then check out our list of net cash growth stocks without delay.
Valuation is complex, but we're here to simplify it.
Discover if Teijin might be undervalued or overvalued with our detailed analysis, featuring fair value estimates, potential risks, dividends, insider trades, and its financial condition.
Access Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About TSE:3401
Teijin
Engages in the fibers, films and sheets, composites, healthcare, and IT businesses in Japan and internationally.
Good value average dividend payer.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Community Narratives


Recently Updated Narratives


Alphabet: The Under-appreciated Compounder Hiding in Plain Sight


MINISO's fair value is projected at 26.69 with an anticipated PE ratio shift of 20x

The Quiet Giant That Became AI’s Power Grid
Popular Narratives


The company that turned a verb into a global necessity and basically runs the modern internet, digital ads, smartphones, maps, and AI.


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success



