Stock Analysis

Some say volatility, rather than debt, is the best way to think about risk as an investor, but Warren Buffett famously said that 'Volatility is far from synonymous with risk.' So it seems the smart money knows that debt - which is usually involved in bankruptcies - is a very important factor, when you assess how risky a company is. We note that Tata Motors Limited (NSE:TATAMTRDVR) does have debt on its balance sheet. But the more important question is: how much risk is that debt creating?
When Is Debt Dangerous?
Debt is a tool to help businesses grow, but if a business is incapable of paying off its lenders, then it exists at their mercy. Ultimately, if the company can't fulfill its legal obligations to repay debt, shareholders could walk away with nothing. However, a more usual (but still expensive) situation is where a company must dilute shareholders at a cheap share price simply to get debt under control. Of course, plenty of companies use debt to fund growth, without any negative consequences. When we think about a company's use of debt, we first look at cash and debt together.
See our latest analysis for Tata Motors
What Is Tata Motors's Debt?
As you can see below, Tata Motors had ₹1.40t of debt, at March 2022, which is about the same as the year before. You can click the chart for greater detail. On the flip side, it has ₹633.8b in cash leading to net debt of about ₹763.0b.
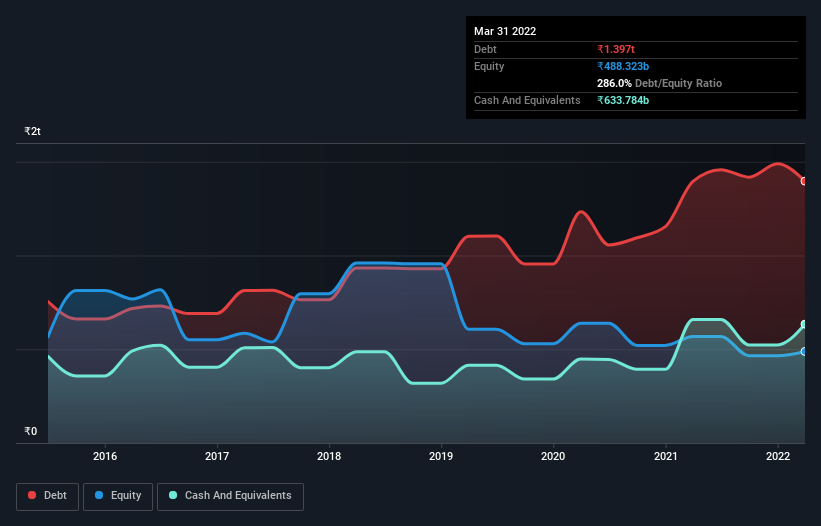
How Healthy Is Tata Motors' Balance Sheet?
Zooming in on the latest balance sheet data, we can see that Tata Motors had liabilities of ₹1.51t due within 12 months and liabilities of ₹1.31t due beyond that. Offsetting these obligations, it had cash of ₹633.8b as well as receivables valued at ₹143.7b due within 12 months. So its liabilities outweigh the sum of its cash and (near-term) receivables by ₹2.04t.
When you consider that this deficiency exceeds the company's huge ₹1.42t market capitalization, you might well be inclined to review the balance sheet intently. In the scenario where the company had to clean up its balance sheet quickly, it seems likely shareholders would suffer extensive dilution.
We measure a company's debt load relative to its earnings power by looking at its net debt divided by its earnings before interest, tax, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) and by calculating how easily its earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) cover its interest expense (interest cover). Thus we consider debt relative to earnings both with and without depreciation and amortization expenses.
While Tata Motors's debt to EBITDA ratio (2.7) suggests that it uses some debt, its interest cover is very weak, at 0.33, suggesting high leverage. It seems that the business incurs large depreciation and amortisation charges, so maybe its debt load is heavier than it would first appear, since EBITDA is arguably a generous measure of earnings. It seems clear that the cost of borrowing money is negatively impacting returns for shareholders, of late. Worse, Tata Motors's EBIT was down 66% over the last year. If earnings continue to follow that trajectory, paying off that debt load will be harder than convincing us to run a marathon in the rain. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. But ultimately the future profitability of the business will decide if Tata Motors can strengthen its balance sheet over time. So if you want to see what the professionals think, you might find this free report on analyst profit forecasts to be interesting.
Finally, a company can only pay off debt with cold hard cash, not accounting profits. So it's worth checking how much of that EBIT is backed by free cash flow. Looking at the most recent three years, Tata Motors recorded free cash flow of 40% of its EBIT, which is weaker than we'd expect. That weak cash conversion makes it more difficult to handle indebtedness.
Our View
On the face of it, Tata Motors's interest cover left us tentative about the stock, and its EBIT growth rate was no more enticing than the one empty restaurant on the busiest night of the year. But at least its conversion of EBIT to free cash flow is not so bad. After considering the datapoints discussed, we think Tata Motors has too much debt. While some investors love that sort of risky play, it's certainly not our cup of tea. There's no doubt that we learn most about debt from the balance sheet. However, not all investment risk resides within the balance sheet - far from it. For example - Tata Motors has 1 warning sign we think you should be aware of.
Of course, if you're the type of investor who prefers buying stocks without the burden of debt, then don't hesitate to discover our exclusive list of net cash growth stocks, today.
Valuation is complex, but we're helping make it simple.
Find out whether Tata Motors is potentially over or undervalued by checking out our comprehensive analysis, which includes fair value estimates, risks and warnings, dividends, insider transactions and financial health.
View the Free AnalysisHave feedback on this article? Concerned about the content? Get in touch with us directly. Alternatively, email editorial-team (at) simplywallst.com.
This article by Simply Wall St is general in nature. We provide commentary based on historical data and analyst forecasts only using an unbiased methodology and our articles are not intended to be financial advice. It does not constitute a recommendation to buy or sell any stock, and does not take account of your objectives, or your financial situation. We aim to bring you long-term focused analysis driven by fundamental data. Note that our analysis may not factor in the latest price-sensitive company announcements or qualitative material. Simply Wall St has no position in any stocks mentioned.
About NSEI:TATAMTRDVR
Tata Motors
Designs, develops, manufactures, and sells various automotive vehicles.
Solid track record with adequate balance sheet and pays a dividend.

