Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. As with many other companies Grasim Industries Limited (NSE:GRASIM) makes use of debt. But the real question is whether this debt is making the company risky.
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more frequent (but still costly) occurrence is where a company must issue shares at bargain-basement prices, permanently diluting shareholders, just to shore up its balance sheet. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we examine debt levels, we first consider both cash and debt levels, together.
View our latest analysis for Grasim Industries
What Is Grasim Industries's Net Debt?
The image below, which you can click on for greater detail, shows that at September 2022 Grasim Industries had debt of ₹877.0b, up from ₹713.6b in one year. However, because it has a cash reserve of ₹146.6b, its net debt is less, at about ₹730.4b.
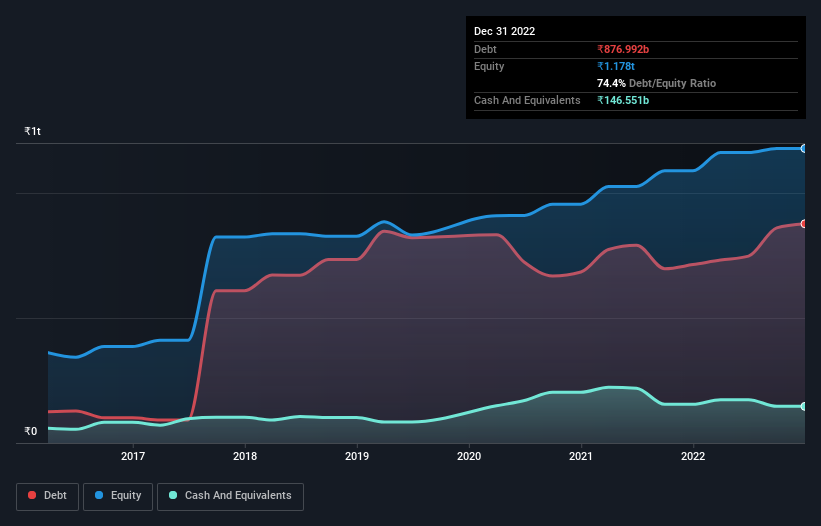
How Strong Is Grasim Industries' Balance Sheet?
According to the last reported balance sheet, Grasim Industries had liabilities of ₹630.4b due within 12 months, and liabilities of ₹1.26t due beyond 12 months. Offsetting this, it had ₹146.6b in cash and ₹231.2b in receivables that were due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by ₹1.52t.
Given this deficit is actually higher than the company's massive market capitalization of ₹1.04t, we think shareholders really should watch Grasim Industries's debt levels, like a parent watching their child ride a bike for the first time. Hypothetically, extremely heavy dilution would be required if the company were forced to pay down its liabilities by raising capital at the current share price.
We use two main ratios to inform us about debt levels relative to earnings. The first is net debt divided by earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), while the second is how many times its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) covers its interest expense (or its interest cover, for short). The advantage of this approach is that we take into account both the absolute quantum of debt (with net debt to EBITDA) and the actual interest expenses associated with that debt (with its interest cover ratio).
Grasim Industries has a debt to EBITDA ratio of 3.6 and its EBIT covered its interest expense 3.3 times. Taken together this implies that, while we wouldn't want to see debt levels rise, we think it can handle its current leverage. More concerning, Grasim Industries saw its EBIT drop by 2.8% in the last twelve months. If it keeps going like that paying off its debt will be like running on a treadmill -- a lot of effort for not much advancement. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But it is future earnings, more than anything, that will determine Grasim Industries's ability to maintain a healthy balance sheet going forward. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a business needs free cash flow to pay off debt; accounting profits just don't cut it. So we clearly need to look at whether that EBIT is leading to corresponding free cash flow. Considering the last three years, Grasim Industries actually recorded a cash outflow, overall. Debt is usually more expensive, and almost always more risky in the hands of a company with negative free cash flow. Shareholders ought to hope for an improvement.
Our View
On the face of it, Grasim Industries's conversion of EBIT to free cash flow left us tentative about the stock, and its level of total liabilities was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. But at least its EBIT growth rate is not so bad. Taking into account all the aforementioned factors, it looks like Grasim Industries has too much debt. That sort of riskiness is ok for some, but it certainly doesn't float our boat. The balance sheet is clearly the area to focus on when you are analysing debt. But ultimately, every company can contain risks that exist outside of the balance sheet. Case in point: We've spotted 2 warning signs for Grasim Industries you should be aware of, and 1 of them is a bit unpleasant.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
New: Manage All Your Stock Portfolios in One Place
We've created the ultimate portfolio companion for stock investors, and it's free.
• Connect an unlimited number of Portfolios and see your total in one currency
• Be alerted to new Warning Signs or Risks via email or mobile
• Track the Fair Value of your stocks
Have feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NSEI:GRASIM
Grasim Industries
Primarily produces cellulosic fibres, diversified chemicals, fashion yarns, and fabrics in india and internationally.
Second-rate dividend payer with low risk.
Similar Companies
Market Insights
Weekly Picks


Crazy Undervalued 42 Baggers Silver Play (Active & Running Mine)


Fiducian: Compliance Clouds or Value Opportunity?

Willamette Valley Vineyards (WVVI): Not-So-Great Value
Recently Updated Narratives

THE KINGDOM OF BROWN GOODS: WHY MGPI IS BEING CRUSHED BY INVENTORY & PRIMED FOR RESURRECTION


The "Molecular Pencil": Why Beam's Technology is Built to Win


ADNOC Gas future shines with a 21.4% revenue surge
Popular Narratives


MicroVision will explode future revenue by 380.37% with a vision towards success


NVDA: Expanding AI Demand Will Drive Major Data Center Investments Through 2026




